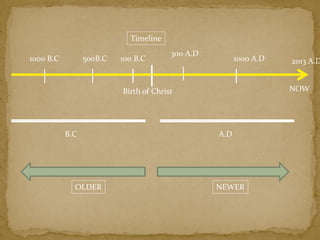
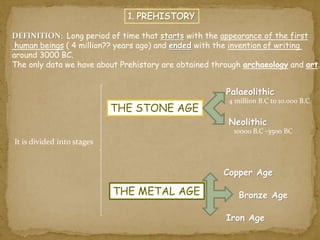
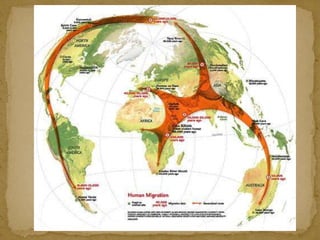
1. The document discusses the Stone Age period of prehistory, which began with the appearance of early humans and ended with the development of writing around 3500 BC.
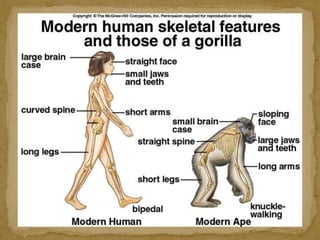
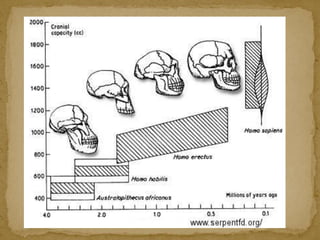
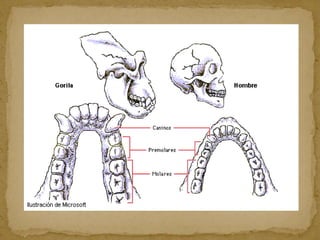
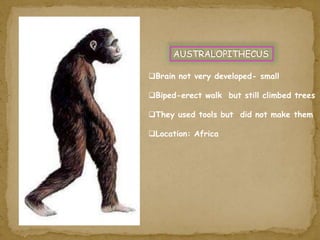
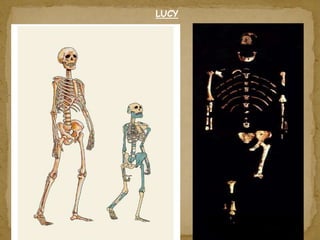
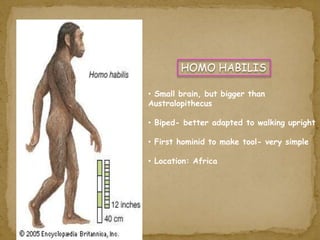
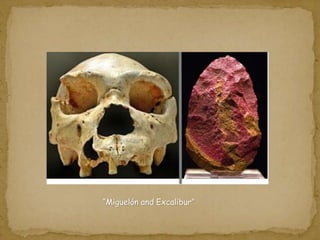
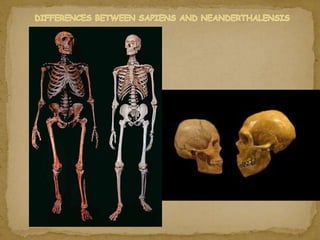
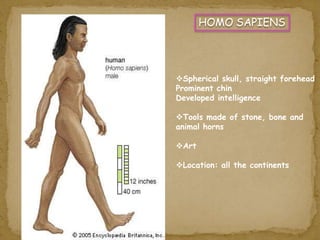
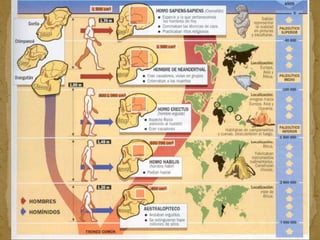
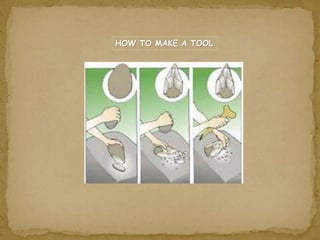
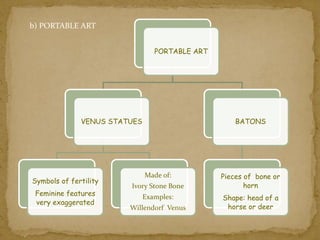
2. During the Stone Age, humans evolved from early hominids like Australopithecus to more advanced species like Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. They developed tools, learned to control fire, and left early examples of art and religious beliefs.
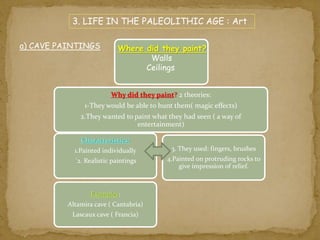
3. Life in the Paleolithic period of the Stone Age was difficult. People lived nomadic lifestyles as hunter-gatherers and had to contend with cold climates. They lived in caves or shelters in small tribes or bands.