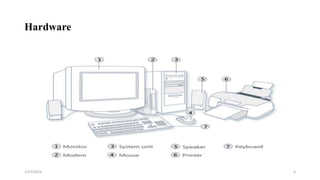
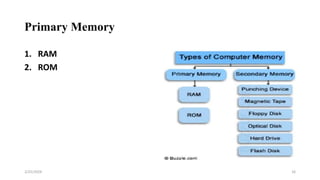
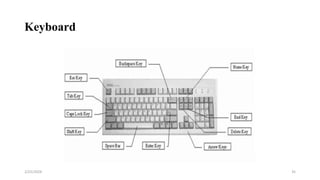
This document provides an introduction to basic computer skills for graduate students at Mattu University. It covers topics such as computer components, hardware and software, input and output devices, using a mouse and keyboard, and the desktop environment. The document defines a computer and its functions. It describes the central processing unit including the arithmetic logic unit and control unit. It also outlines primary and secondary memory, input devices, and how to start and shut down a computer properly.