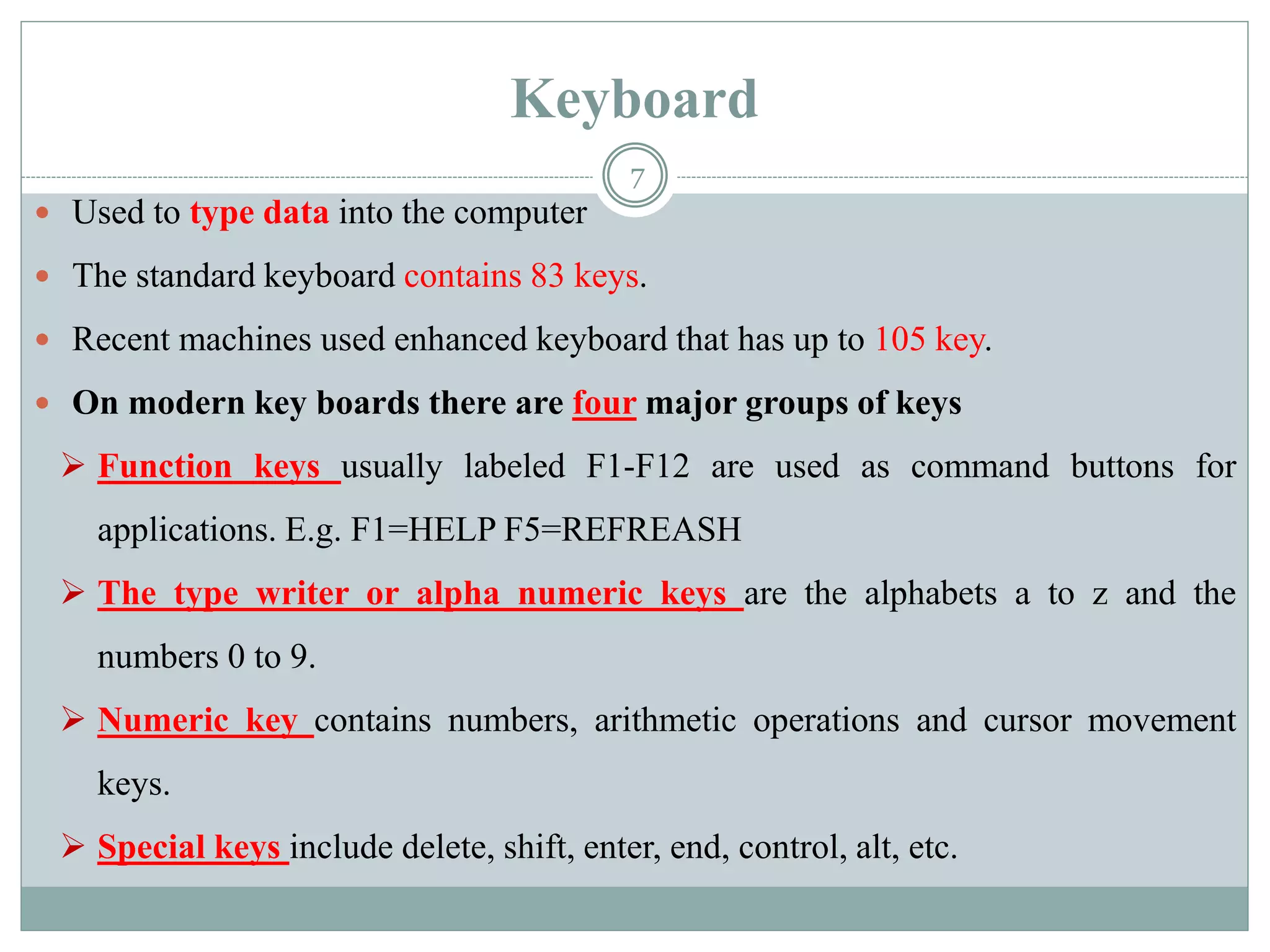
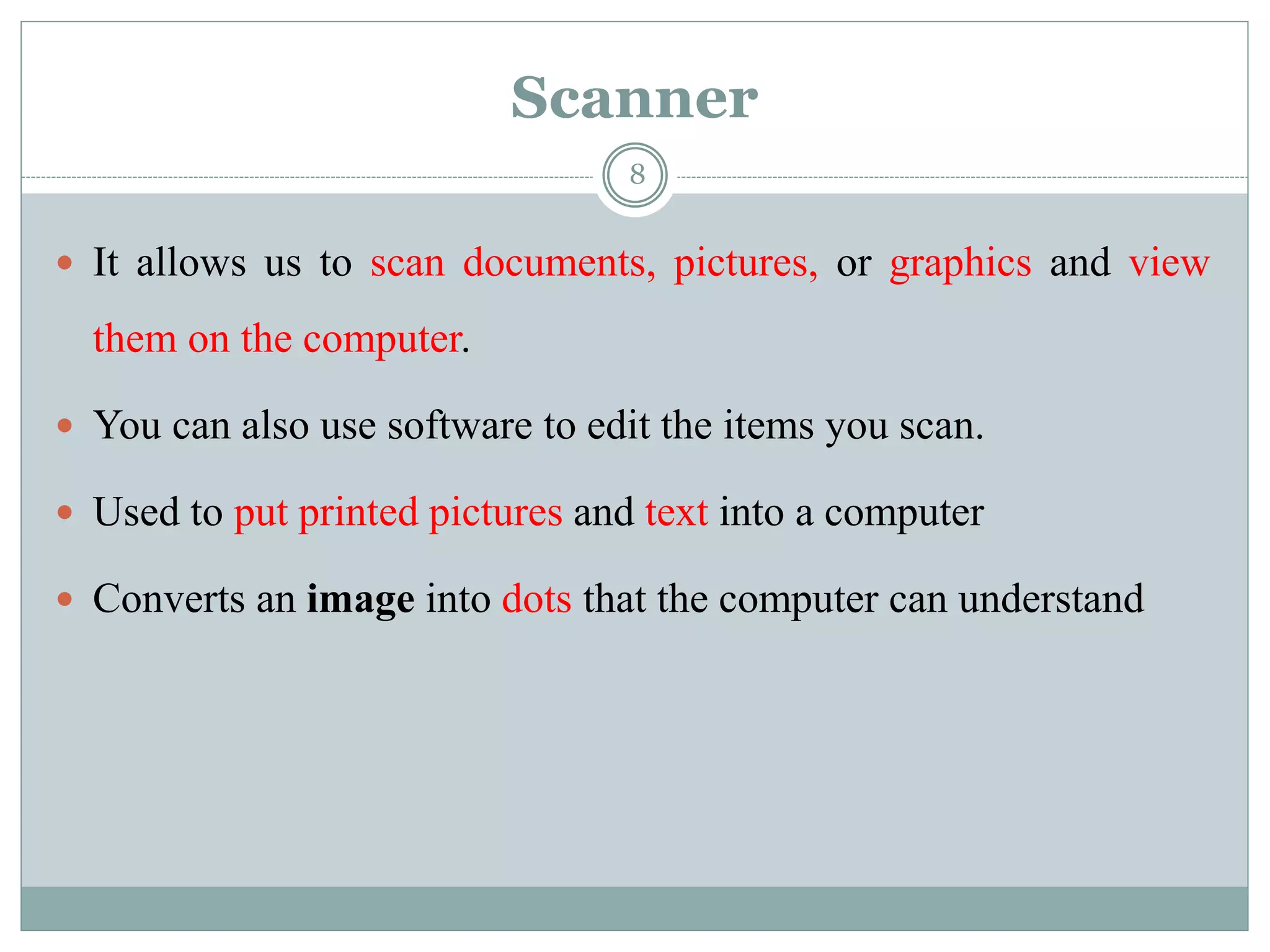
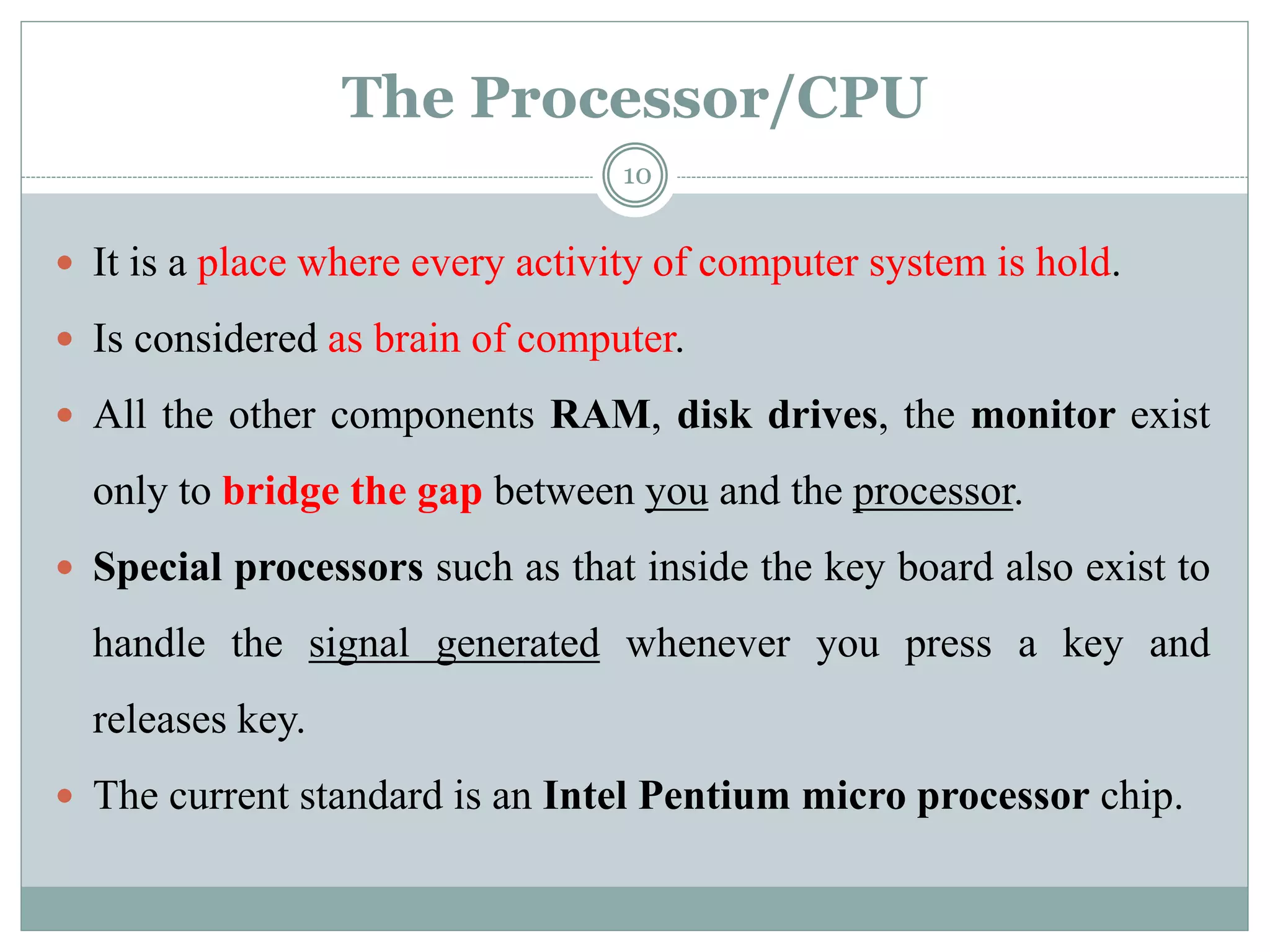
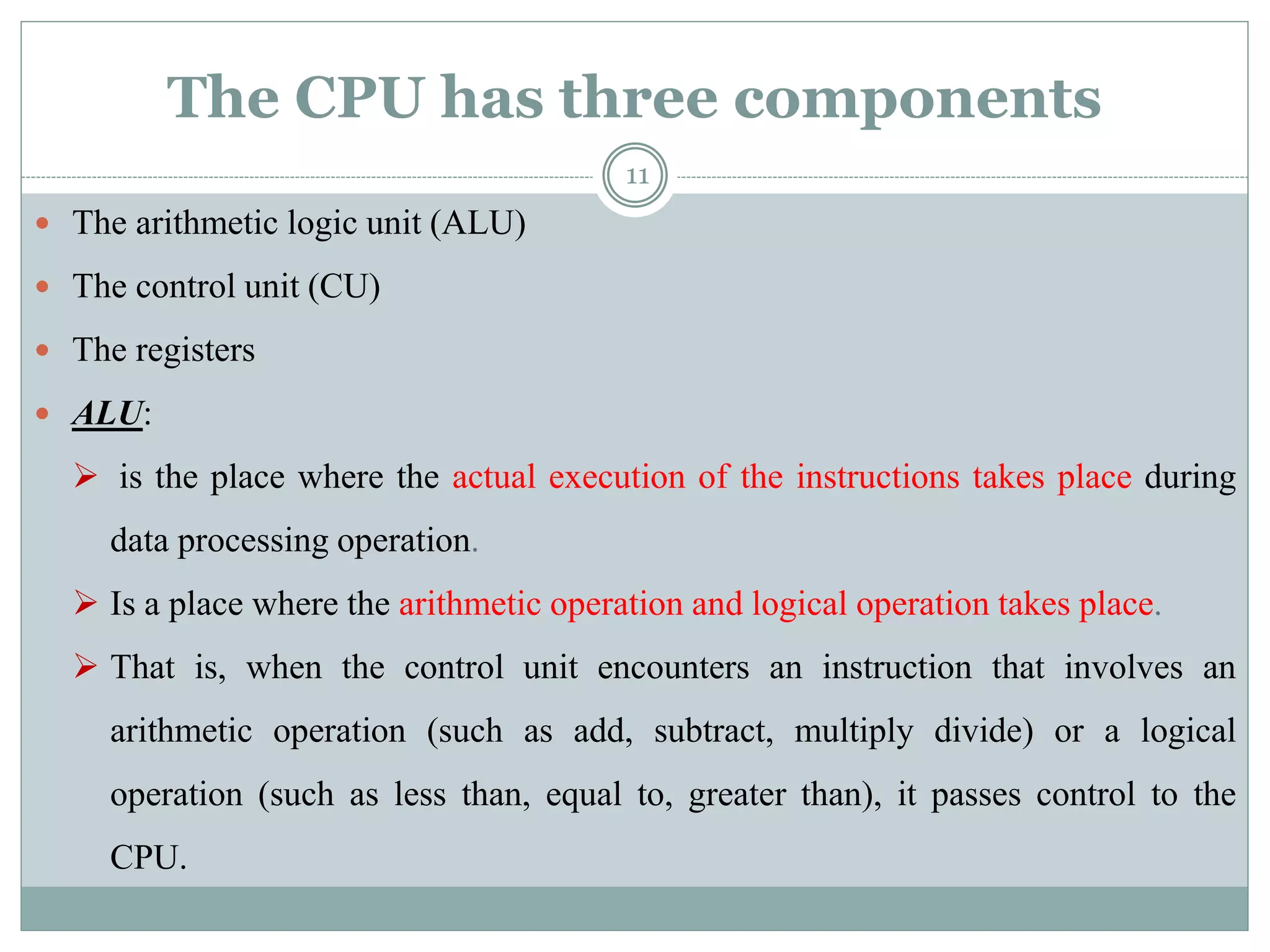
The document describes the components of a computer system, emphasizing hardware and software, with a focus on various types of input and output devices, the CPU, and memory configurations. It elaborates on the roles of input devices like keyboards and mice, the CPU's functions, and distinctions between primary and secondary storage types. Additionally, it addresses factors affecting computer speed, including memory amount, processor speed, and bus speed.