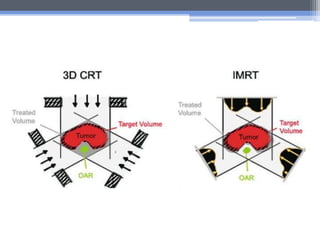
Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) is an advanced form of 3D conformal radiation therapy that uses computer-controlled linear accelerators to modulate beam intensities within each beam's projection. This allows for higher radiation doses to be delivered to tumors while reducing doses to surrounding healthy tissues. Treatment planning for IMRT involves inverse planning where optimization software determines the optimal beam intensities to meet dose requirements. Intensity is modulated during treatment using multileaf collimators which shape the beam as it is delivered. IMRT has applications in treating many types of cancer as it improves target dose conformity and reduces doses to organs-at-risk compared to other radiation therapy techniques.