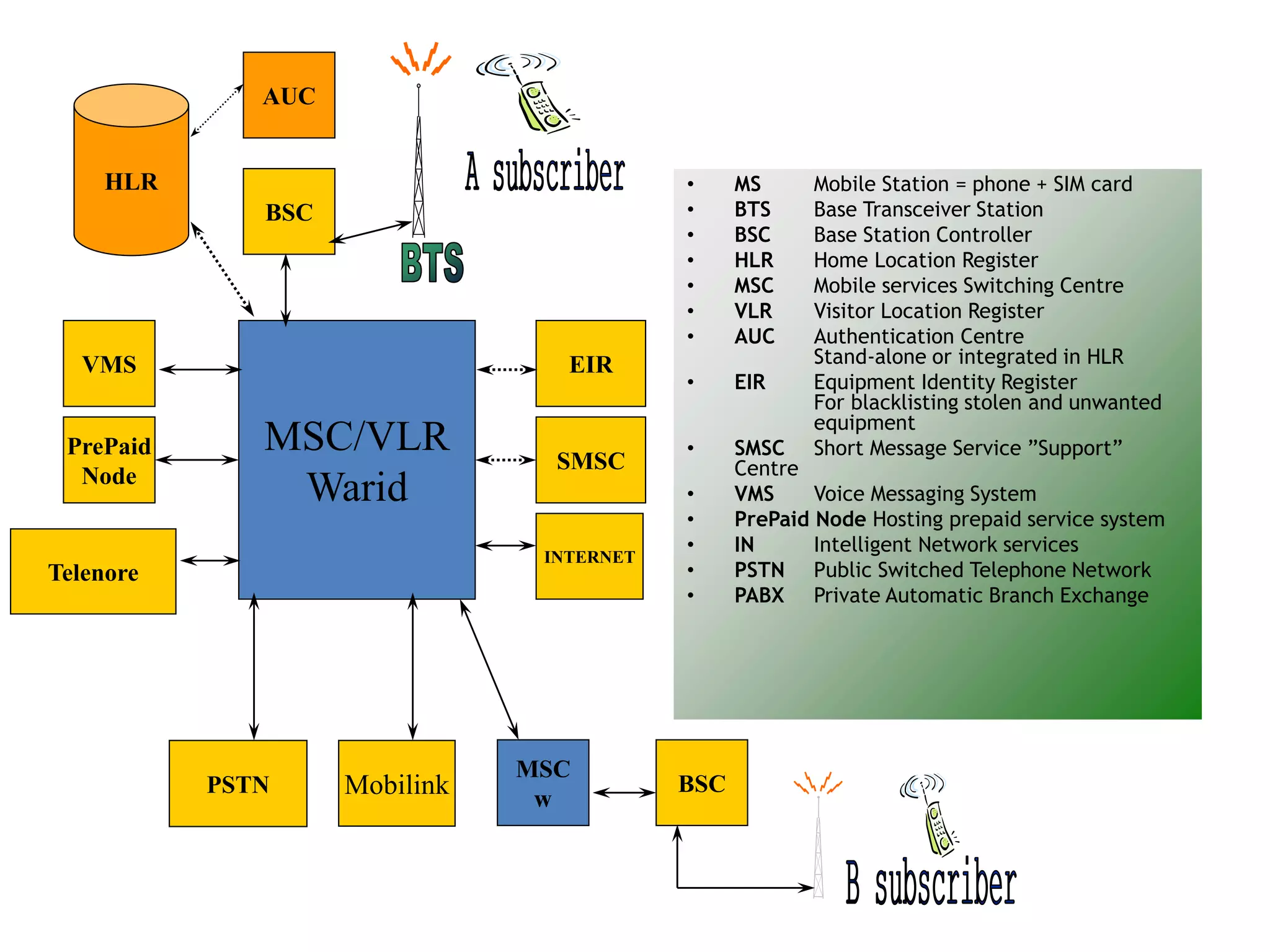
