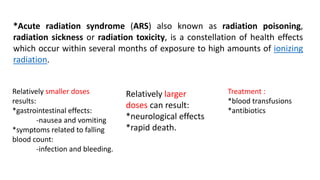
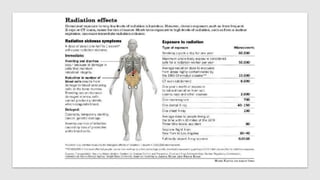
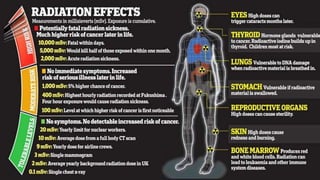
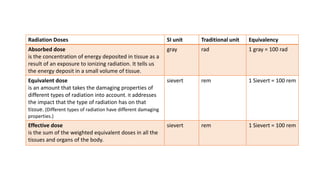
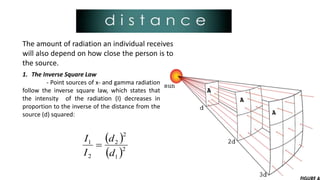
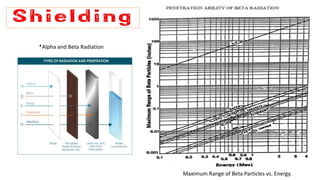
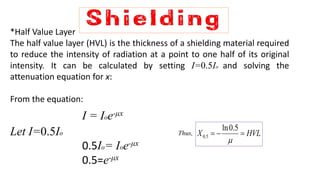
Radiation can cause both acute and chronic effects depending on the exposure level. Acute radiation poisoning occurs with high, short-term exposure and can cause gastrointestinal issues, falling blood counts, and even rapid death. Chronic radiation syndrome occurs after long-term, low-level exposure and may result in blood problems and neurological issues over time. Radiation dose is measured in grays or sieverts, and exposure can be reduced through increasing distance from the source, limiting exposure time, and using appropriate shielding materials like lead or concrete.