Embed presentation
Downloaded 78 times




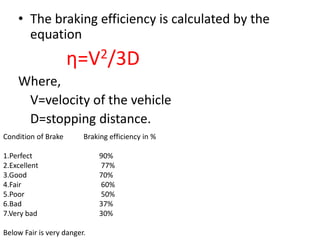
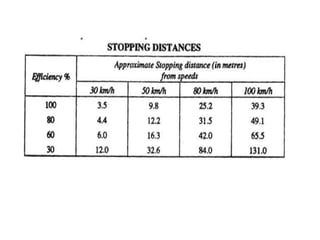
The document discusses stopping distance and braking efficiency. Stopping distance can be divided into three parts: reaction time, time for brakes to engage, and net stopping distance depending on deceleration. Braking efficiency is measured by the minimum distance needed to stop a vehicle from its speed after brakes are applied. Stopping distance depends on tire tread, inflation, and road surface conditions as well as the vehicle's velocity. Stopping distance can be calculated using the equation D=kV^2, where k depends on the braking system. Braking efficiency can be calculated as η=V^2/3D and is rated from perfect to very bad depending on the percentage.





