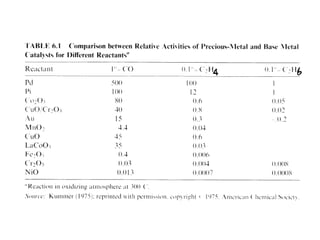
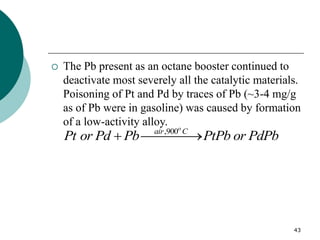
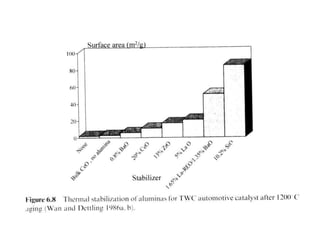
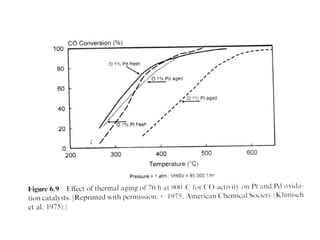
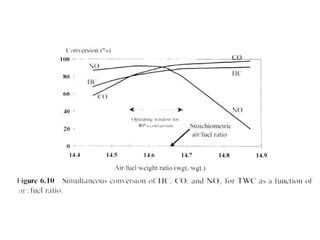
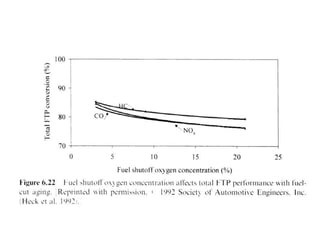
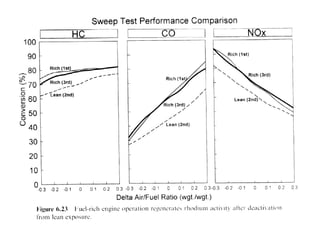
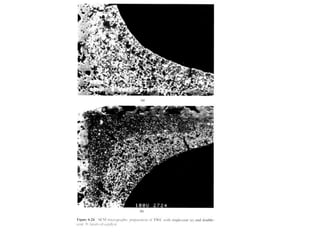
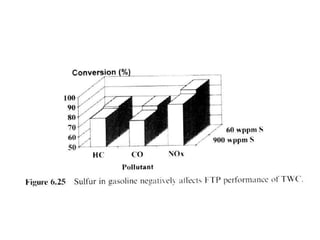
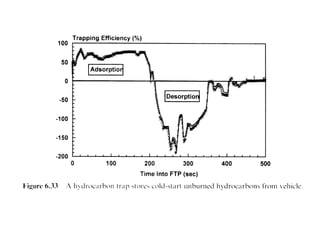
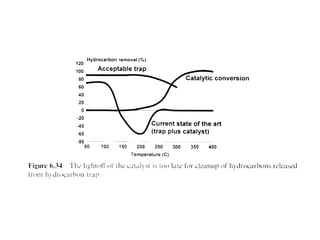
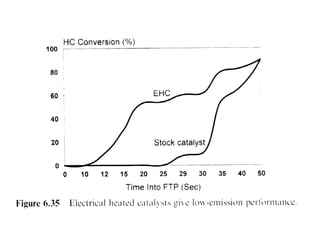
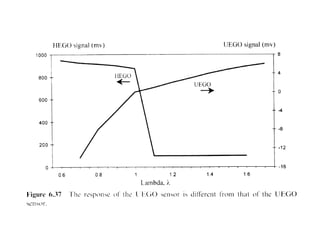
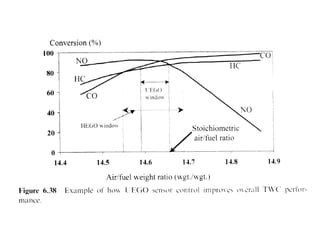
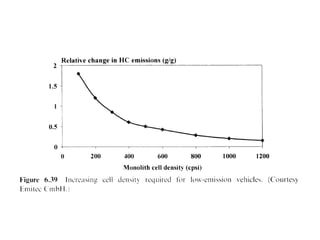
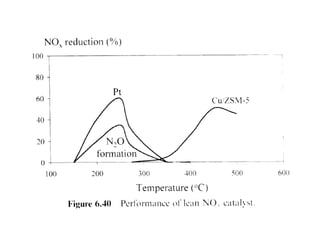
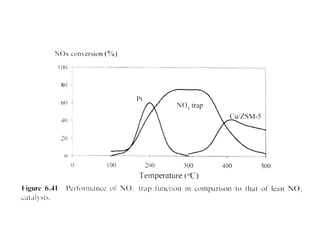
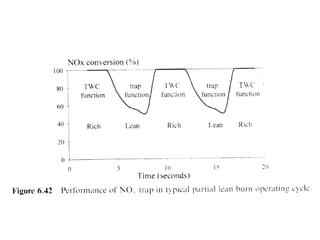
1. This document discusses the history and development of automotive catalysts used to reduce vehicle emissions. It describes the regulations that led to the development of catalytic converters and the different generations of converters used.
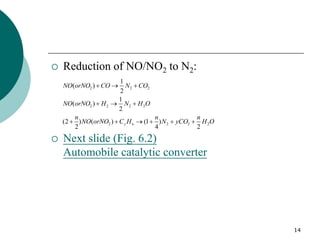
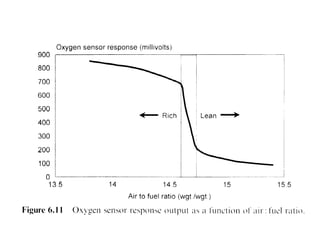
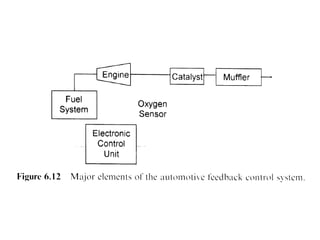
2. Early oxidation catalysts from 1976-1979 used platinum and palladium on bead or honeycomb supports to reduce carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons from gasoline engines. Subsequent three-way catalysts introduced from 1979-1986 added rhodium to also reduce nitrogen oxides through precise fuel control enabled by oxygen sensors.
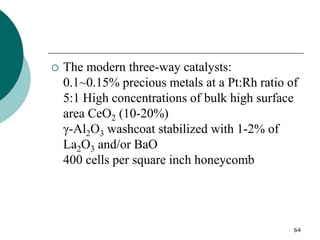
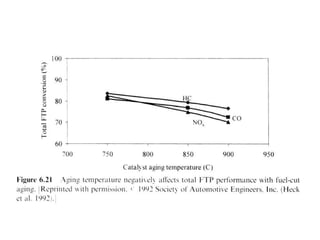
3. More recent generations of catalysts focus on improving durability, temperature operation, and meeting increasingly stringent emissions standards through substrate and washcoat modifications as well as alternative precious metal formulations.