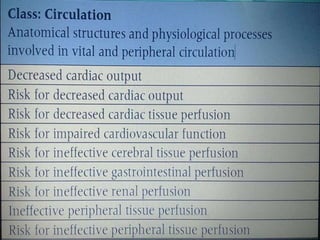
The document discusses the nursing process, which consists of five main components: assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It describes each component in detail. Assessment involves collecting, organizing, validating, and documenting client data. Nursing diagnosis involves analyzing the assessment data to identify client health problems. Planning involves prioritizing problems, setting goals, and selecting nursing interventions. Implementation is providing the planned nursing care. Evaluation compares outcomes to goals and determines if the nursing care plan needs modifying. The nursing process is a cyclic problem-solving approach used by nurses to plan and provide individualized patient care.