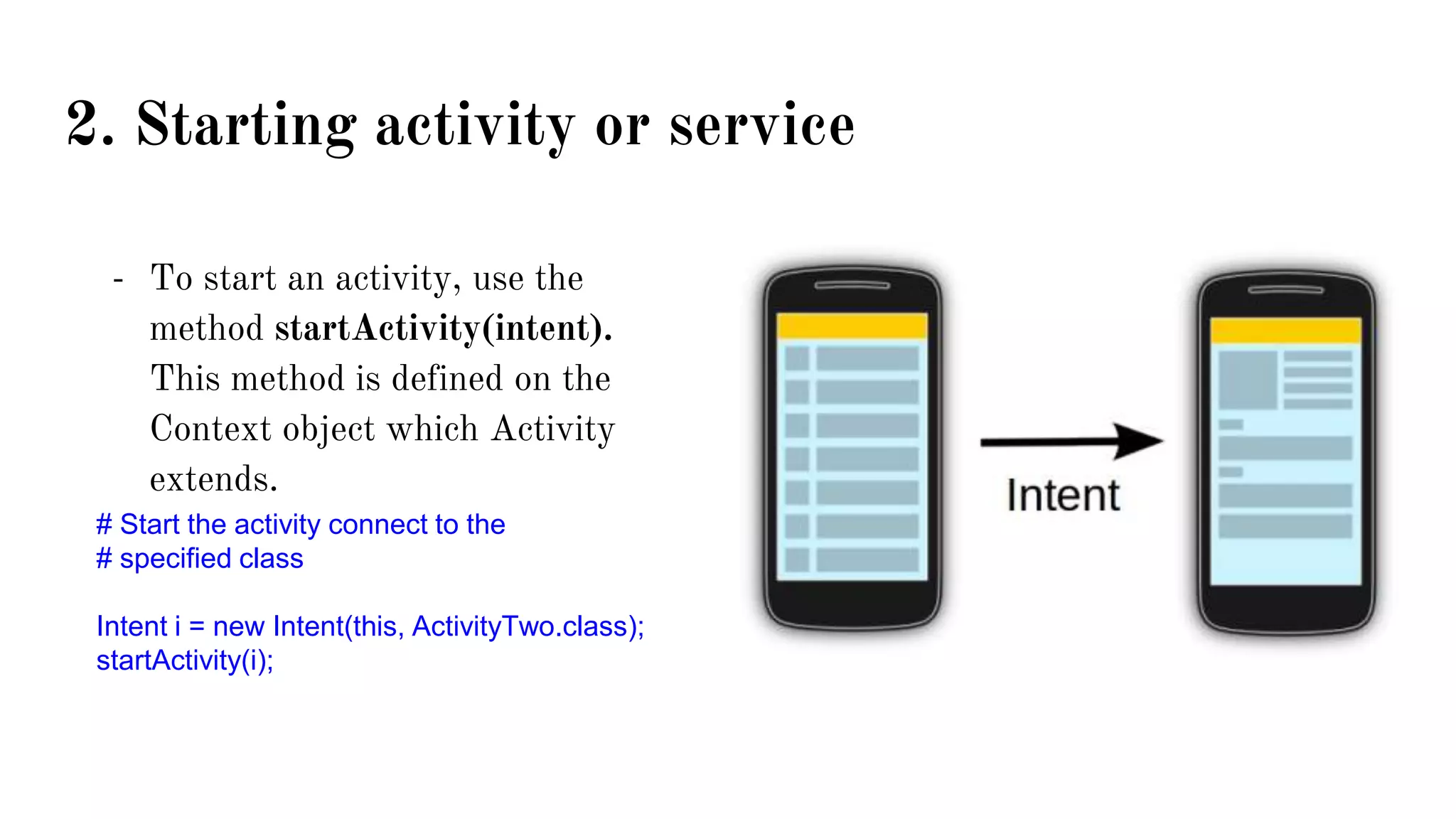
The document explains intents in Android, which are asynchronous messages allowing components to request functionality from others, categorized into explicit and implicit intents. It covers how to start activities or services, transfer data using bundles and extras, and define intent filters in an app's manifest. Examples include launching activities, web browsers, and other built-in applications with supplied data.