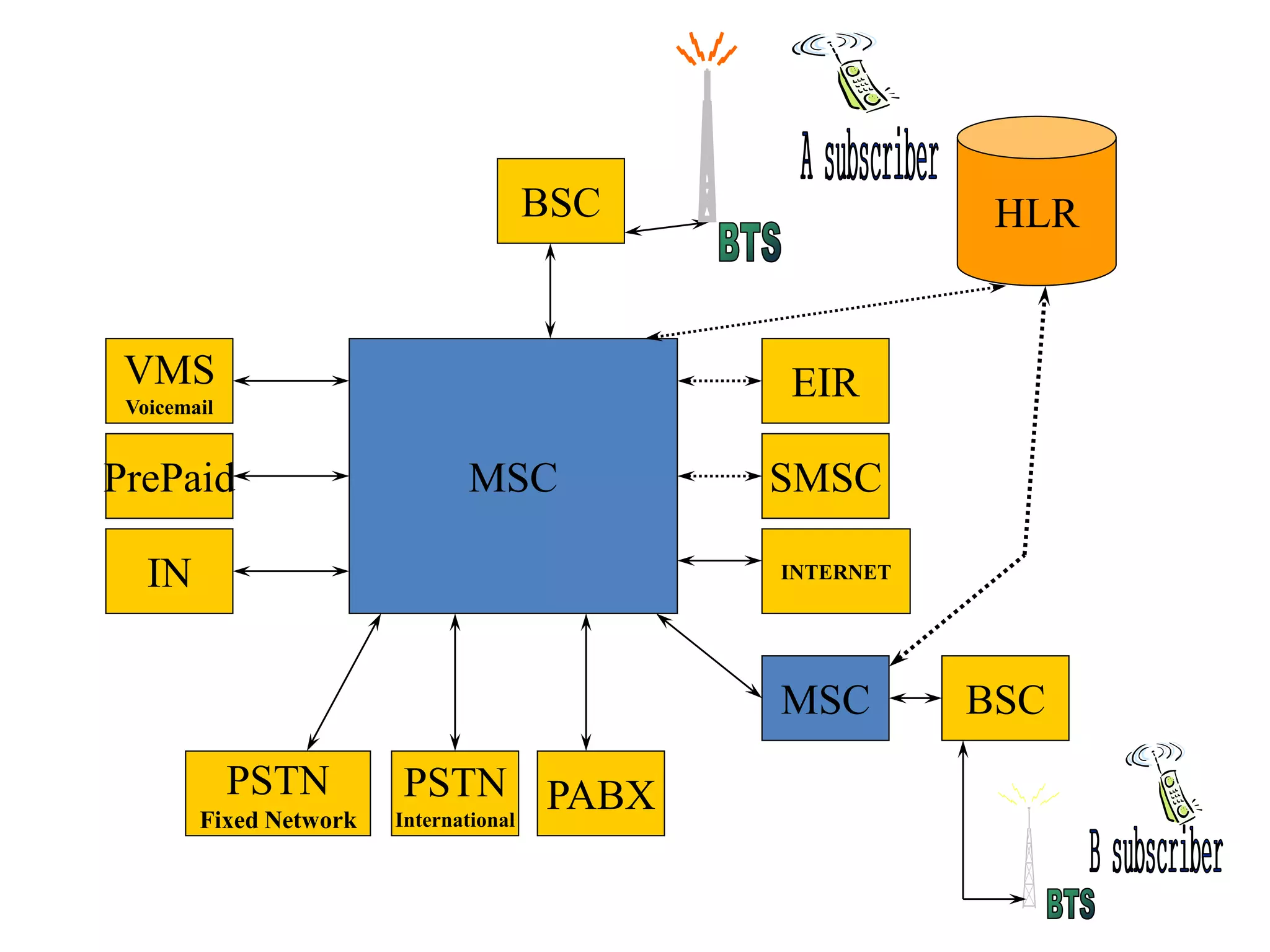
