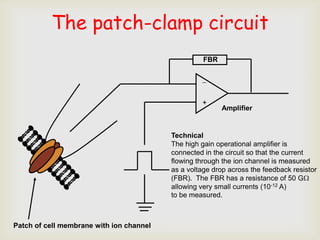
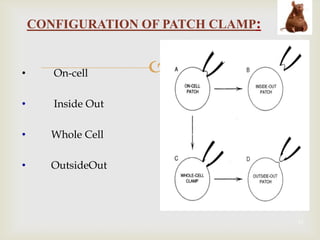
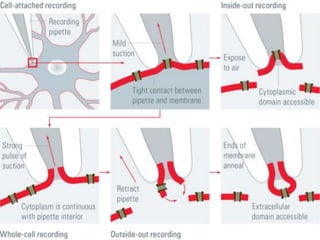
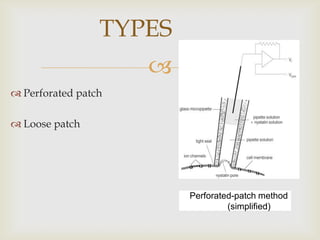
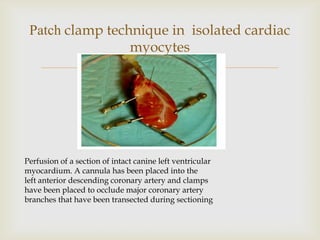
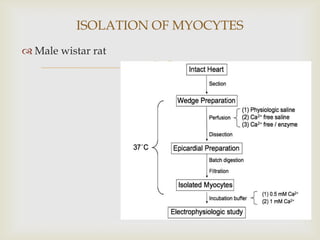
The patch clamp technique allows for the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. Developed in the 1970s-1980s by Sakmann and Neher, it involves pressing a glass pipette against a cell to form a high resistance seal, and then recording small currents through ion channels. There are different configurations (whole-cell, outside-out, etc) depending on the scientific question. Applications include evaluating drug interactions with ion channels and measuring electrophysiological properties of cells. Recent developments incorporate microfluidics for improved measurements.