This document provides guidance on key aspects of delivering effective sales presentations, including:
1) Linking product features to meaningful benefits that address the buyer's needs in order to persuade them to purchase.
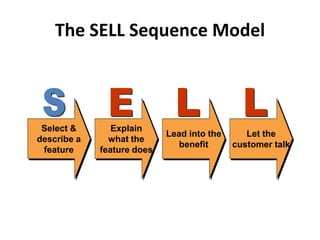
2) Using selling points, examples, comparisons, and other techniques to clearly explain how product features translate into specific benefits for the buyer.
3) Strategically employing various presentation tools, sales aids, and techniques depending on whether making an individual or group presentation in order to engage the buyer and overcome any objections.