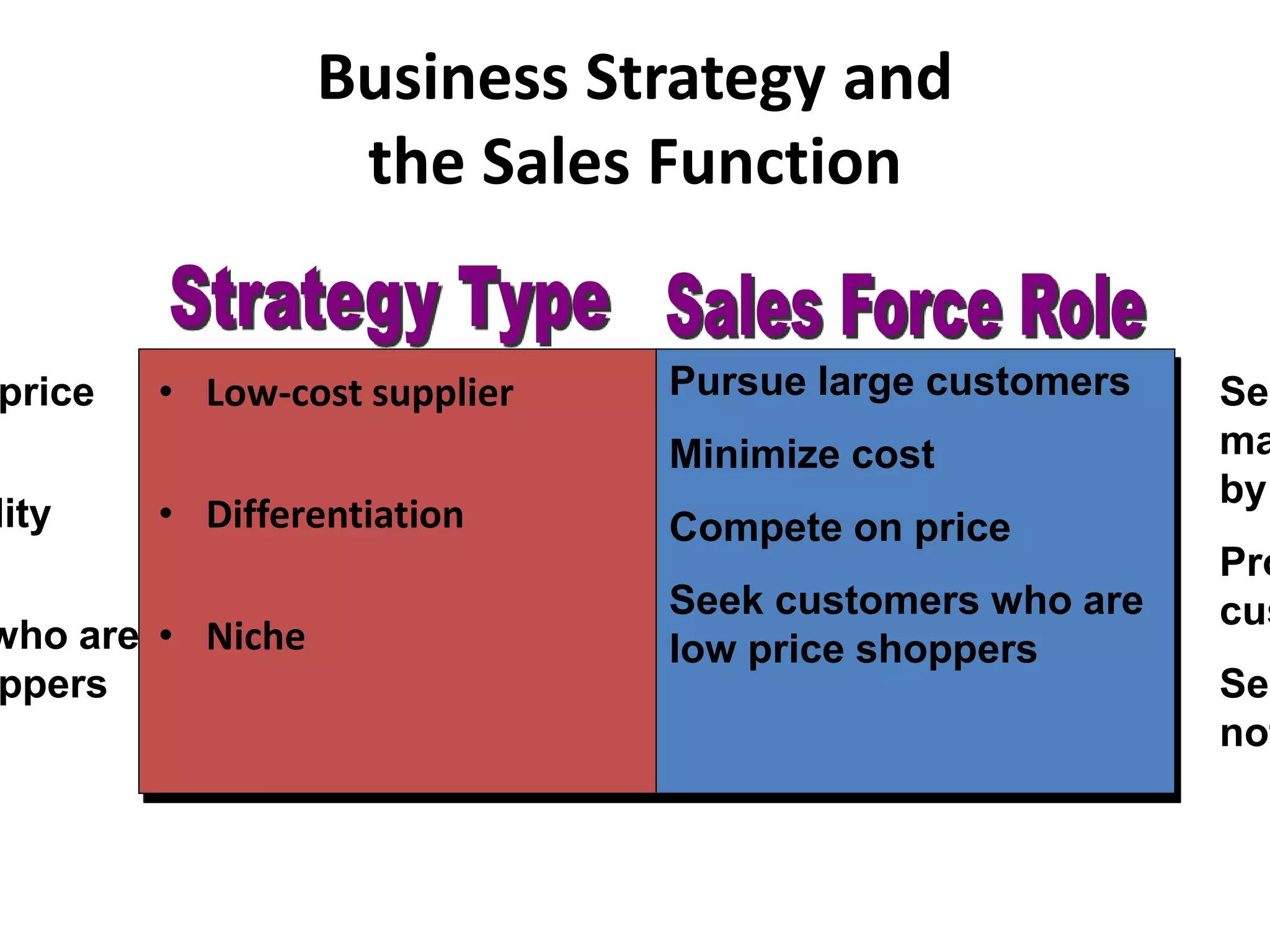
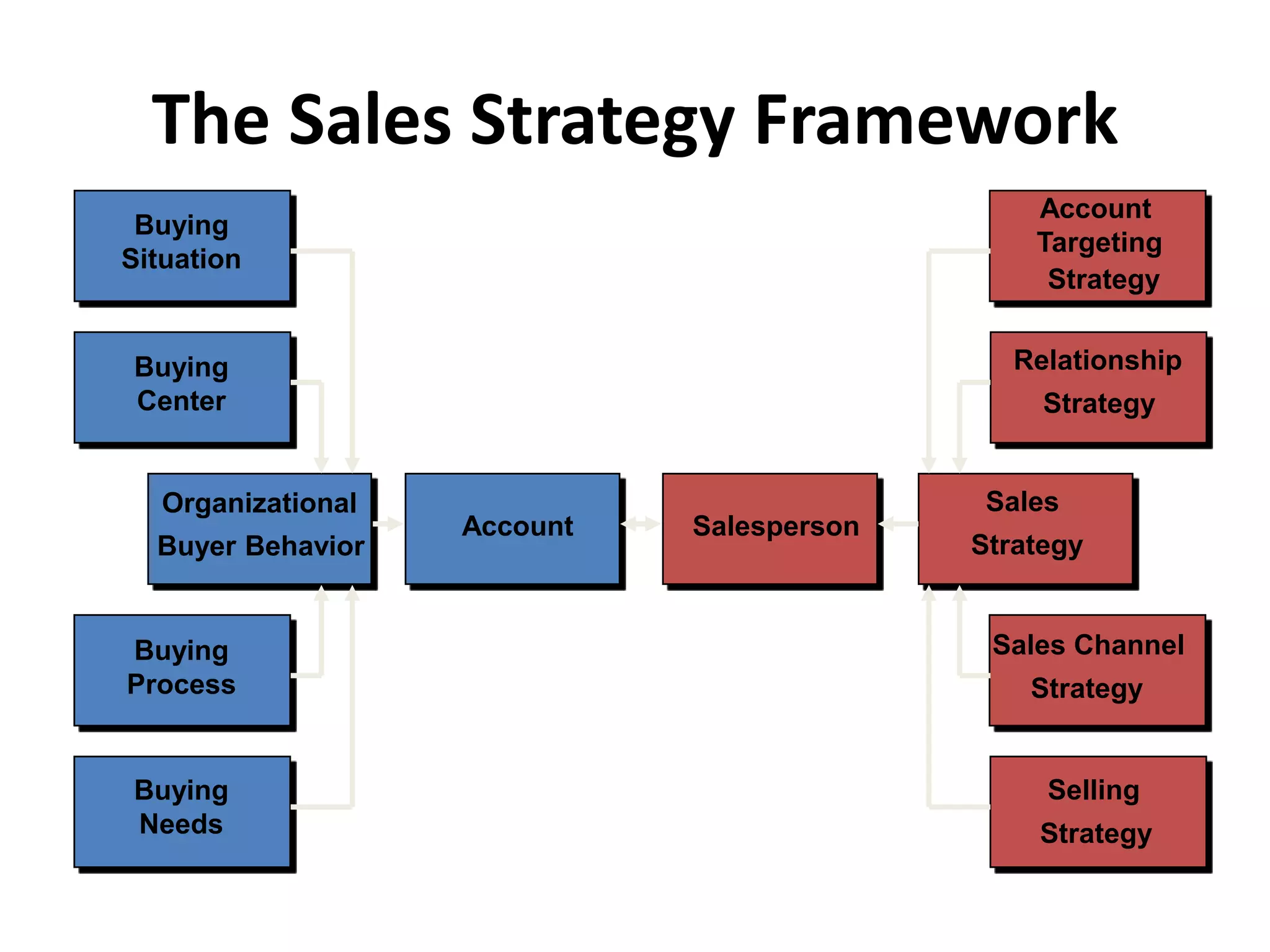
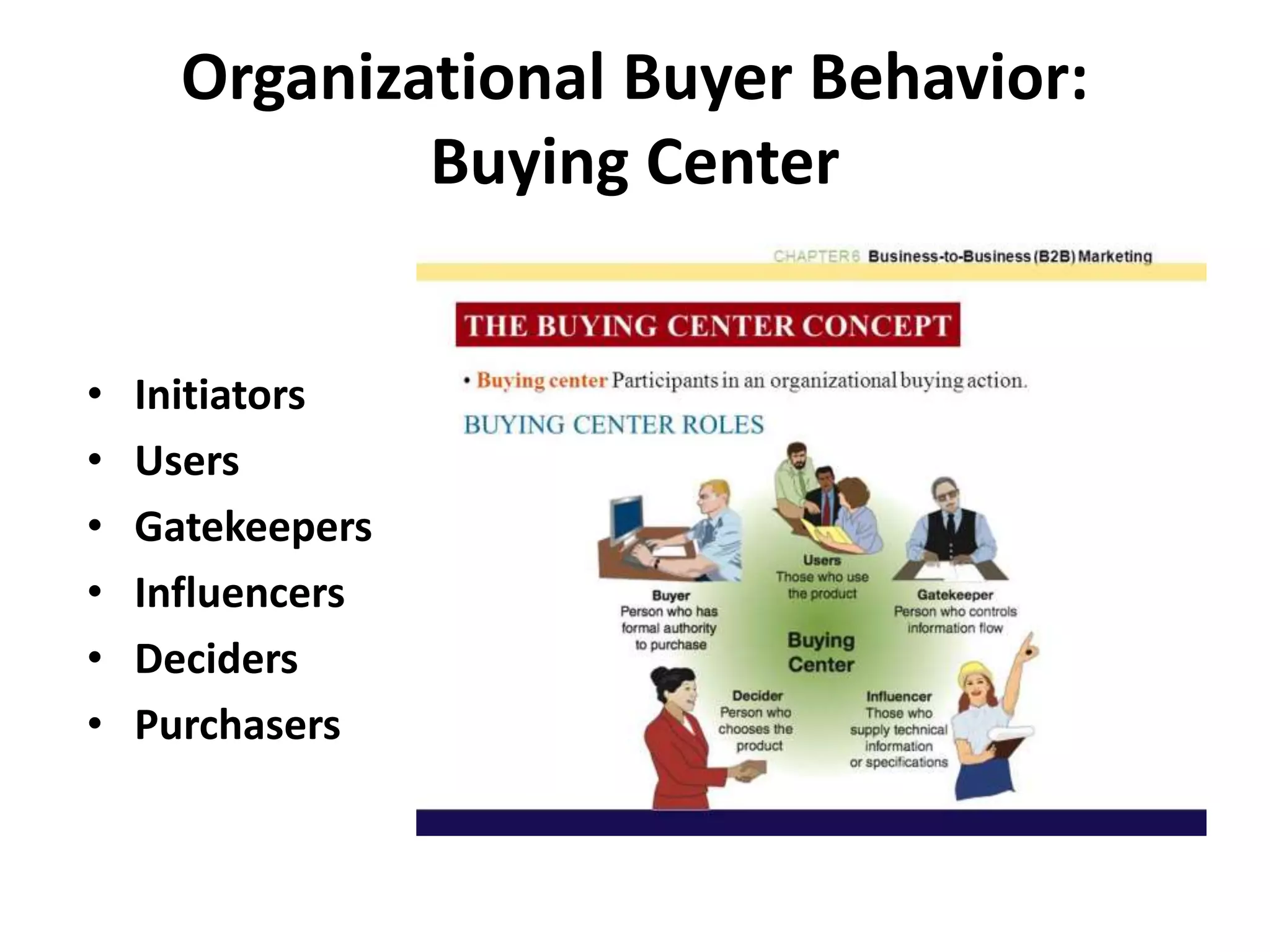
