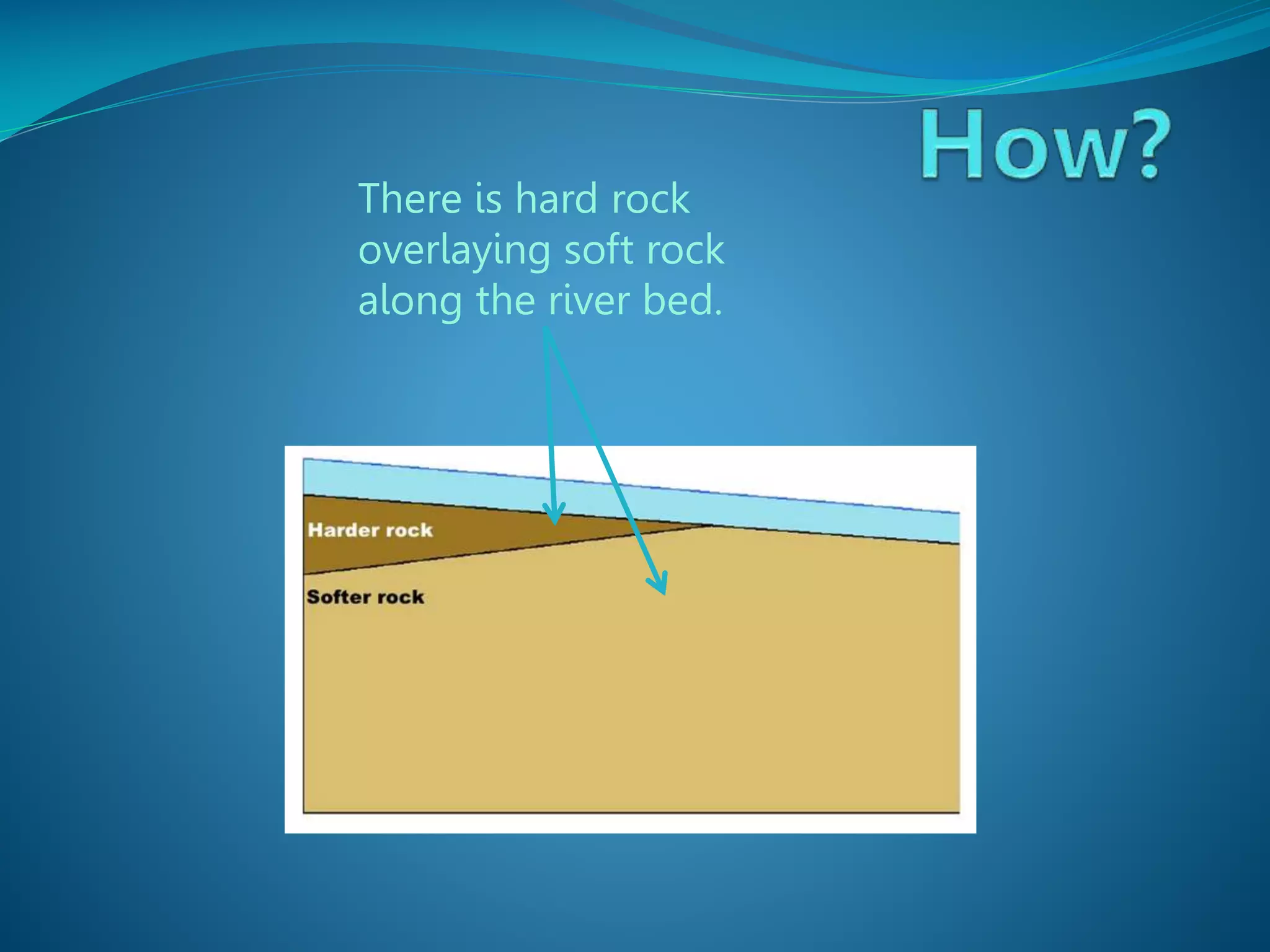
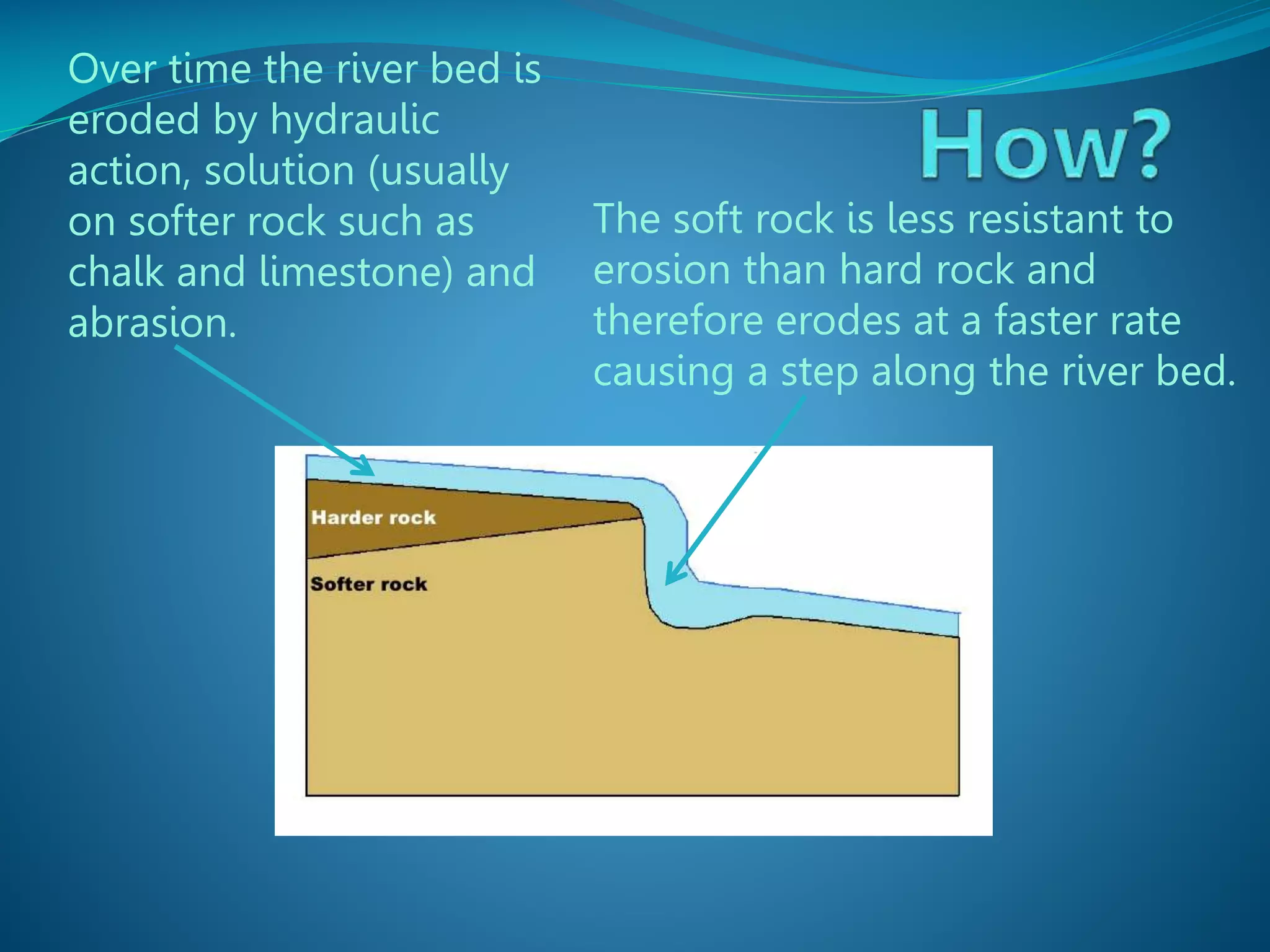
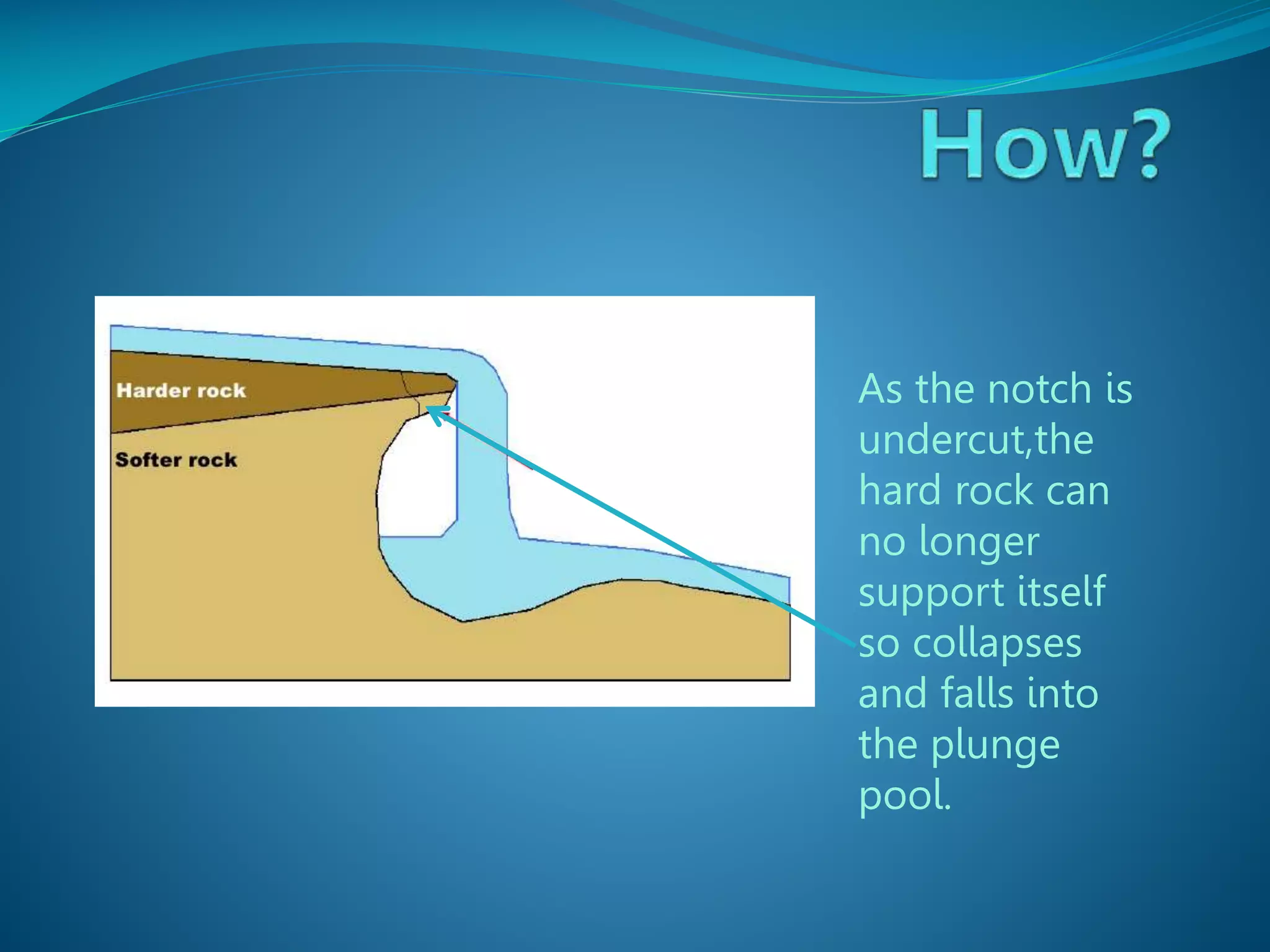