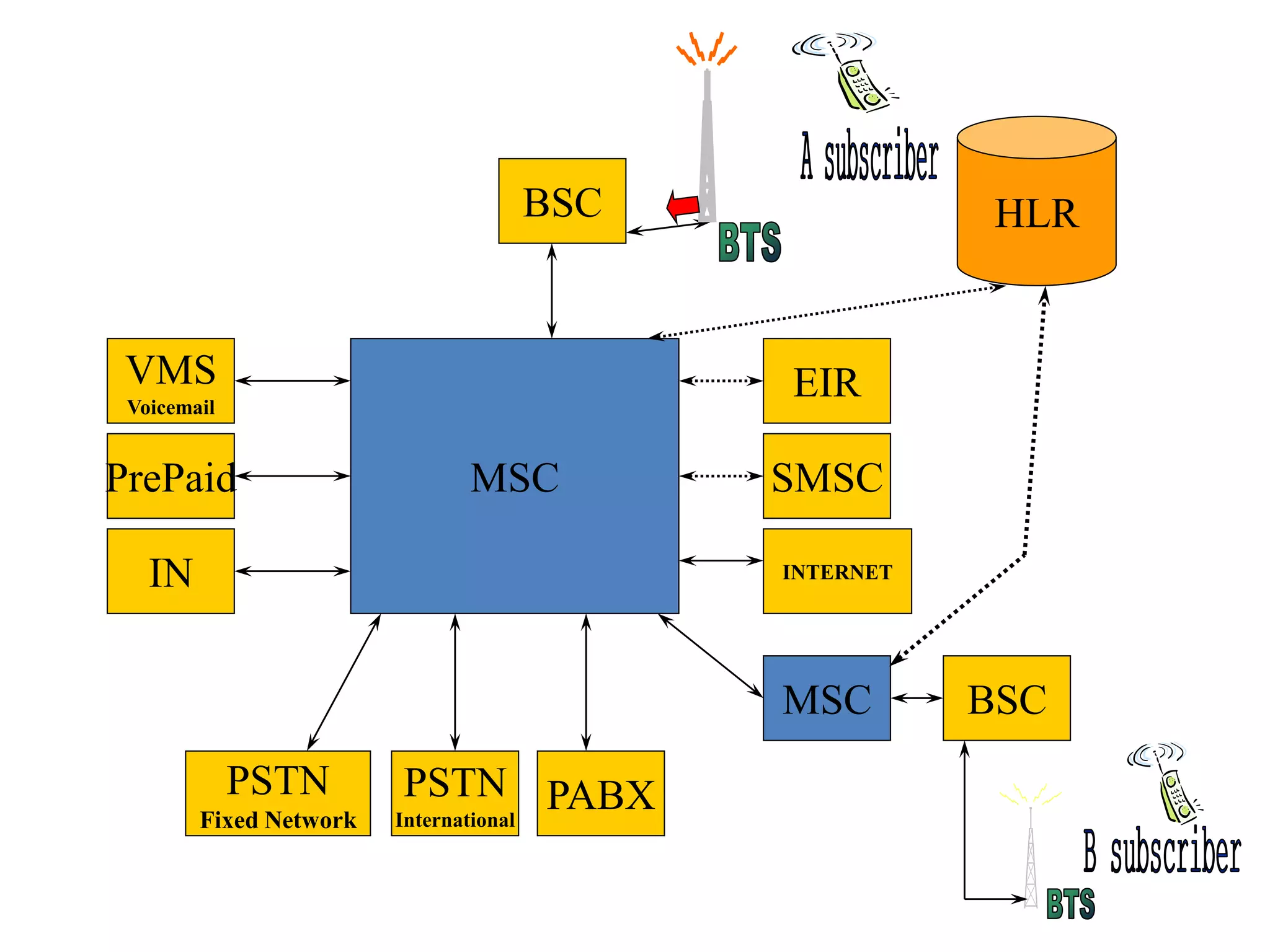
