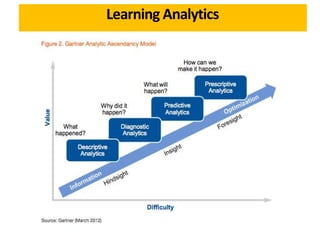
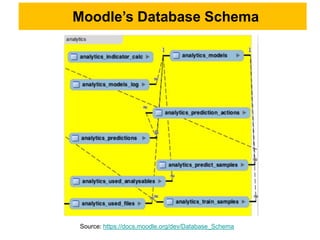
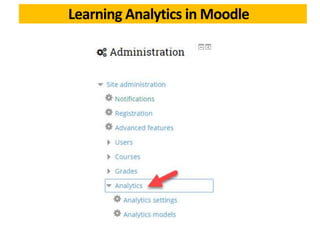
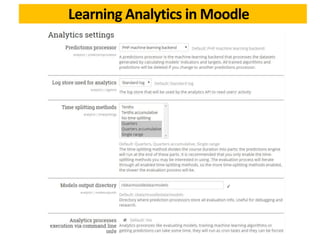
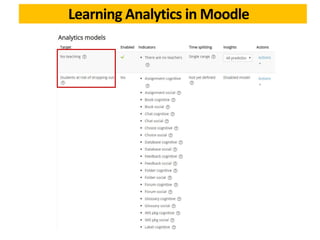
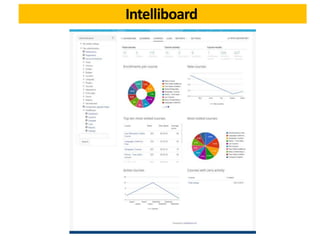
This document discusses learning analytics and how it can be used in Moodle. It defines learning analytics as the measurement, collection, analysis and reporting of data about learners and their contexts in order to understand and optimize learning. It describes how learner interactions in Moodle leave behind data that can be analyzed. It provides examples of how learning analytics can be used in Moodle to identify at-risk students, adapt teaching styles, and make curricular changes based on where students struggle. Finally, it discusses some native and third-party tools that can be used to implement learning analytics in Moodle like Inspire Analytics, Intelliboard, and Zoola.