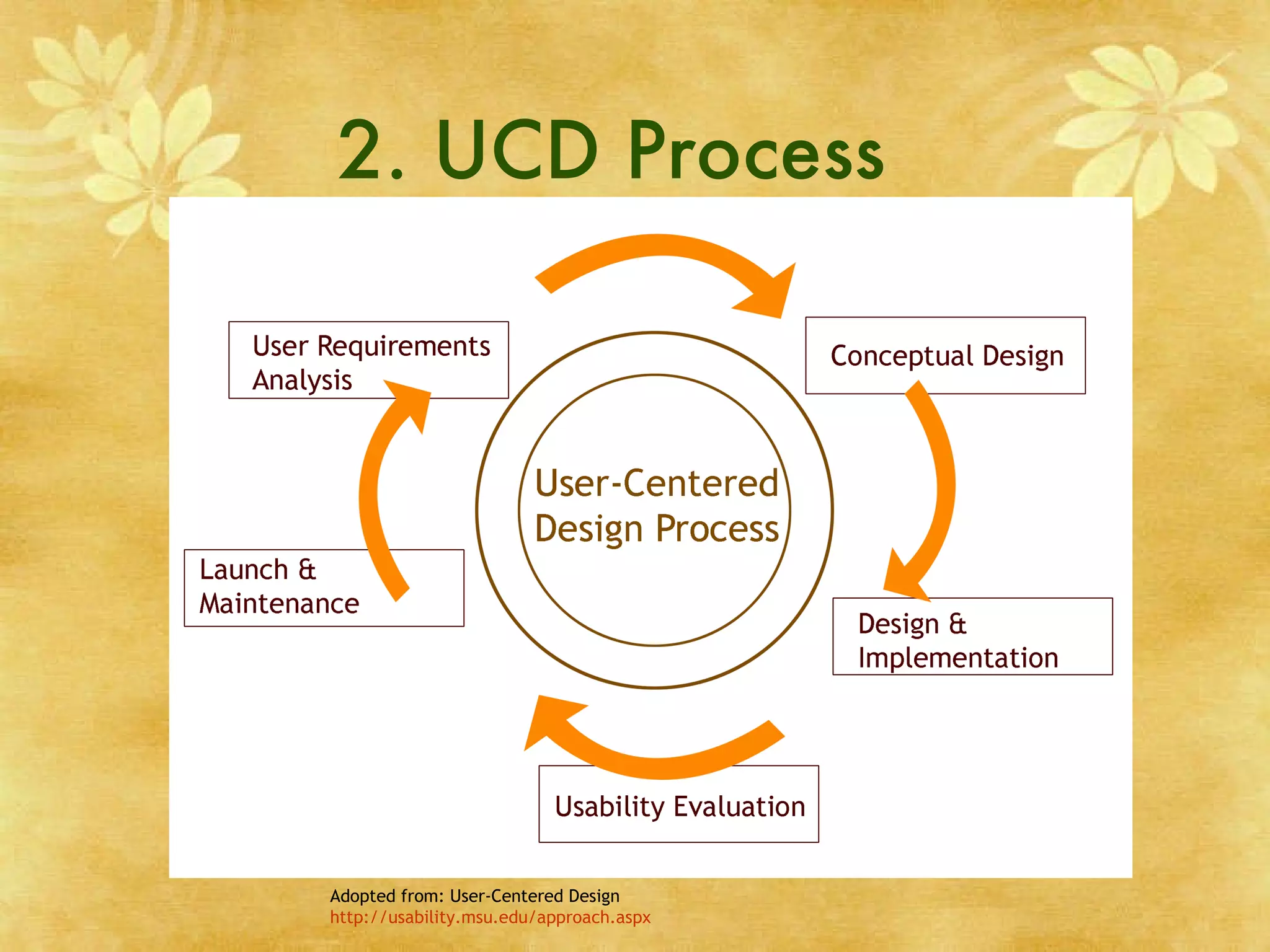
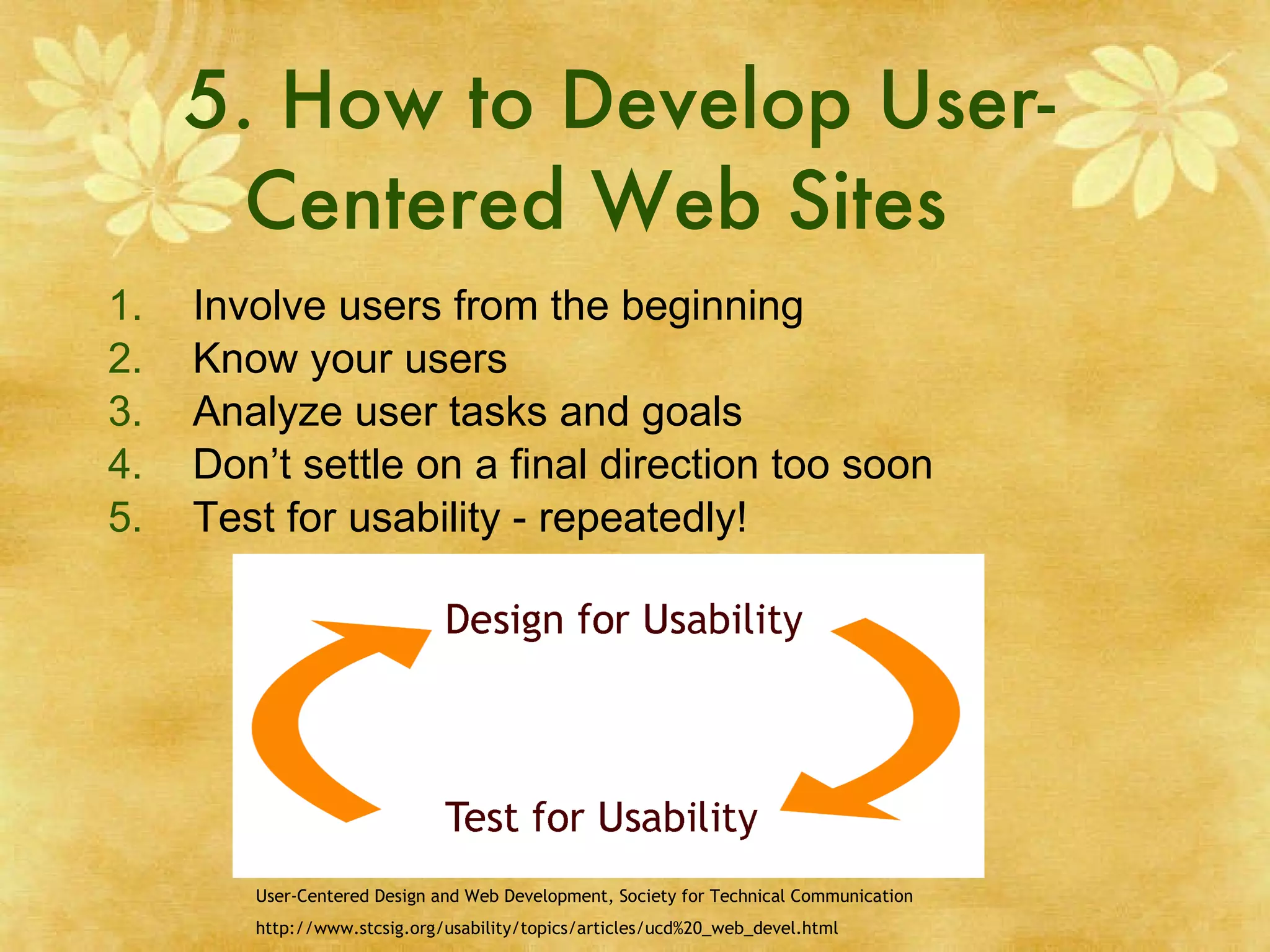
User Centered Design (UCD) is a design philosophy that places users at the center of the product development process. The UCD process involves understanding who the users are, what tasks they need to accomplish, and their experience levels. It also focuses on understanding what functions and information users need and how they think the product should work. Elements of UCD include usability, accessibility, and involving users from the beginning through repeated testing. The goal of UCD is to cut costs and increase user satisfaction and productivity.