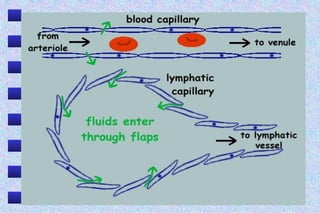
This document summarizes the exchange of tissue fluid and lymph across capillaries. It explains that as blood flows through capillaries, plasma passes into tissues to form tissue fluid which bathes and supplies cells. Not all fluid returns to capillaries, with 10% entering lymph capillaries to form lymph, which flows slowly through lymph vessels towards the heart before reentering blood. Lymph nodes along lymph vessels contain lymphocytes that help fight infection.