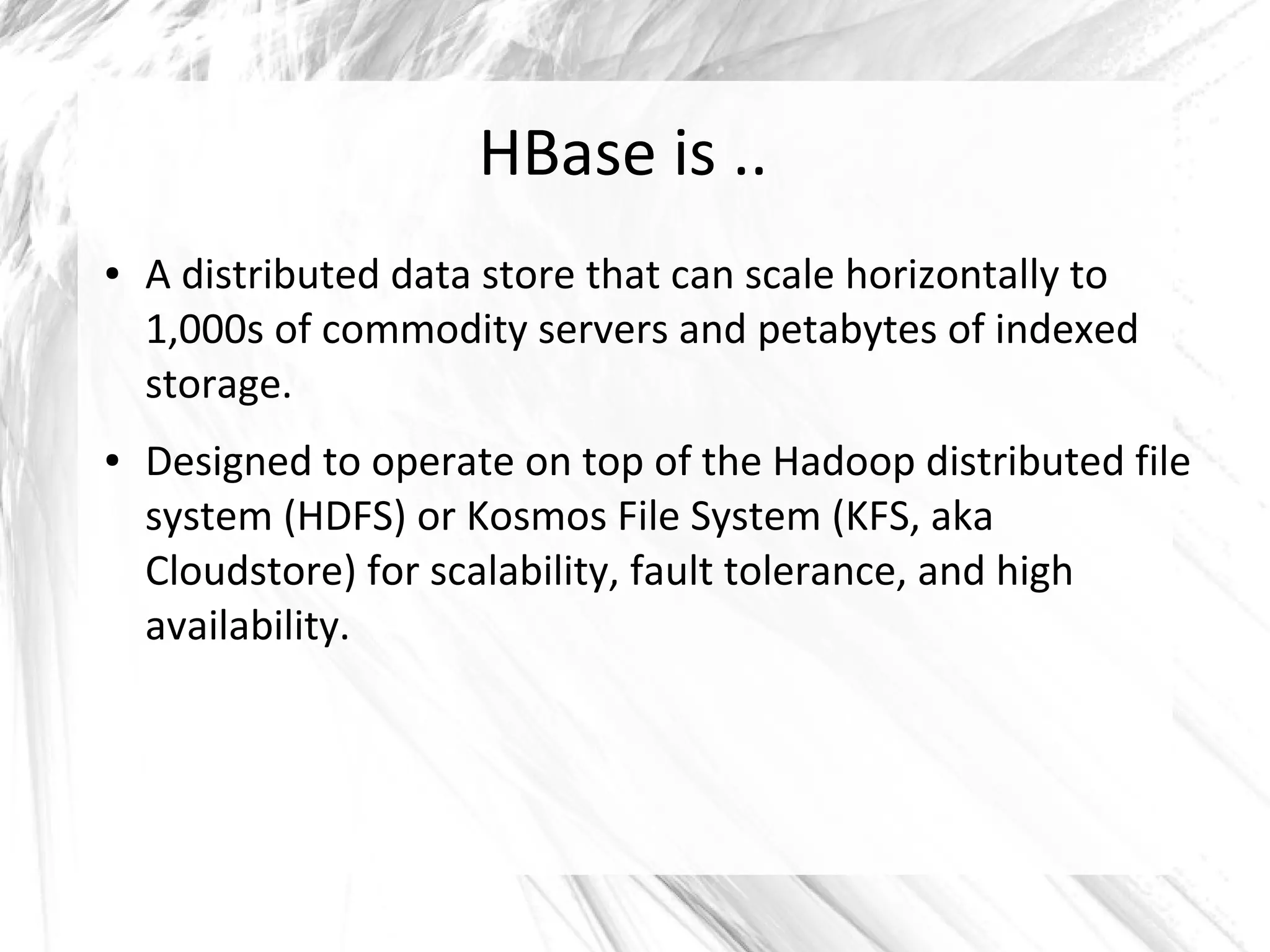
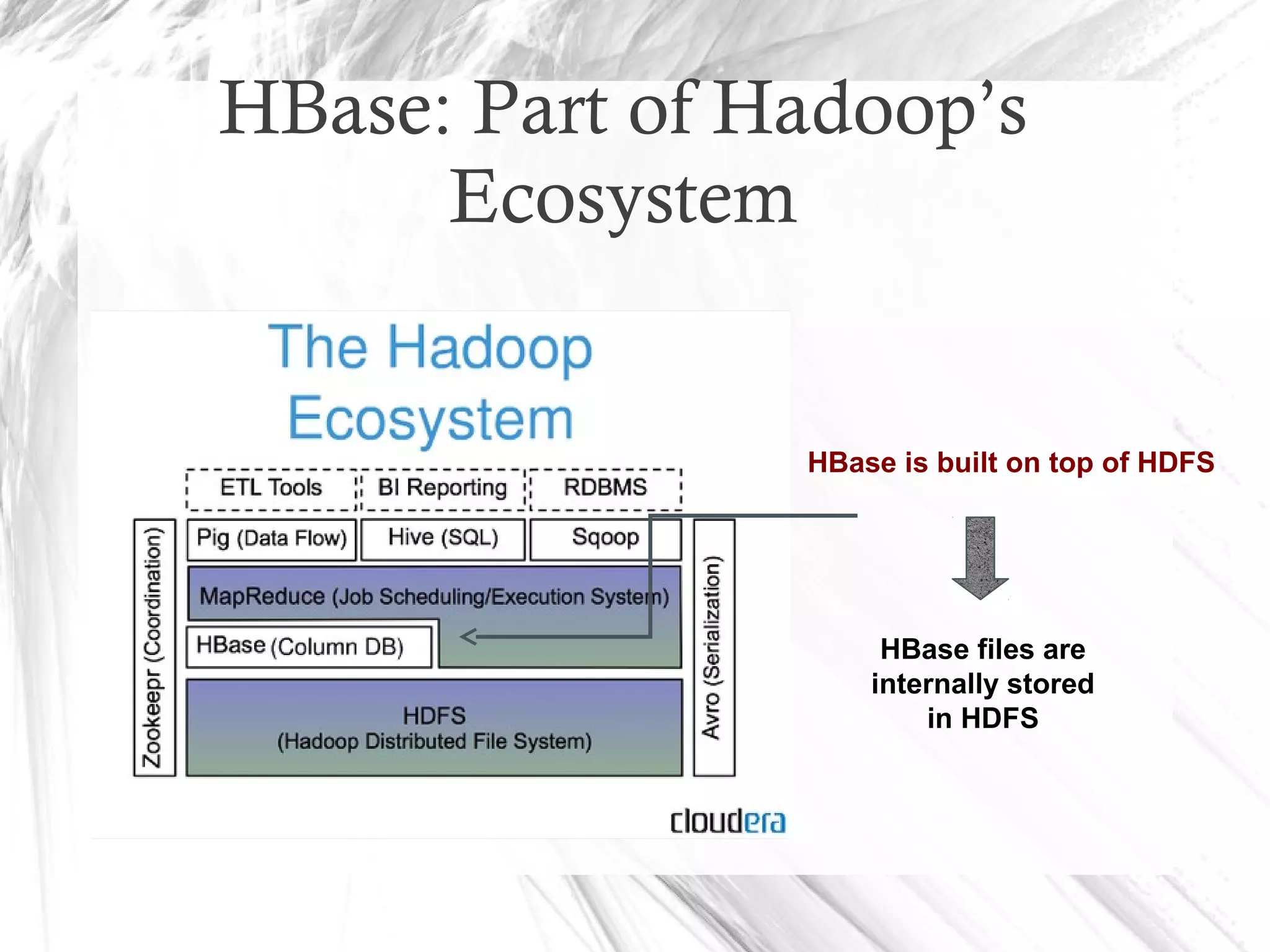
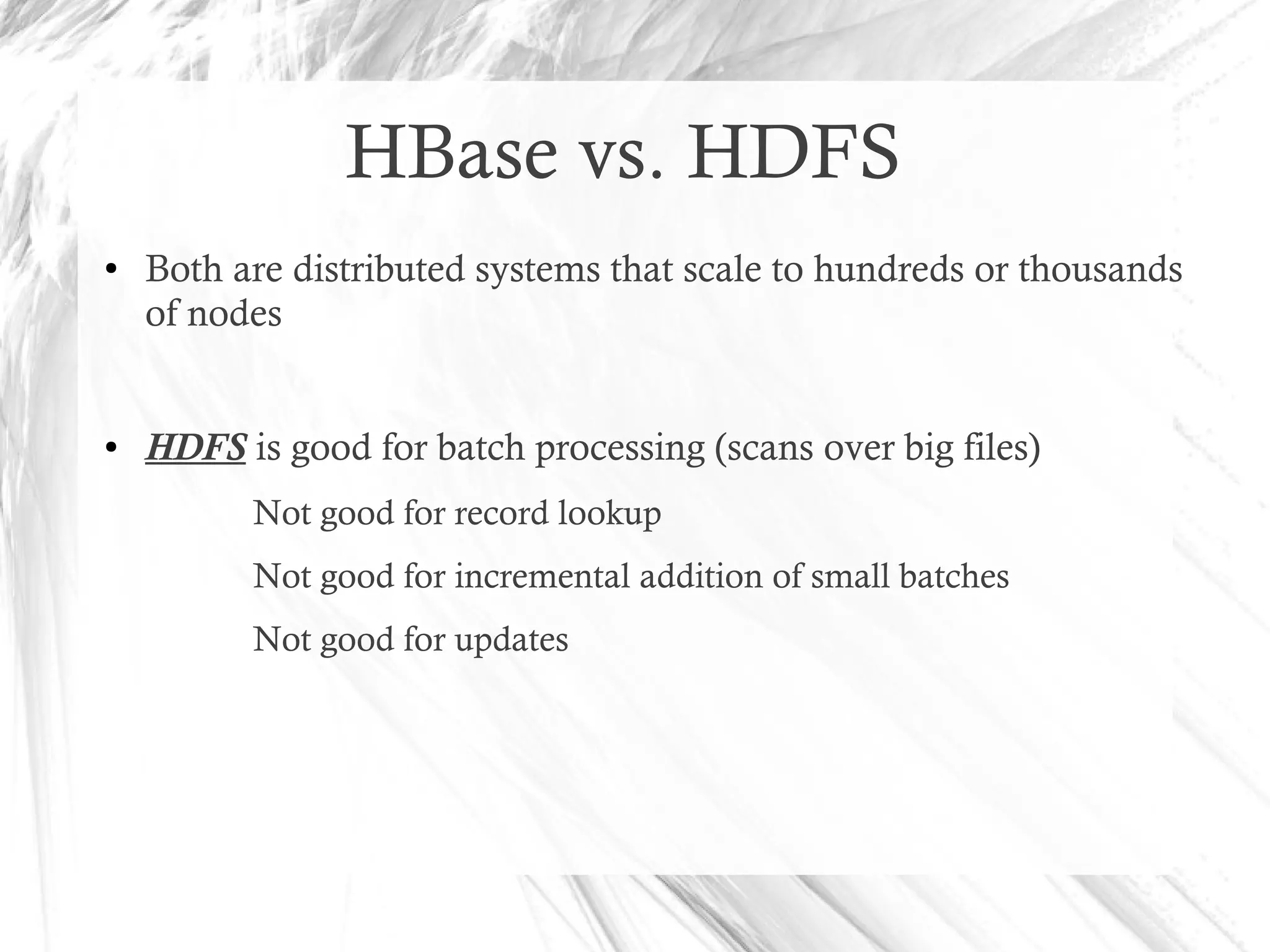
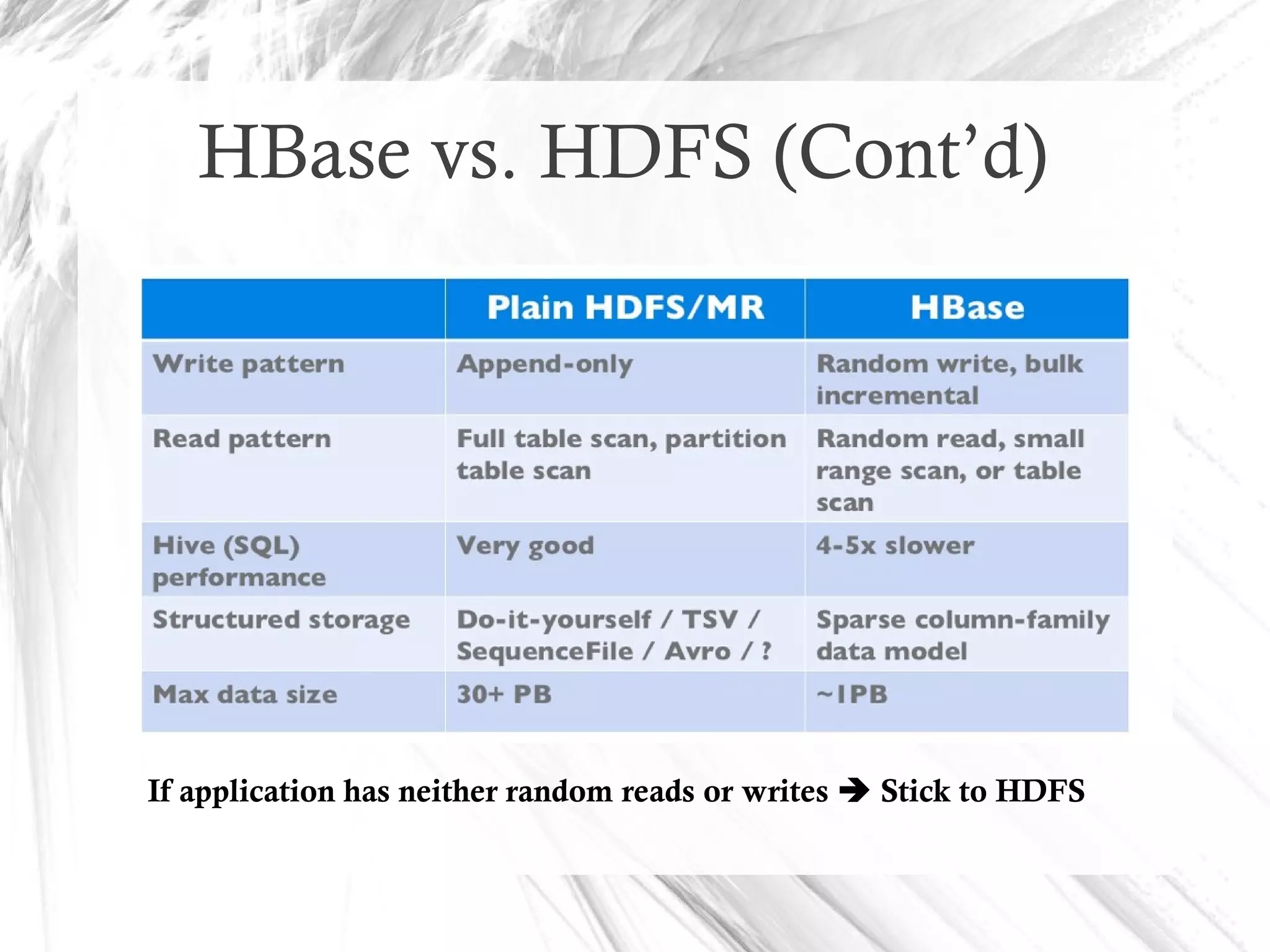
