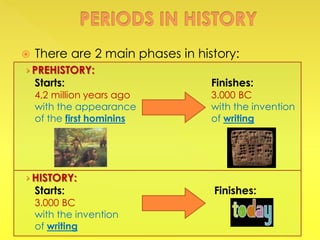
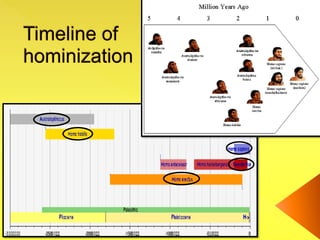
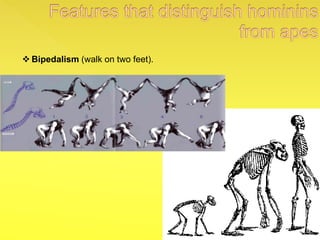
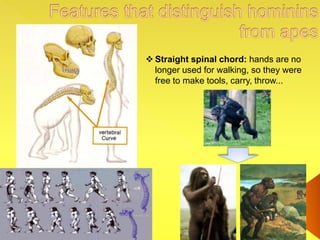
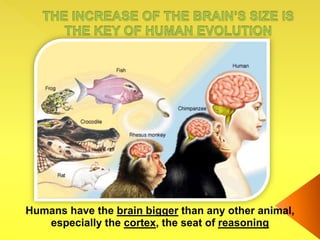
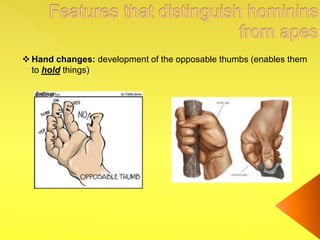
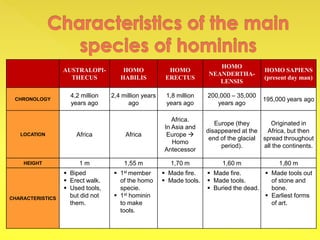
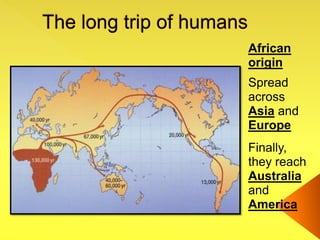
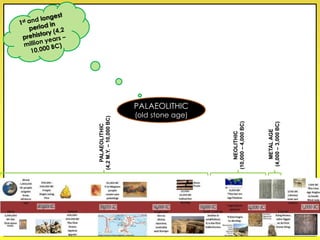
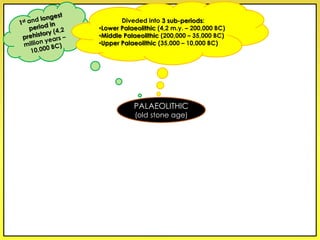
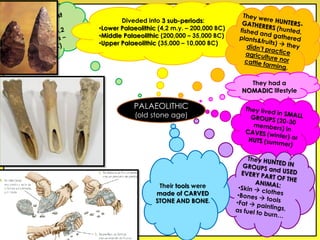
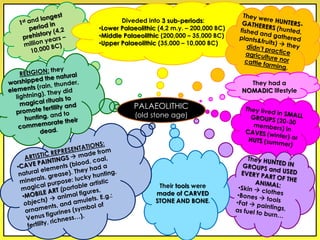
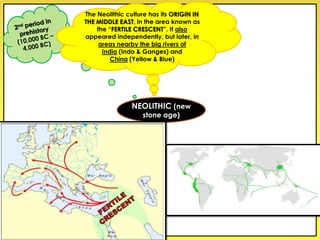
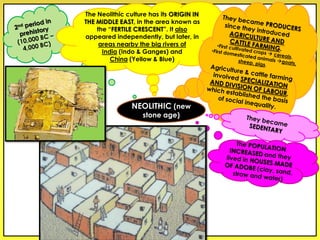
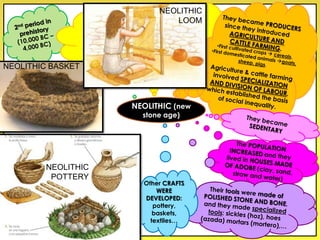
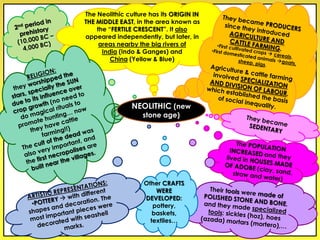
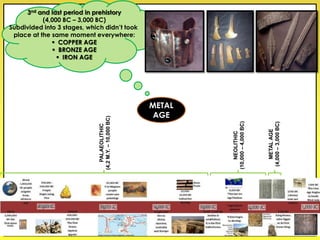
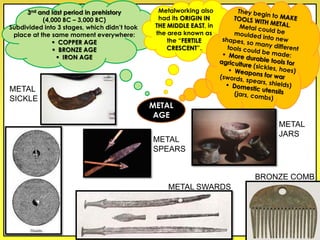
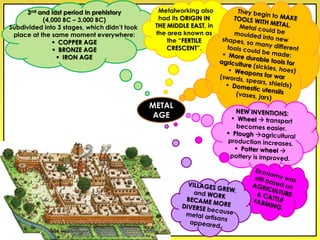
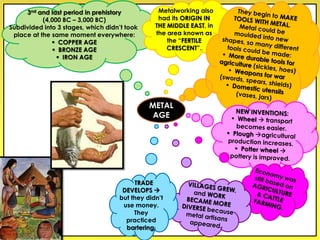
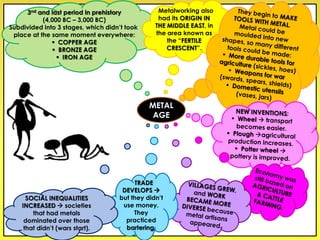
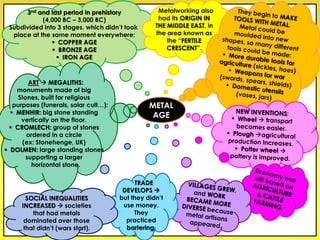
The document provides an overview of the study of history and prehistory. It discusses how historians use observations, readings, and studies of physical remains, written documents, and oral histories to understand past societies. Prehistory is divided into the Palaeolithic, Neolithic, and Metal Ages. The Palaeolithic began over 4 million years ago and saw the development of tools made of carved stone and bone. The Neolithic started around 10,000 BC and featured polished stone tools as well as early pottery, baskets, and textiles. The Metal Age between 4,000-3,000 BC comprised the Copper, Bronze, and Iron Ages defined by advances in metalworking.