Fungi
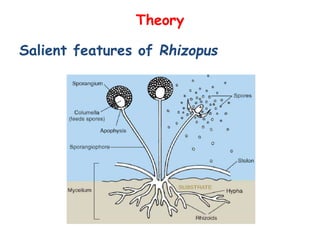
- 1. Theory Salient features of Rhizopus
- 2. Rhizopus Rhizopus is a saprophytic organism that is found in damp warm weather especially on dead organic matter. The mycelium during the vegetative phase is white fluffy mass of loosely entangled hyphae. The hyphae are aseptate or coenocytic During the vegetative growth the mycelium consists of stolon hyphae and rhizoidal hyphae. The former helps in spread of mycelium and the latter in anchoring and absorption of nutrients from the substratum. When the reproductive phase sets in the mycelium becomes mouldy and develops a third kind of hyphae called sporangiophore. They arise in the air from the stolon. They are unbranched. Reproduction takes place by formation of non-motile multinucleated sporangiospores produced endogenously inside the sporangium. The sporangium arise terminally at the tip of sporangiophore.
- 3. Life cycle of Rhizopus Asexual reproduction Each sporangium has a vacuolate central portion known as columella, which is surrounded by a zone containing large number of sporangiospores. The sporangiospores are released when the sporangial wall breaks. The sporangiospores are globose to oval and multinucleate. Under favourable conditions, the sporangiospores germinate by a germ tube to form white, aerial mycelium and thus complete the asexual cycle.
- 4. Sexual reproduction It requires the presence of two physiologically distinct compatible mycelia (+) and (-). When two opposite strains come in contact with one another, copulating branches called progametangia are formed. Cytoplasm and nuclei flow to the contacting tips which enlarge. A septum then forms near tip of each progametangium, separating it into two cells, a terminal gametangium and the adjacent suspensor cell. The walls of two contacting gametangia dissolve at the pint of contact. After plasmogamy, the nuclei fuse in pairs, + and -, to form diploid nuclei.
- 5. The unfused nuclei disintegrate and the young zygosporangium enlarges with its wall thickening, becoming black and warty. This thick walled structure is the zygosporangium that contains a single zygospore. After a rest period of 1-3 months, the zygospore gets activated to germinate. During germination, zygosporangium cracks open, a sporangiophore emerges from the zygospore and develops a germ sporangium at its tip. Meiosis takes place during the process of zygospore germination The germ sporangium may contain either + spores or – spores.
- 6. Economic Importance • Rhizopus stolonifer called common black bread mould grows and spoils bread. • Rhizopus stolonifer causes fruit rot on strawberry, tomatoes. • Rhizopus oryzae is used for production of alcoholic beverages. • Rhizopus oligosporus is used to make tempeh which is a fermented food.
- 7. Theory Salient features of Aspergillus Aspergillus colonies are usually fast growing white, yellow, brown or black in color. It mostly consists of a dense collection of erect conidiophore. Conidiophore terminate in a vesicle covered with either a single layer of phylides or a layer of subtending cells which bears small whorl of phylides (uniseriate/ biseriate) Conidia are single celled, rough/smooth walled, hyaline or pigmented and are borne basipetally forming long chains which maybe divergent or aggregated in compact column. Asexual reproduction : While still young the mycelium of Aspergillus produces conidiophores. The hyphae compartment or cell which give rise to a conidiophore is called a foot cell.
- 8. Foot cell Foot cell
- 10. Asexual reproduction It takes place by means of conidia ,which are formed in chains externally on conidiophores. 1. When asexual reproduction takes place a certain cell of the hyphae become larger and thick walled (foot cell). 2. From each foot cell a vertical, conidiophore which ends in a vesicle. 3. A large number of nuclei and cytoplasm migrate into the vesicle. 4. From each vesicle a tubular outgrowths are produced(sterigmata). 5. From the tips of sterigmata a chain of conidia are formed.
- 11. Sexual Reproduction • Three perfect states of Aspergillus are : – Eurotium, Emericella and Sartorya • In Eurotium, the antheridium and ascogonium are produced close to each other on the somatic hyphae. • Both are multinucleate, elongate, often helical structures coiling around each other. • The antheridium may/maynot be functional but pairing of nuclei takes place in the ascogonium. • If antheridium is functional, its nuclei enter the ascogonium and pair with the ascogonial nuclei but when the antheridium is non-functional, the ascogonial nuclei themselves pair with each other. • After pairing of the nuclei, the ascogonium produces a number of ascogenous hypahe that branch within the developing ascocarp (cleistothecium), which begins to develop as a single layer of cells. • Mature cleistothecia are small, globose with smooth walls generally of yellow color. • The asci are formed at the tips of ascogenous hyphae at different levels. • They are globose, ovoid orpear shaped, 8 spored, dissolving soon after ascospore formation, leaving the ascospores free within the cleistothecium. • The ascospores are broadly lenticular, colourless and without surface ornamentations. • On germination, the ascospores produce germ tubes, which gives rise to the mycelium.
- 12. Economic Importance • It is used for commercial production of enzymes and organic acids. • Aspergillus niger is used in the production of citric acid in large scale. • Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae are used in production of amylase. • Aspergillus oryzae is used in production of food products such as soya sauce and koji. • Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus niger cause a group of diseases called aspergillosis. • Aspergillus clavattus and Aspergillus flavous produce mycotoxins (Aflatoxin).
- 13. Saccharomyces • Unicellular thallus and may produce pseudomycelium. • They reproduce asexually by multilateral budding. • Lifecycle is haplodiplobiontic in which both the haploid and diploid phases are equally important and are perpetuated by budding. • Sexual reproduction is initiated when two haploid cells of opposite mating types fuse and give rise to diploid cells, which initiate diploid phase by budding. • After several generations of diploid cells, the diploid nucleus undergoes meiosis and forms four haploid nuceli around which four ascospores are developed. • The ascal wall is thin and soon breaks, releasing the mature, hapoid ascospores. • These ascospores multiply by budding producing several generations before copulation.