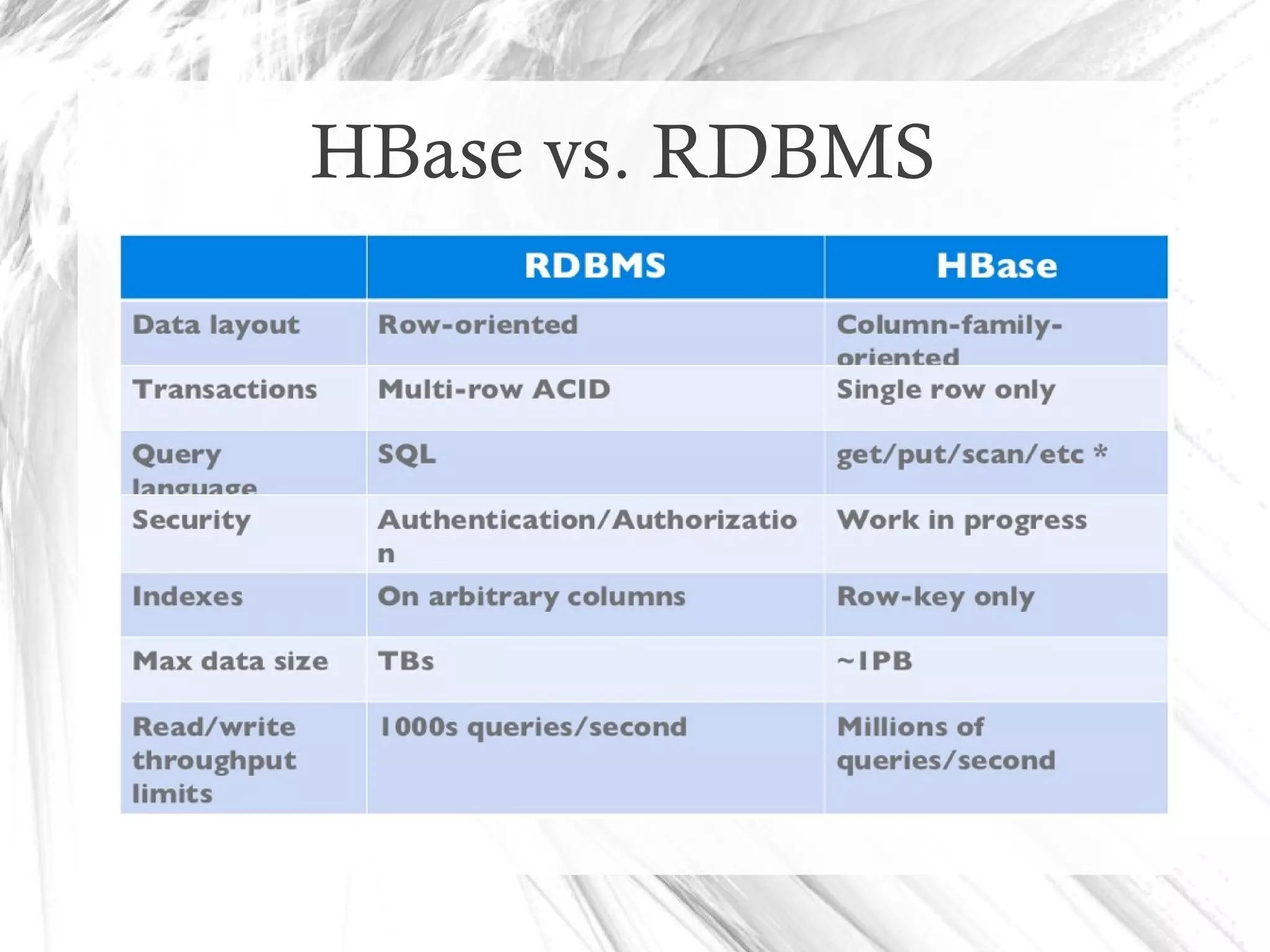
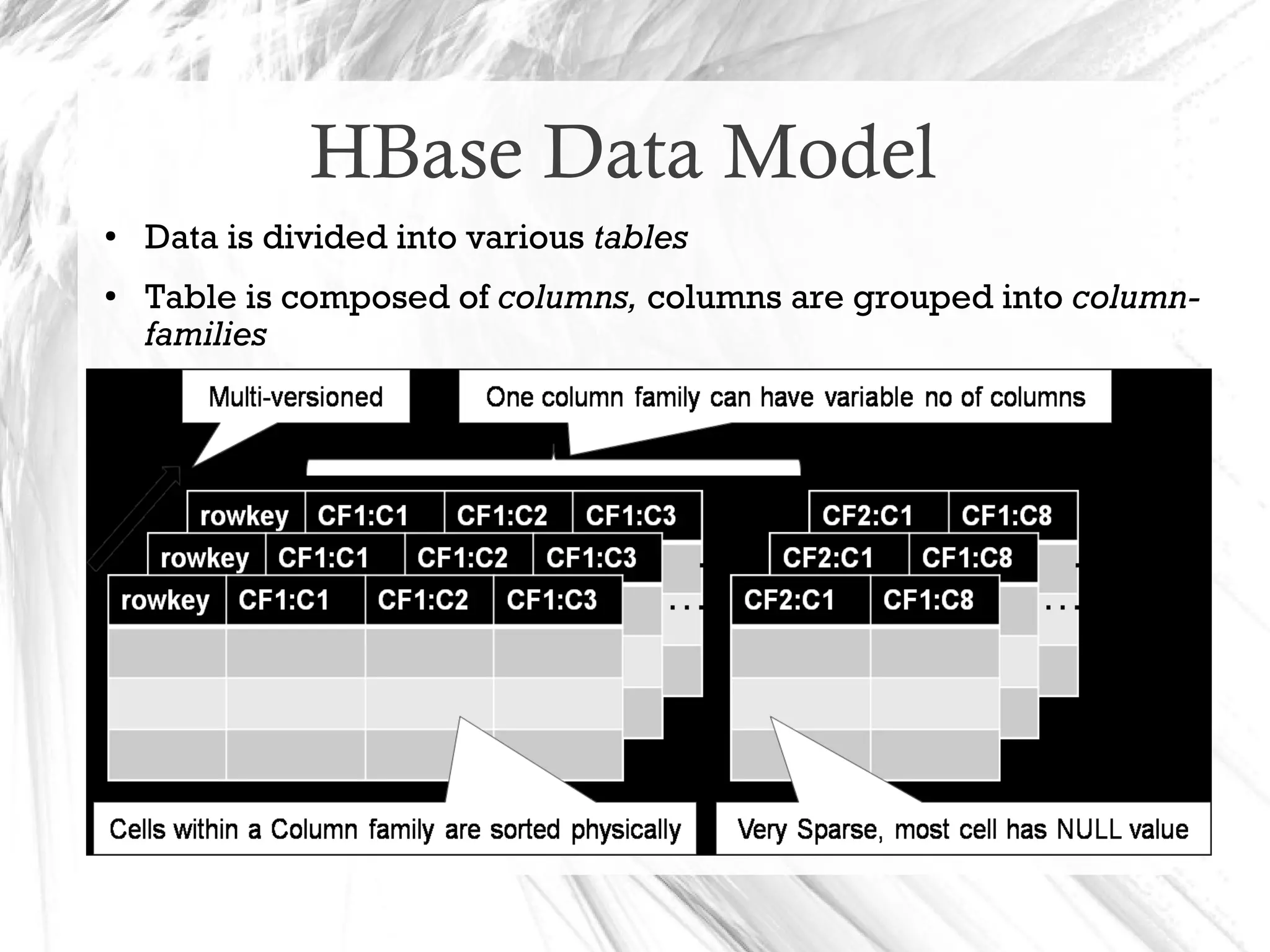
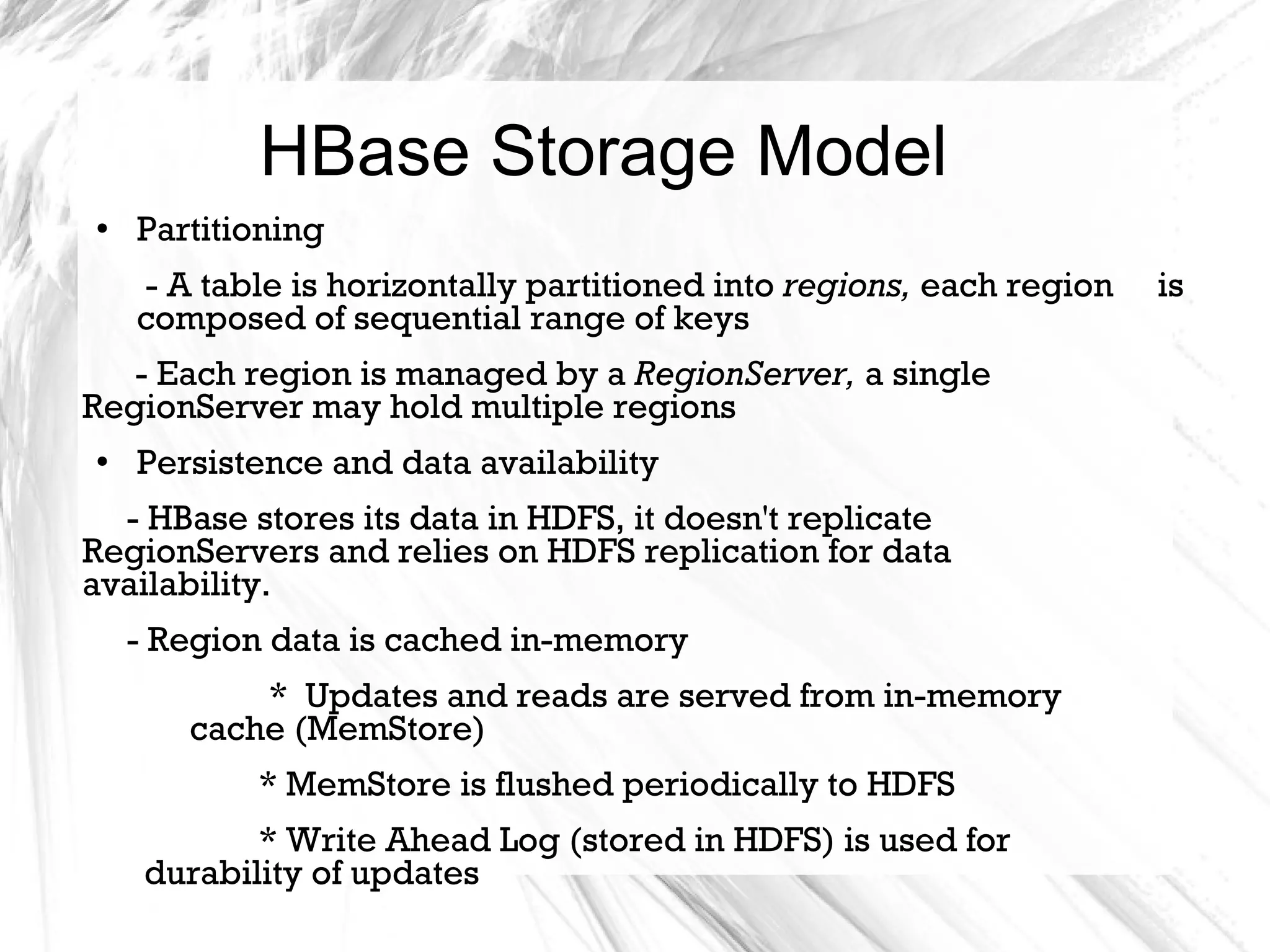
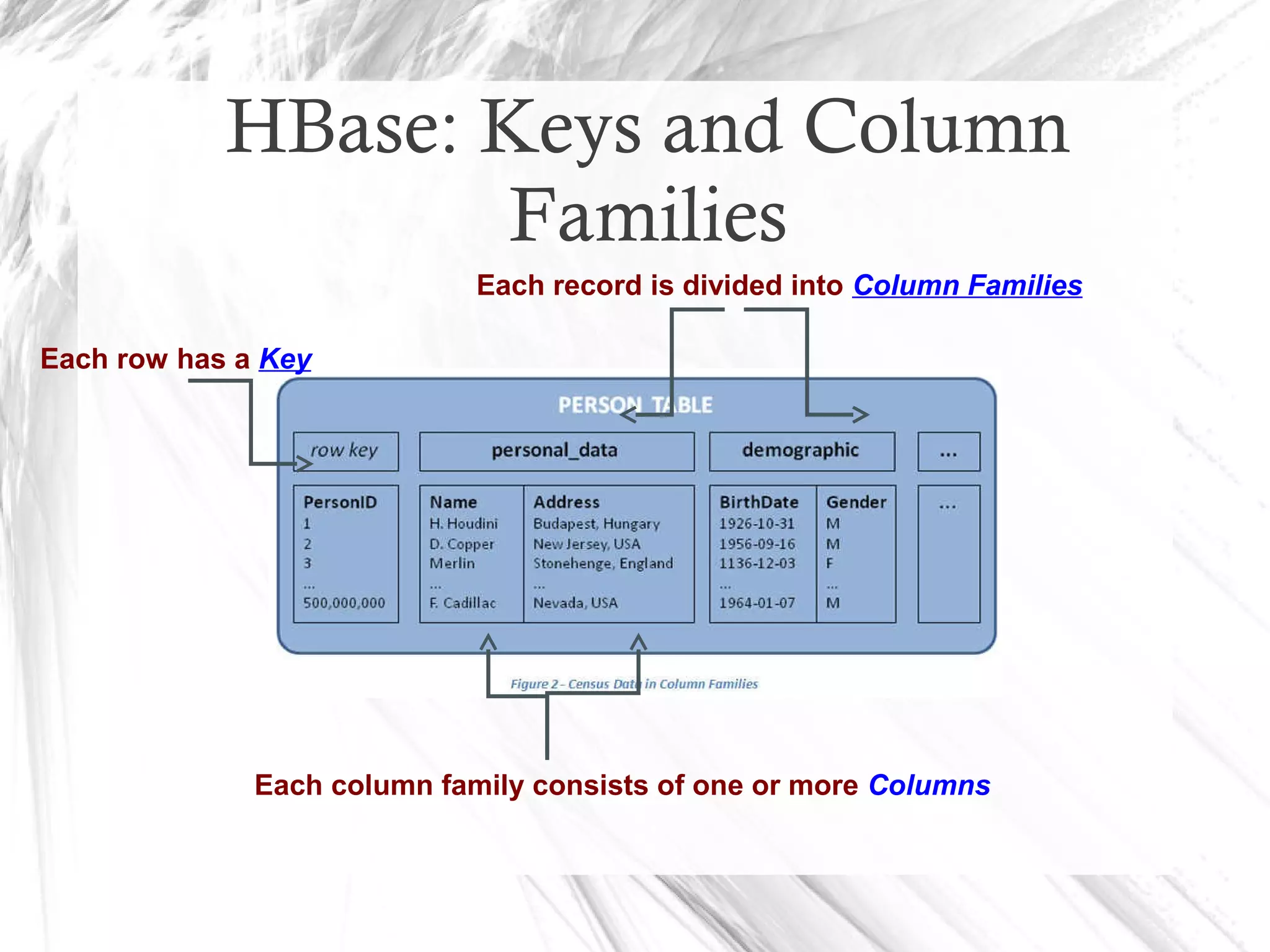
