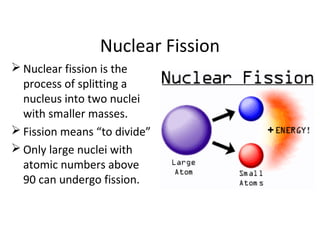
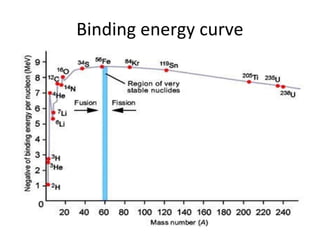
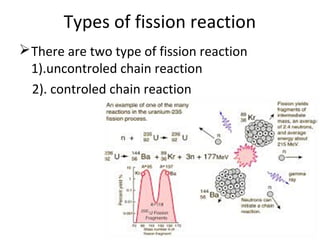
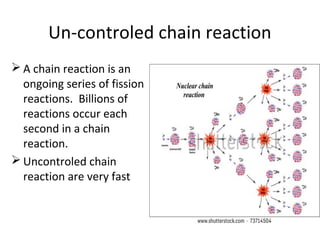
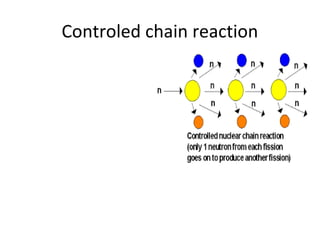
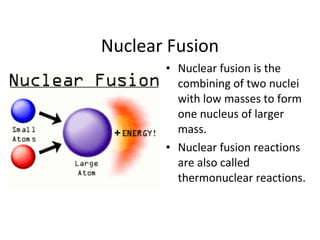
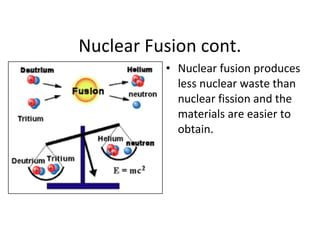
Nuclear energy is emitted from radioactive elements during nuclear fission or fusion reactions. Nuclear fission involves splitting heavy radioactive nuclei, while nuclear fusion combines lighter nuclei. Fission is used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity through controlled chain reactions, using elements like uranium. Fusion occurs in stars and requires extremely high temperatures. While nuclear energy produces less waste than fossil fuels, the byproducts are radioactive and require careful treatment or storage due to their harmfulness.