Embed presentation
Downloaded 316 times

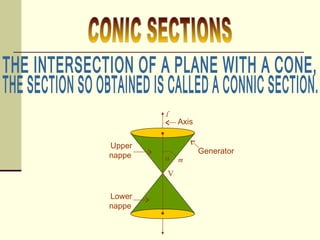








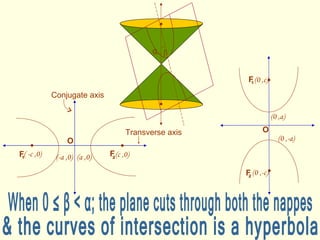
The document discusses different types of conic sections formed by the intersection of a plane with a cone. It defines a conic section as the section obtained from this intersection. It then explains that a circle is formed when the plane is perpendicular to the cone's axis. An ellipse is formed when the plane intersects at an angle between the circle and parabola. A parabola is formed when the plane is tangent to the cone. A hyperbola is formed when the plane intersects both nappes of the cone at different points.










