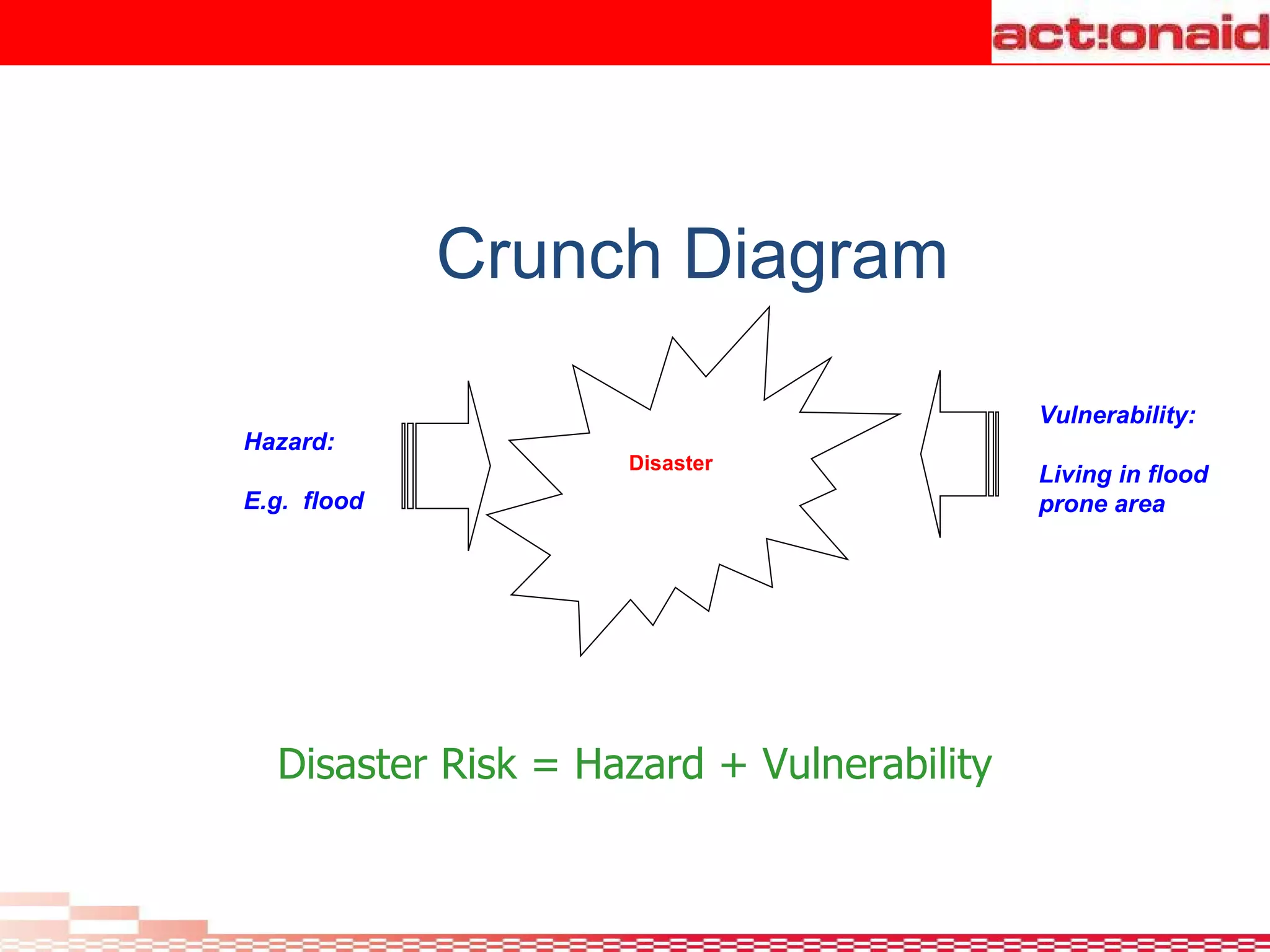
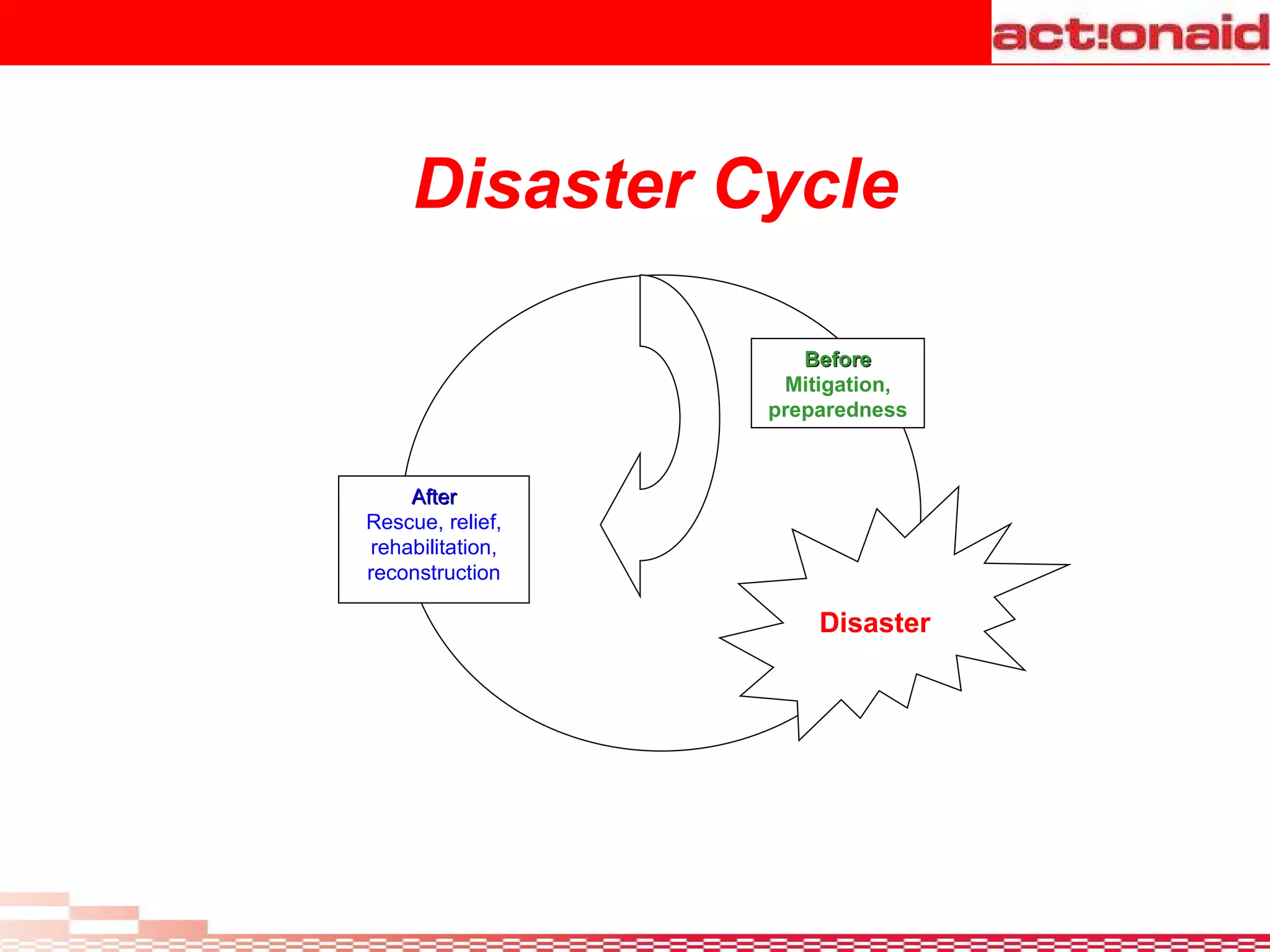
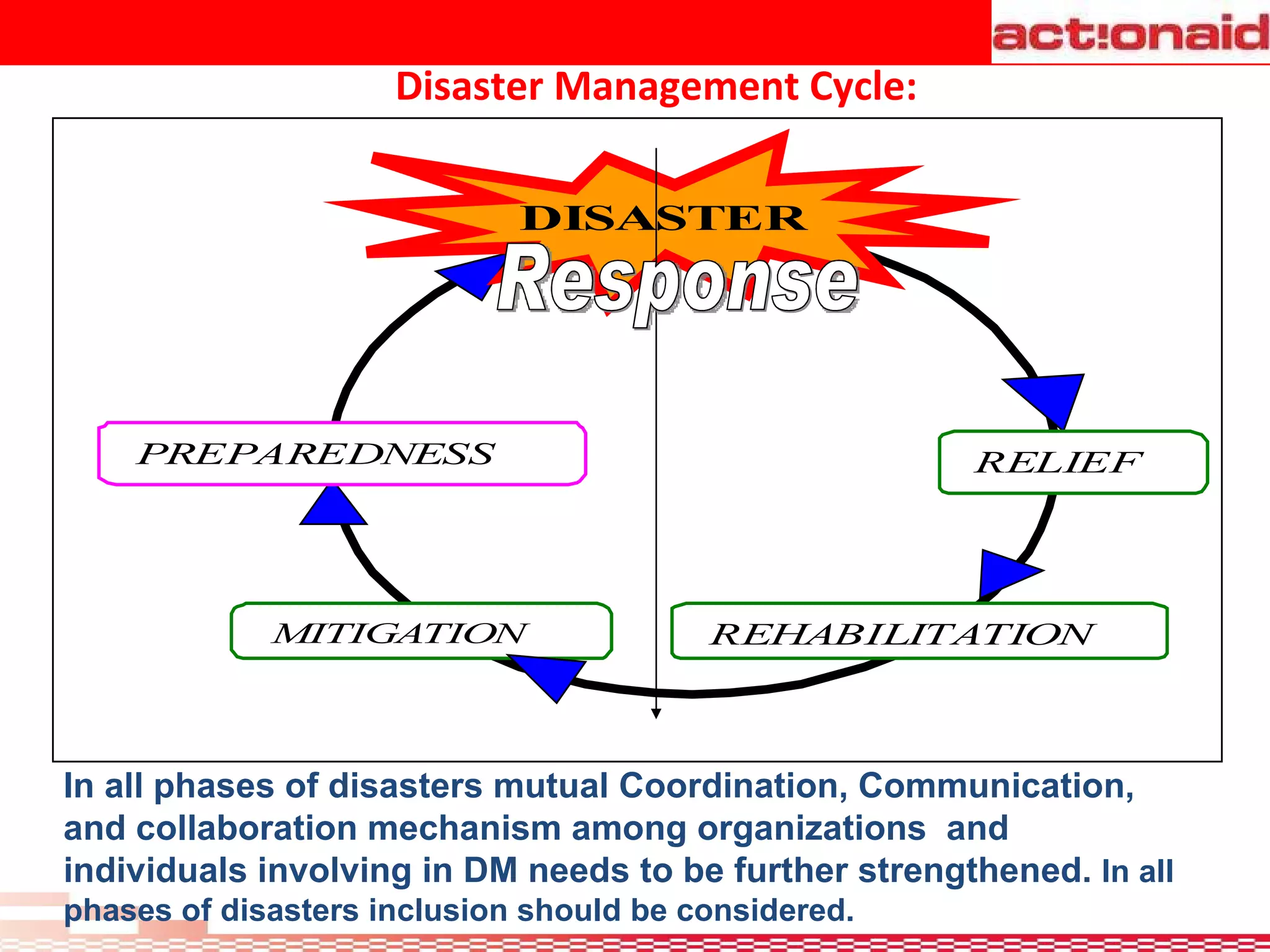
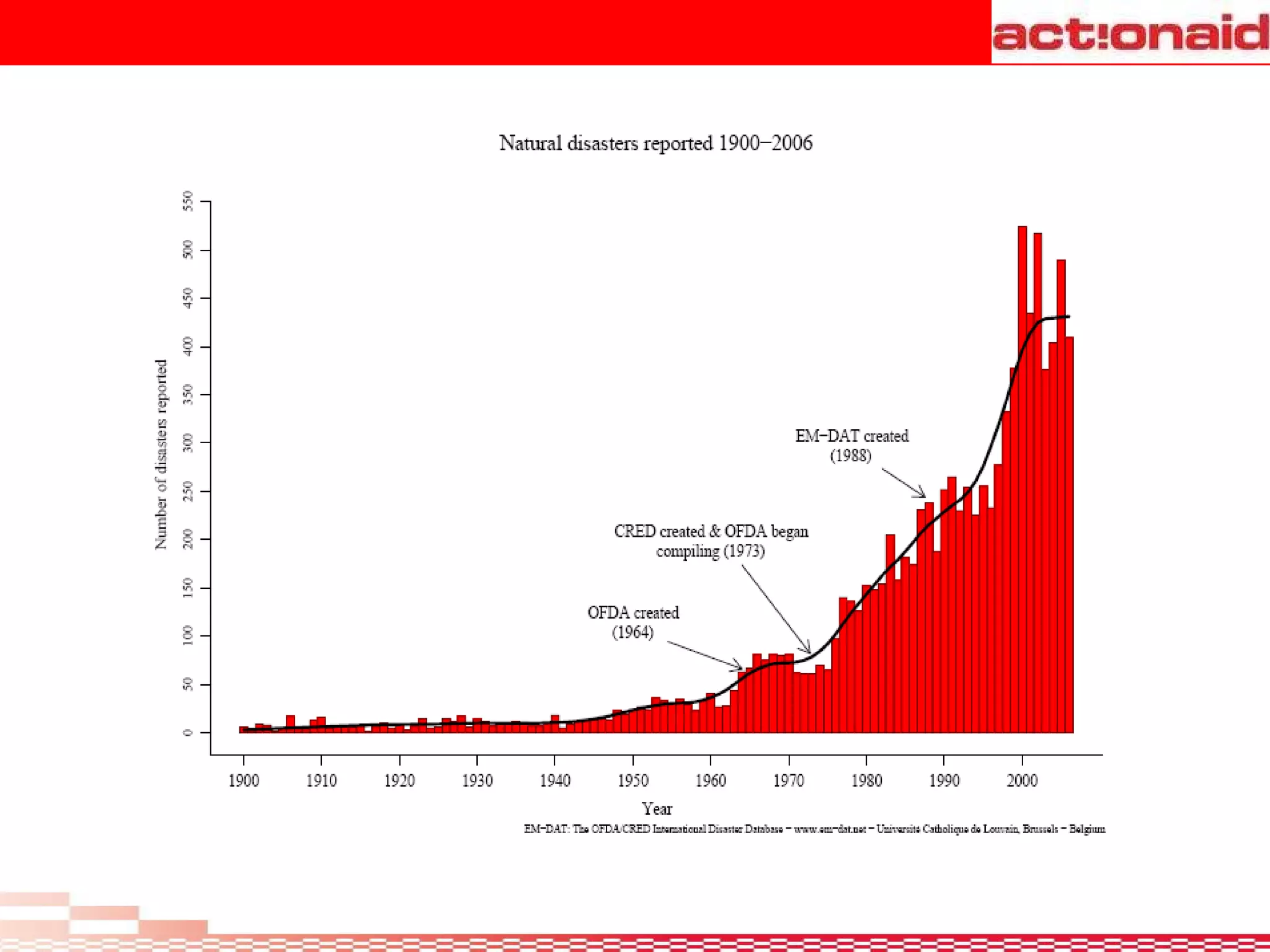
A disaster is defined as any event, natural or man-made, that threatens lives and property and disrupts normal life. Disasters exceed the ability of affected communities and governments to cope. Hazards threaten people, structures, and assets and can cause disasters. Vulnerability is the likelihood of damage from a hazard due to factors like proximity and susceptibility. Risk is the probability of consequences from hazards people are exposed to. Disaster management involves coordination across organizations in preparedness, response, and recovery phases of disasters to reduce risks and improve capacity to handle disasters.