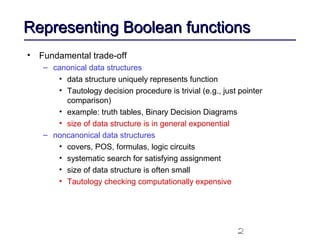
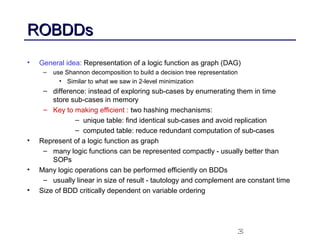
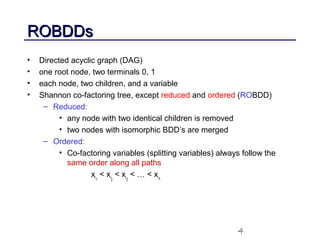
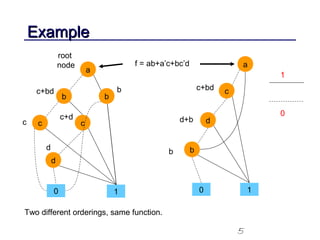
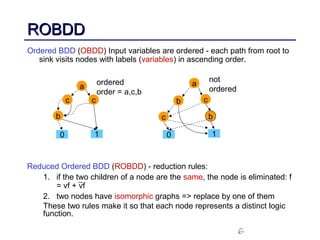
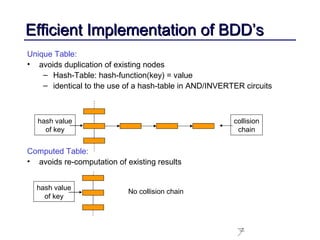
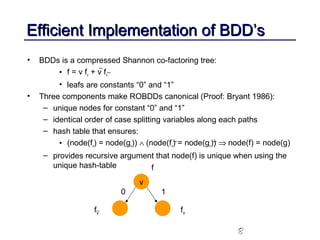
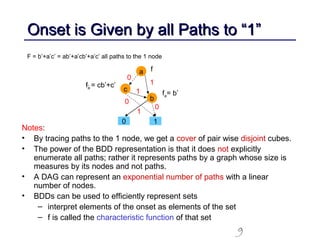
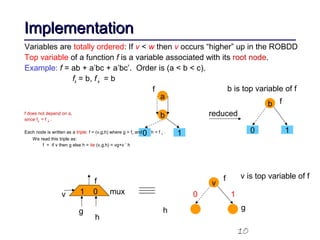
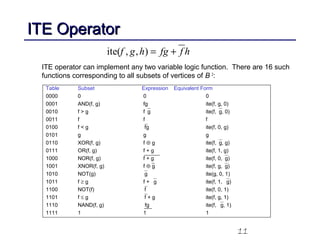
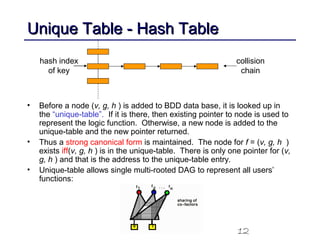
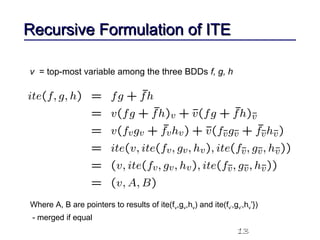
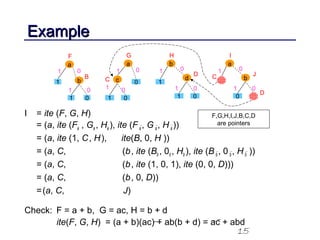
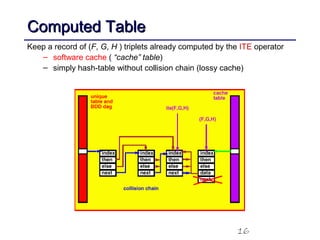
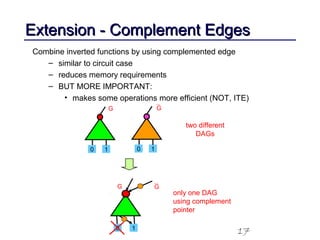
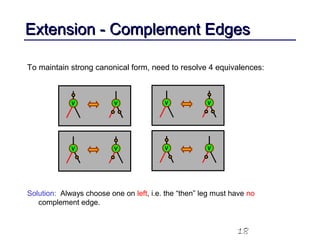
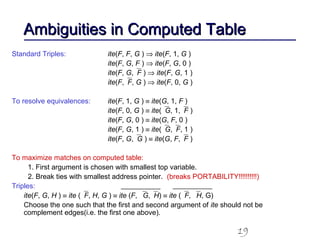
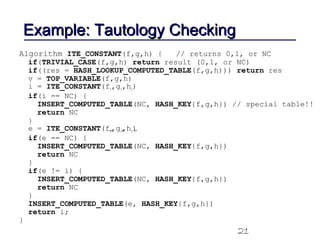
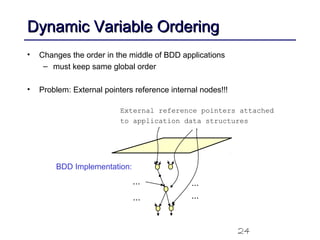
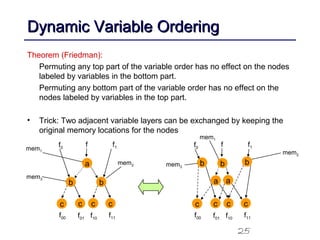
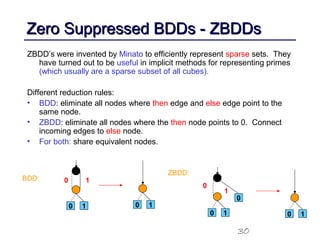
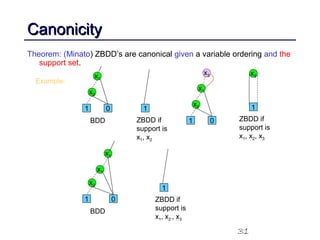
This document discusses binary decision diagrams (BDDs) and their efficient implementation. It begins by contrasting canonical and non-canonical data structures for representing Boolean functions. It then introduces reduced ordered binary decision diagrams (ROBDDs) which represent functions as directed acyclic graphs. The document details how ROBDDs use unique and computed tables along with variable ordering to efficiently represent and operate on Boolean functions. It provides examples and algorithms for ROBDD operations like ITE, compose, and dynamic variable reordering.