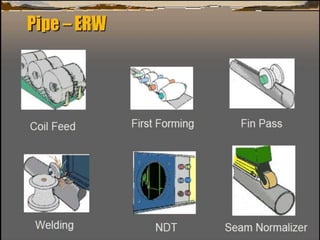
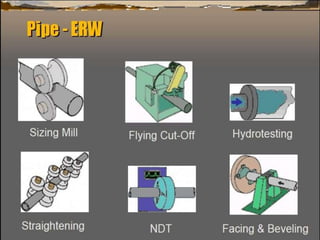
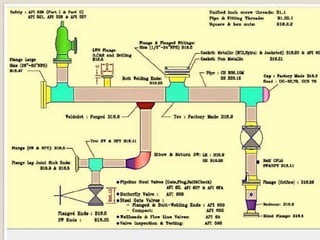
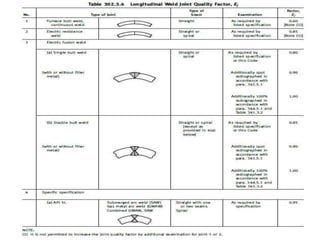
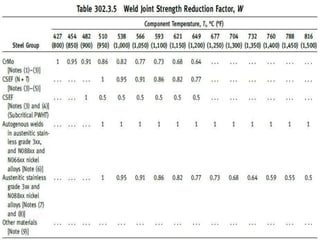
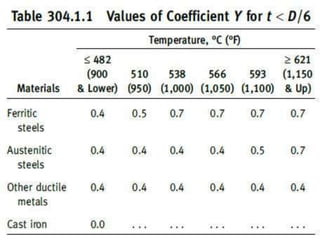
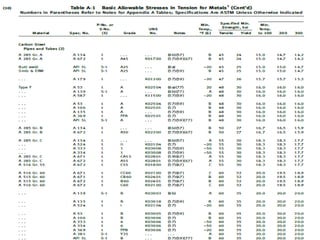
This document discusses the calculation of pipe wall thickness for pressure applications. It begins with an introduction to different pipe types and materials. It then explains that pipe wall thickness is designated by schedules or weight, and provides the equation to calculate thickness based on internal pressure, outer diameter, and allowable stress. The document outlines two methods for calculating thickness: line rating condition for individual lines, and flange rating condition to make procurement more economical. Corrosion allowance and mill tolerance must be added to the required thickness. Minimum thicknesses are provided for carbon steel and stainless steel pipes.