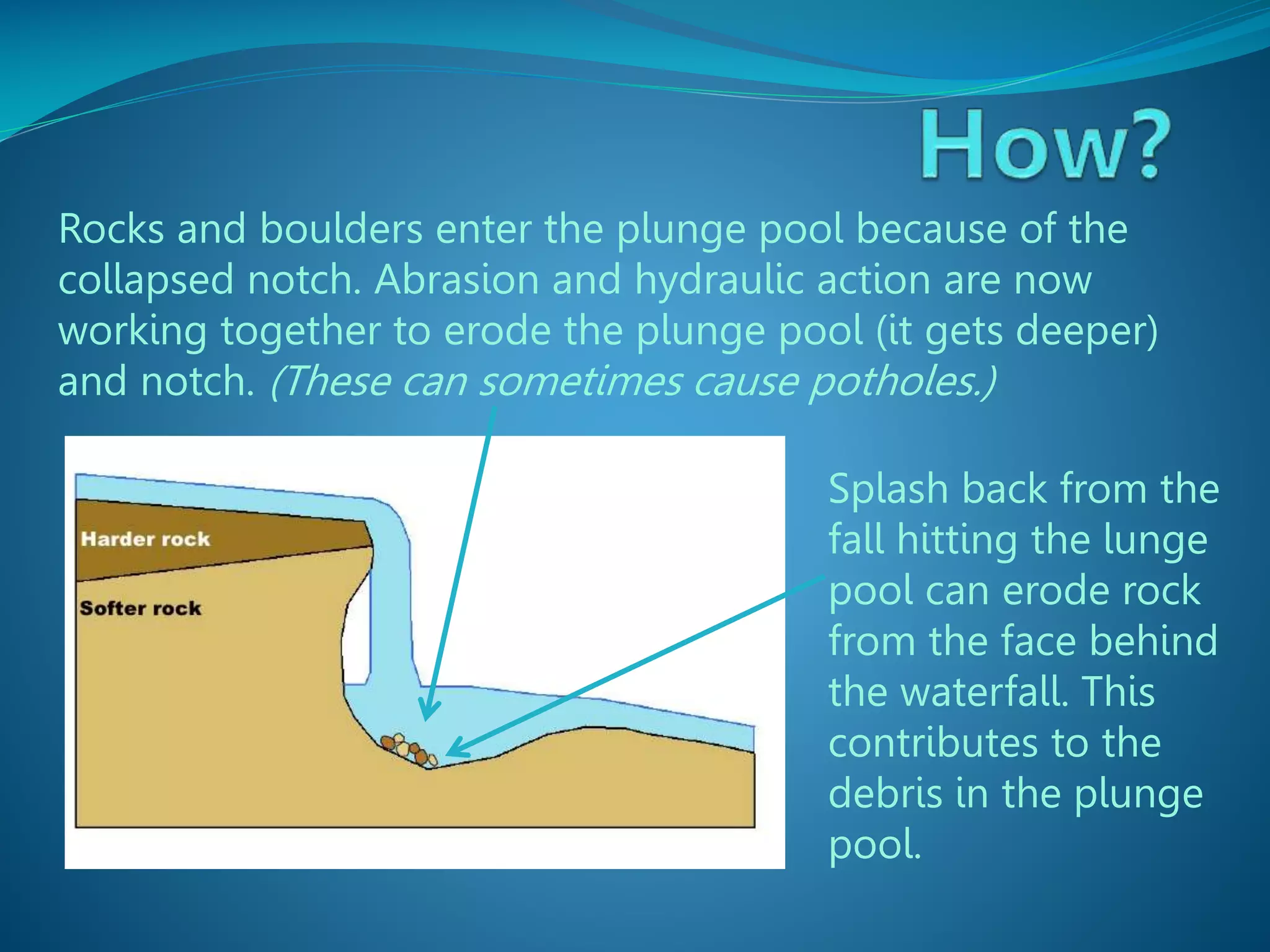
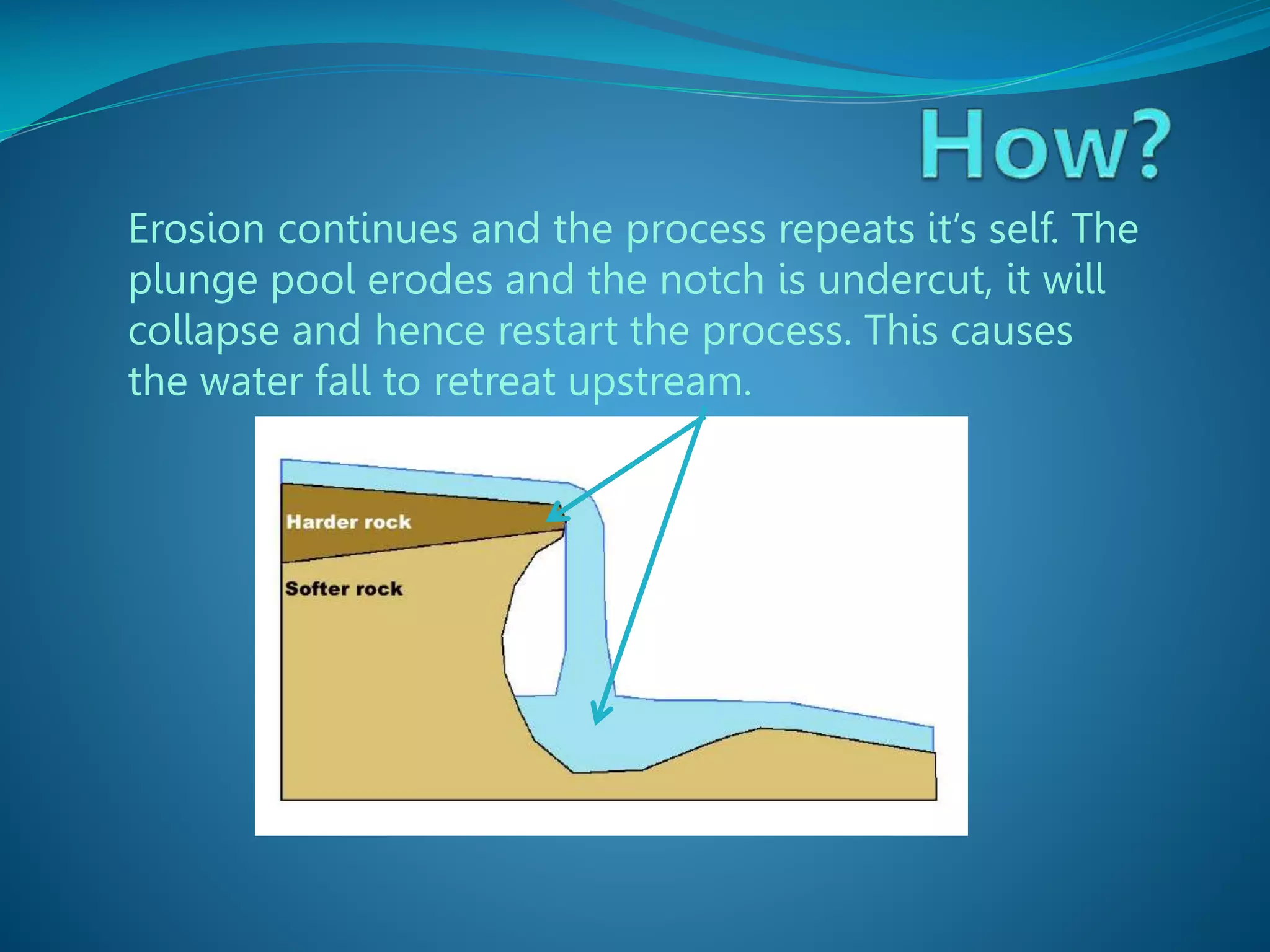
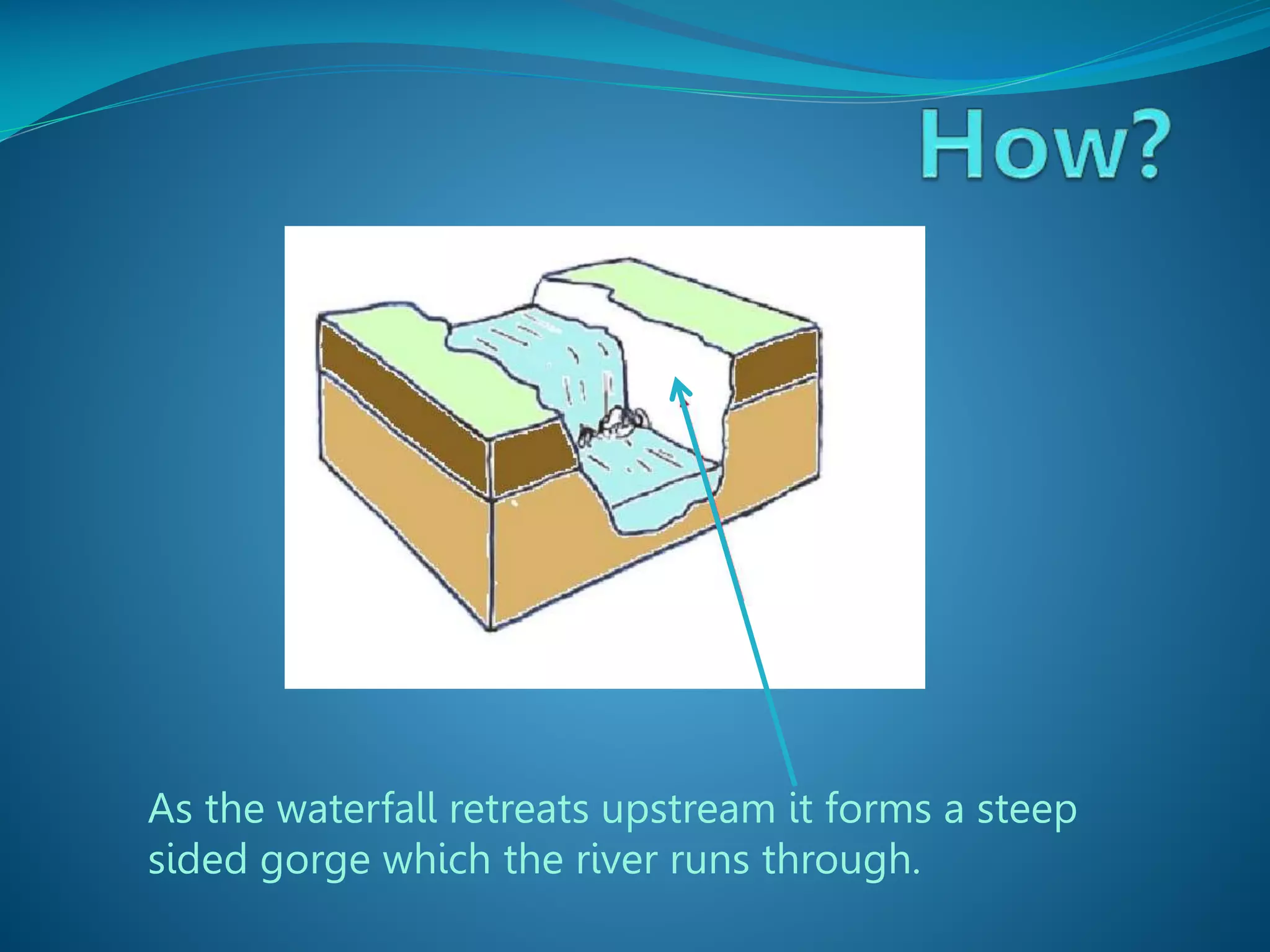
The document describes the formation and characteristics of waterfalls, detailing the erosion processes that create them, including hydraulic action and abrasion. It specifically mentions Victoria Falls, highlighting its dimensions, position between Zimbabwe and Zambia, and its status as the largest sheet of falling water in the world. The document also notes the geological formations associated with Victoria Falls, including its gorges and rock types.