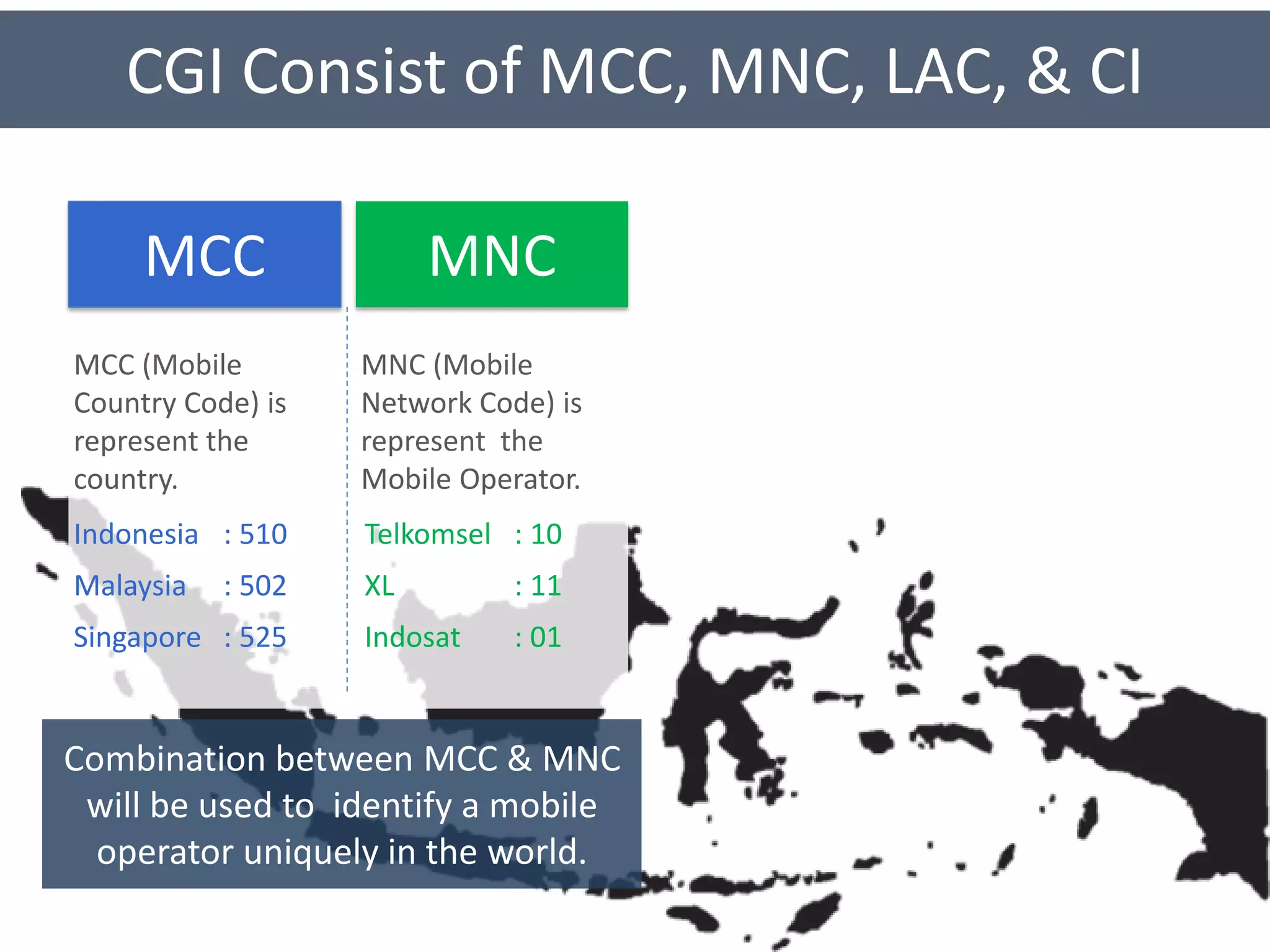
LAC-CI is a unique identifier for cells in mobile networks that consists of the Location Area Code (LAC) and Cell Identity (CI). The LAC identifies a serving area, while the CI identifies a specific cell. Properly configuring LAC-CI is important for call establishment and routing, charging subscribers correctly, and ensuring operation and business support systems have valid location data. Invalid LAC-CI configuration could result in subscribers being charged the wrong rates or systems producing invalid information.