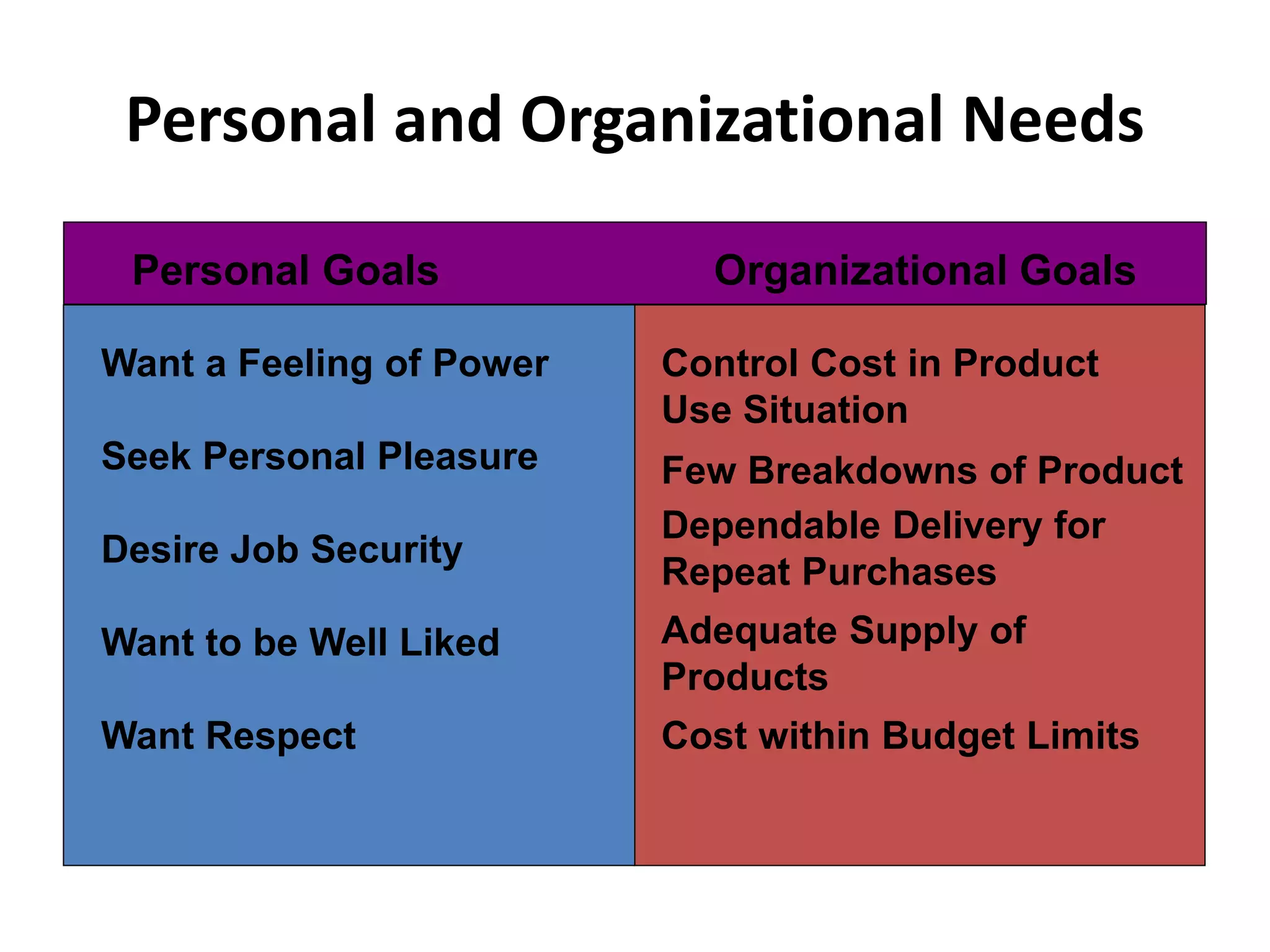
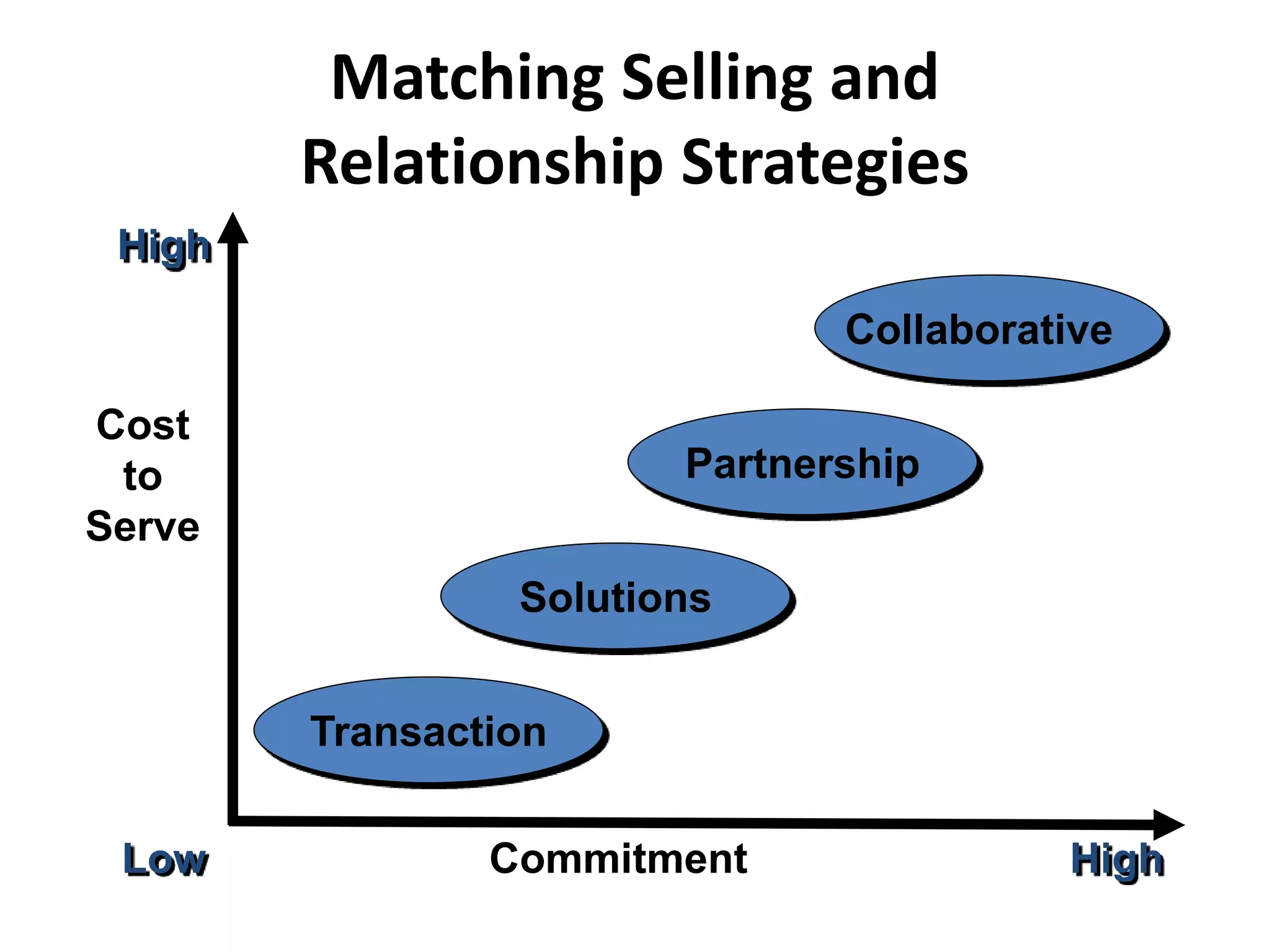
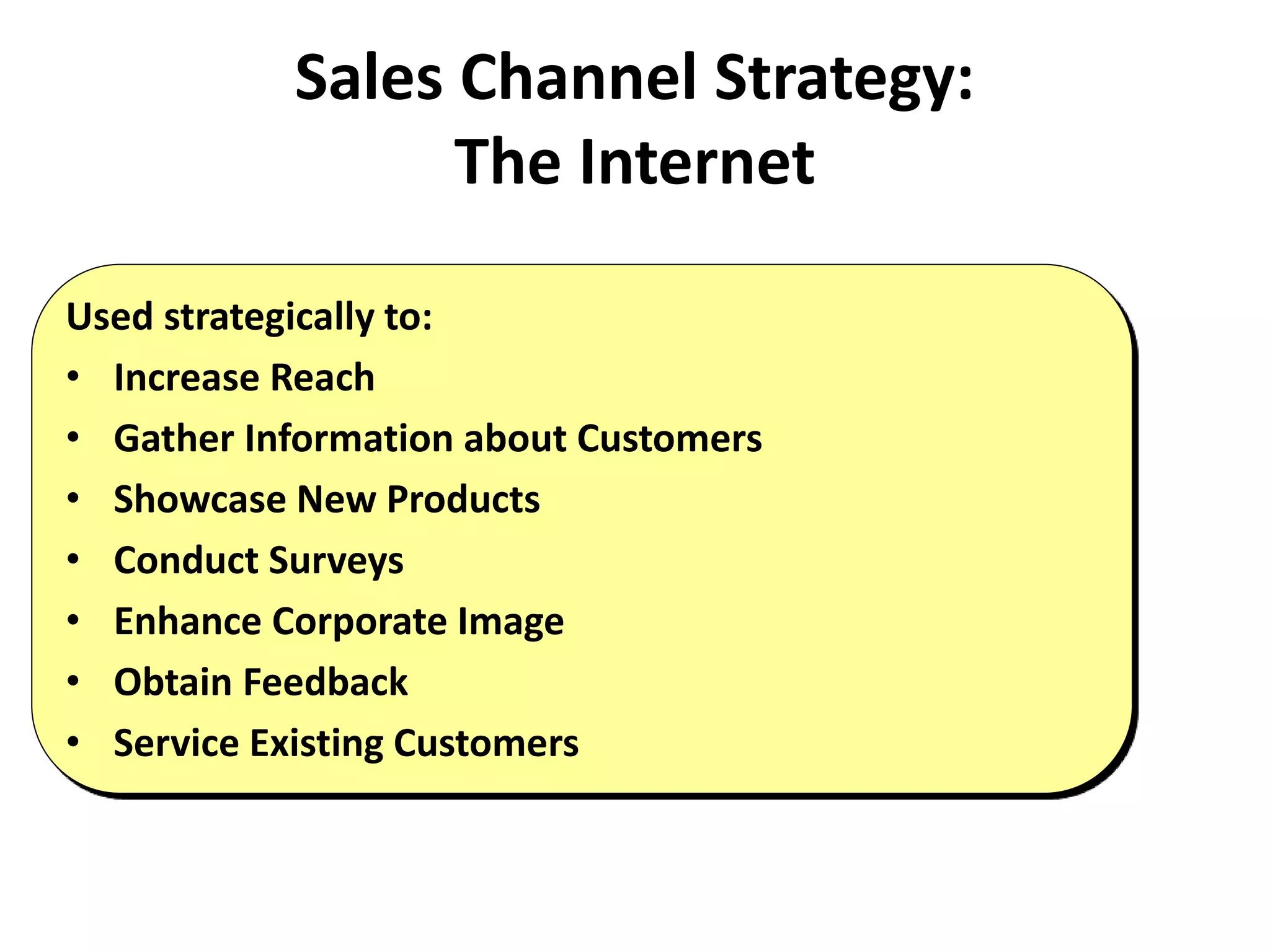
The document discusses organizational strategies and the sales function. It covers topics like corporate strategy development processes, strategic business units, matching selling strategies to relationship strategies, and different sales channel strategies. The key aspects are organizational strategy levels, business strategy and the sales function, personal selling vs advertising strategies, and how sales strategies should be tailored based on the target market, buying center, buying process, and relationship goals.