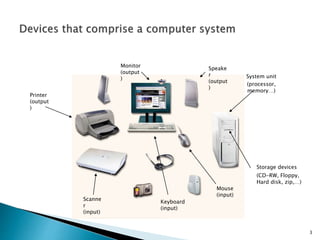
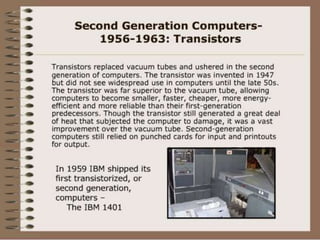
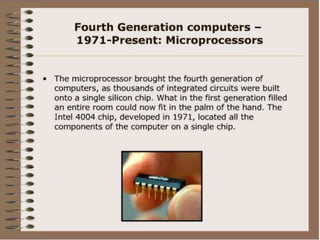
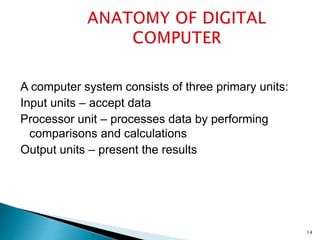
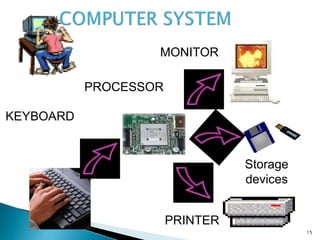
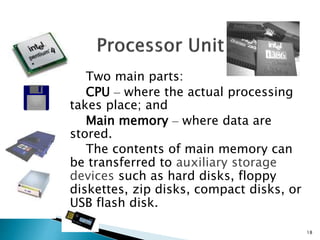
The document discusses the basic components and functions of a computer system. It explains that a computer consists of input, processing, output, and storage units that work together. The key components include the processor, memory, storage devices, input devices like a keyboard and mouse, and output devices like a monitor and printer that allow a computer to accept data, process it, and produce information.