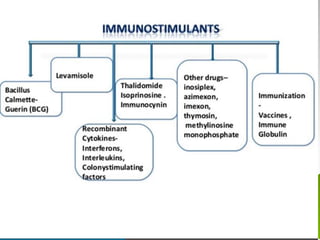
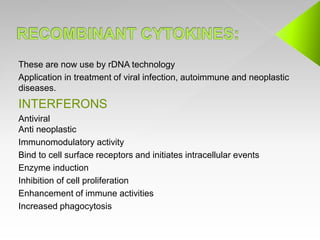
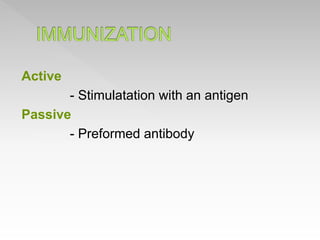
This document discusses immunomodulators, which are drugs that suppress or stimulate the immune system. It describes various immunostimulants and immunosuppressants, along with their characteristics, uses, and classifications. Specific drugs that are discussed include BCG, levamisole, interferons, interleukin-2, and vaccines. Adverse effects are also summarized for some of these immunomodulating drugs.