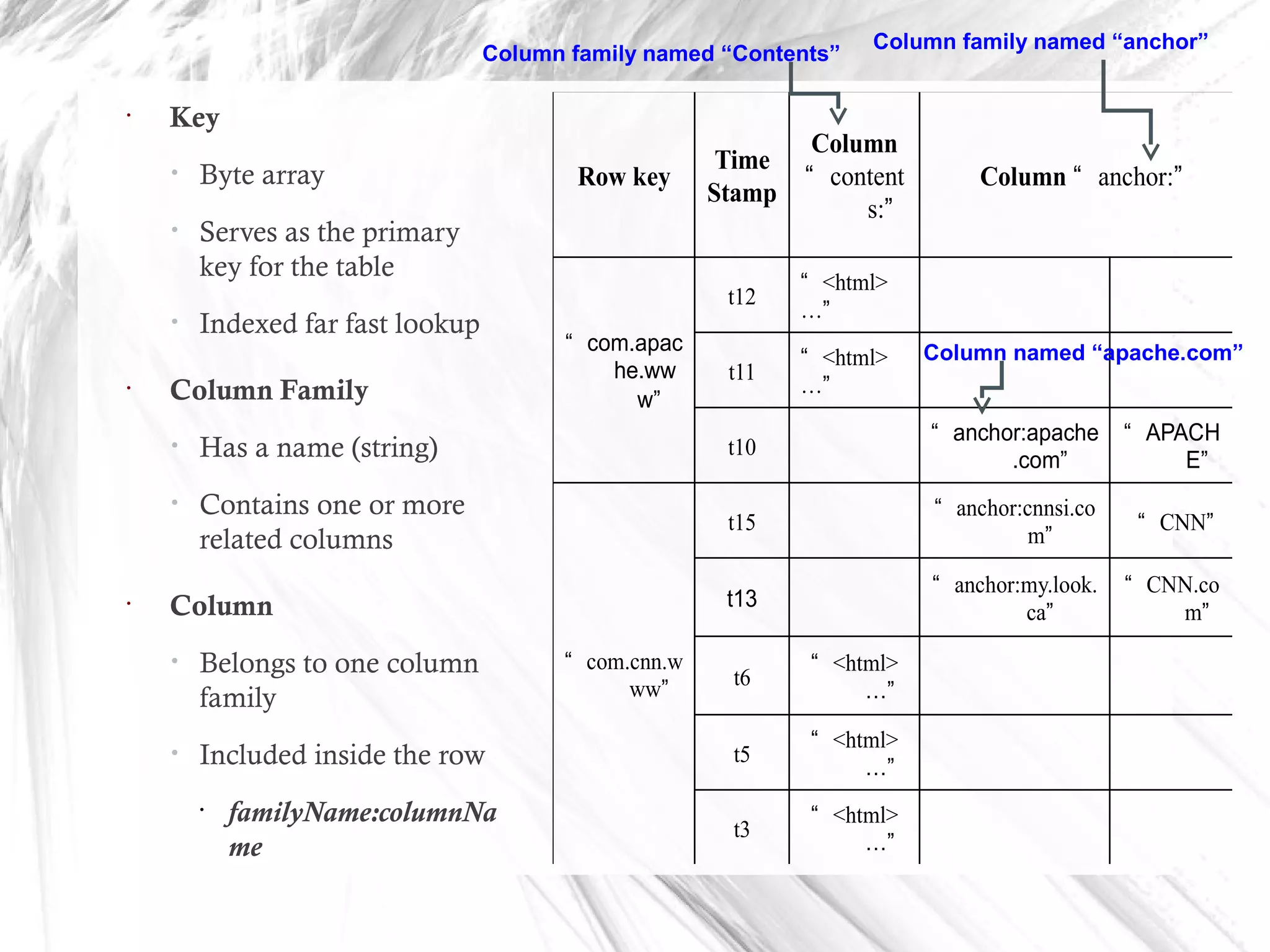
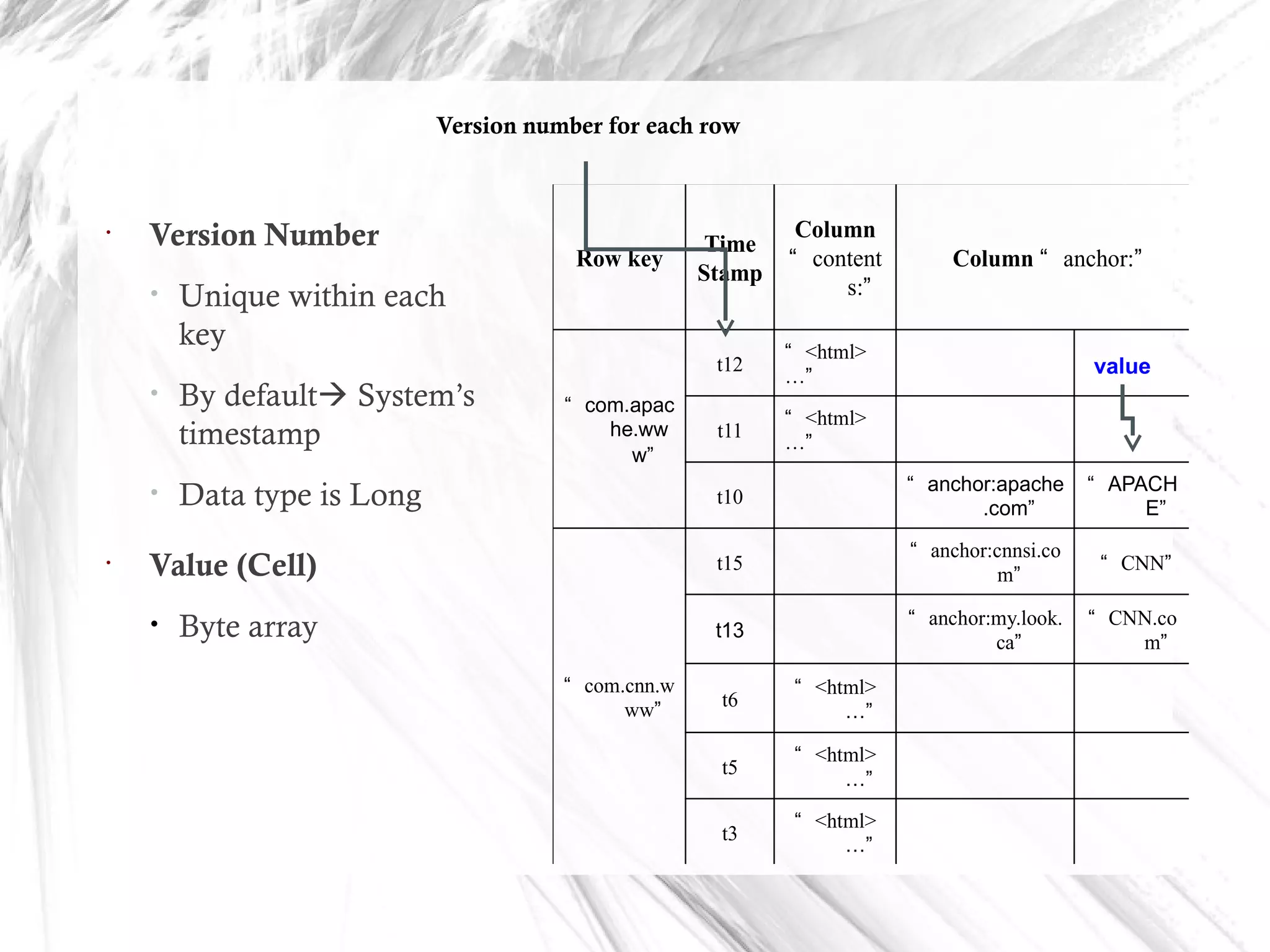
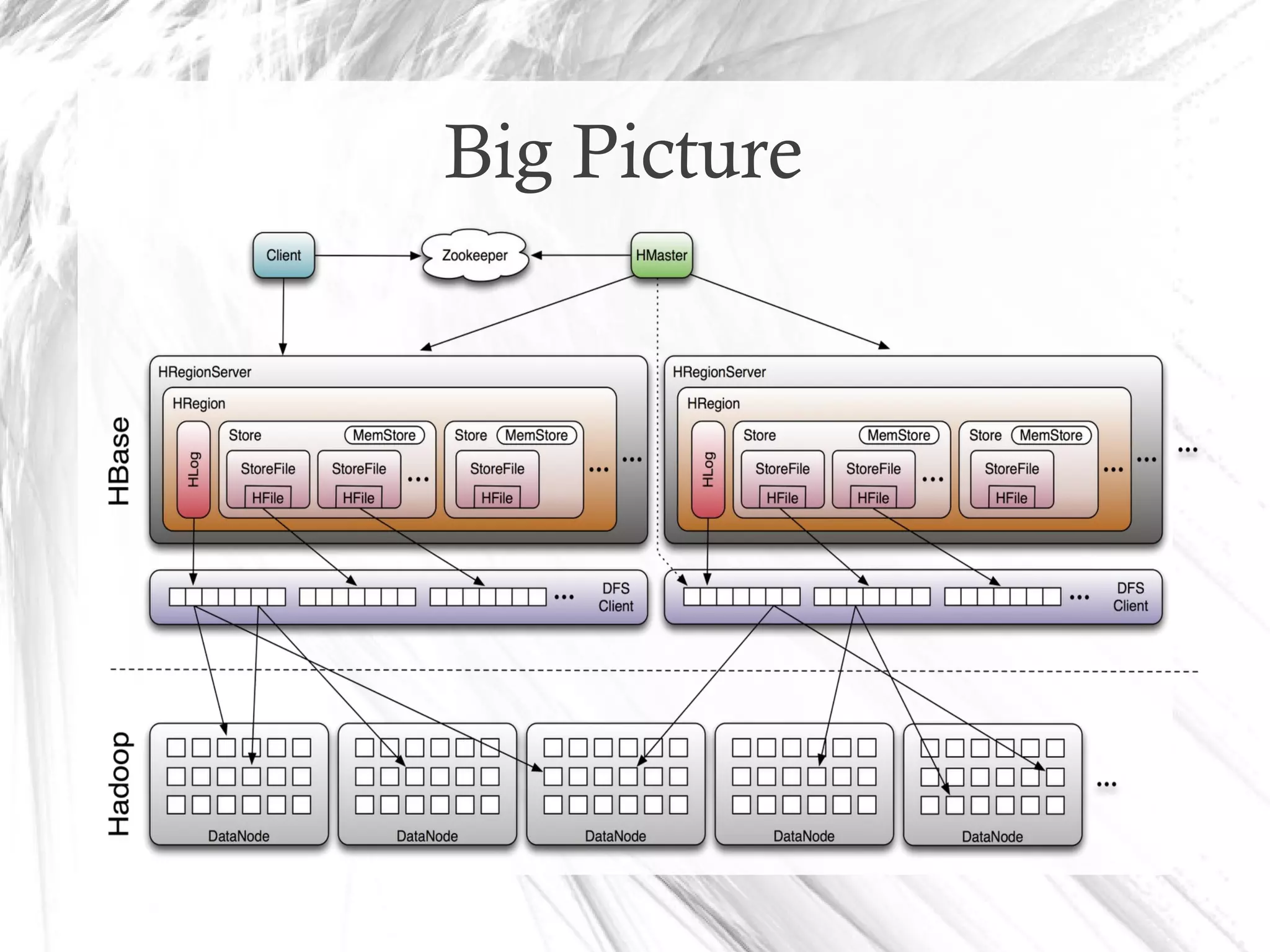
HBase is a distributed data store designed for scalability and high performance, operating on top of Hadoop's HDFS. It features a table-like data structure with high availability, but has limitations such as no SQL access and limited transaction support. HBase is suitable for applications needing fast record retrieval and is integrated into the Hadoop ecosystem, allowing for efficient data management and storage.








![Creating a Table
HBaseAdmin admin= new HBaseAdmin(config);
HColumnDescriptor []column;
column= new HColumnDescriptor[2];
column[0]=new HColumnDescriptor("columnFamily1:");
column[1]=new HColumnDescriptor("columnFamily2:");
HTableDescriptor desc= new
HTableDescriptor(Bytes.toBytes("MyTable"));
desc.addFamily(column[0]);
desc.addFamily(column[1]);
admin.createTable(desc);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachehadoophbase-150615063550-lva1-app6891/75/Apache-hadoop-hbase-23-2048.jpg)