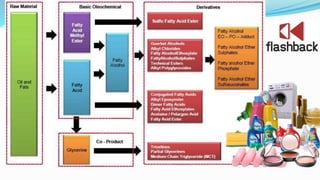
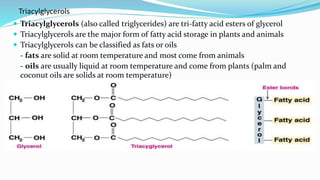
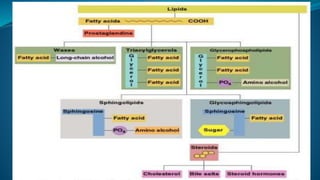
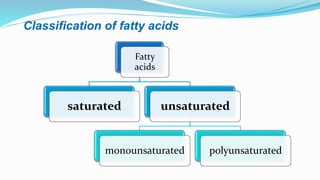
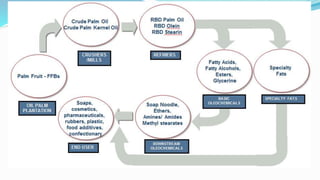
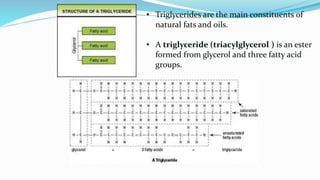
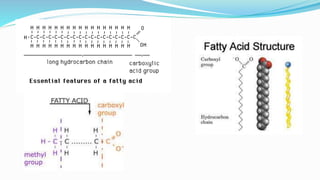
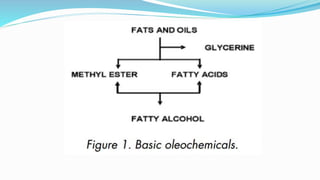
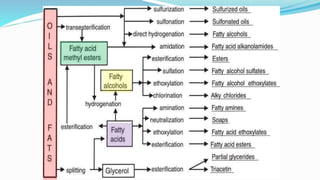
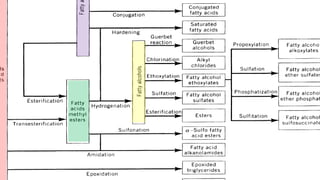
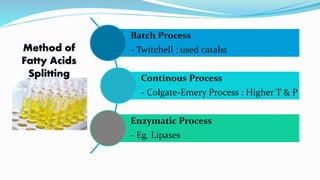
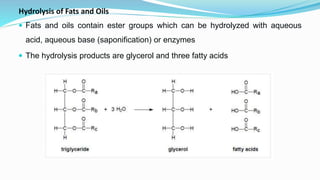
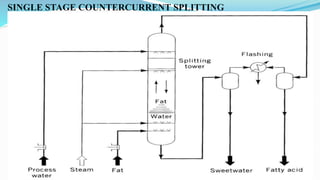
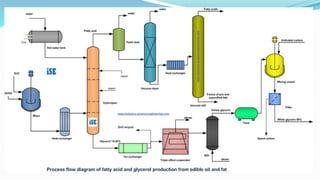
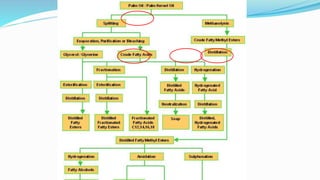
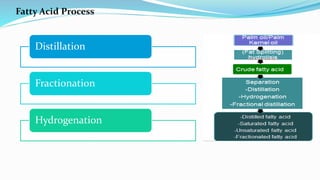
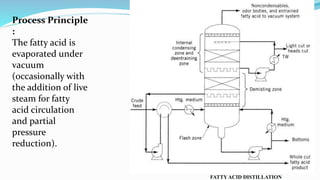
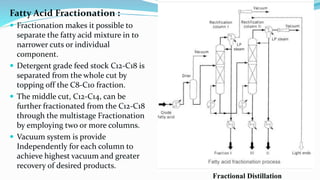
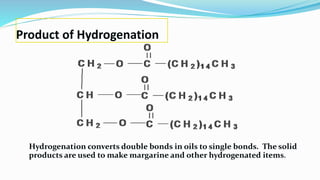
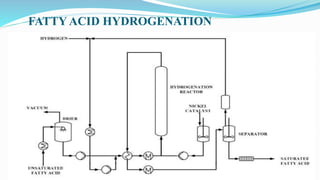
Fatty acids are the basic units of fat composed of hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl group at one end. They can be saturated, containing only single bonds between carbon atoms, or unsaturated with one or more double bonds. Saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature due to close packing, while unsaturated fatty acids are usually liquid due to kinks in their structure. Fatty acids are produced via hydrolysis of triglycerides from plants and animals, which involves splitting the triglyceride into glycerol and three fatty acid molecules. The fatty acids can then be purified by distillation and fractionation.