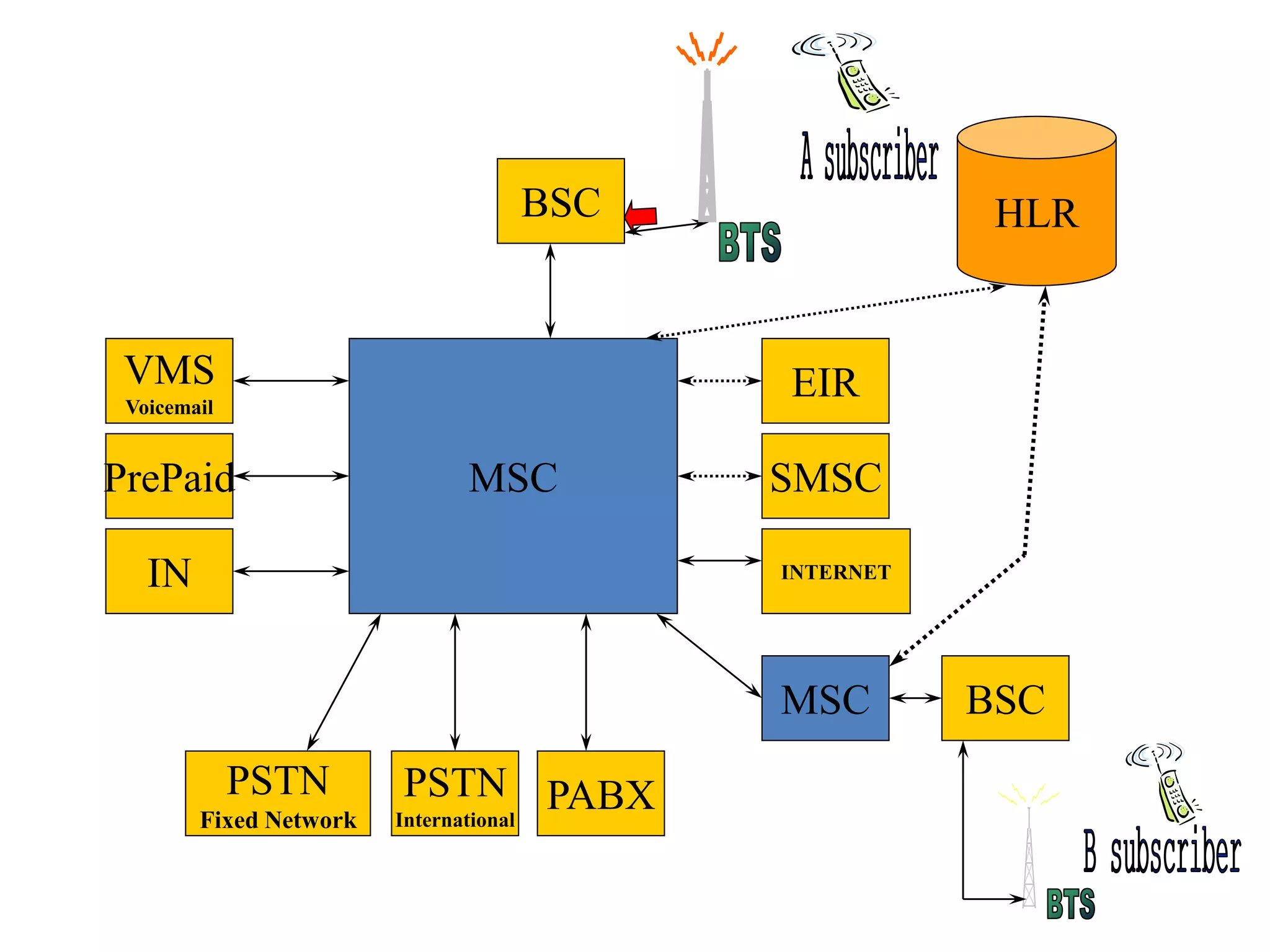
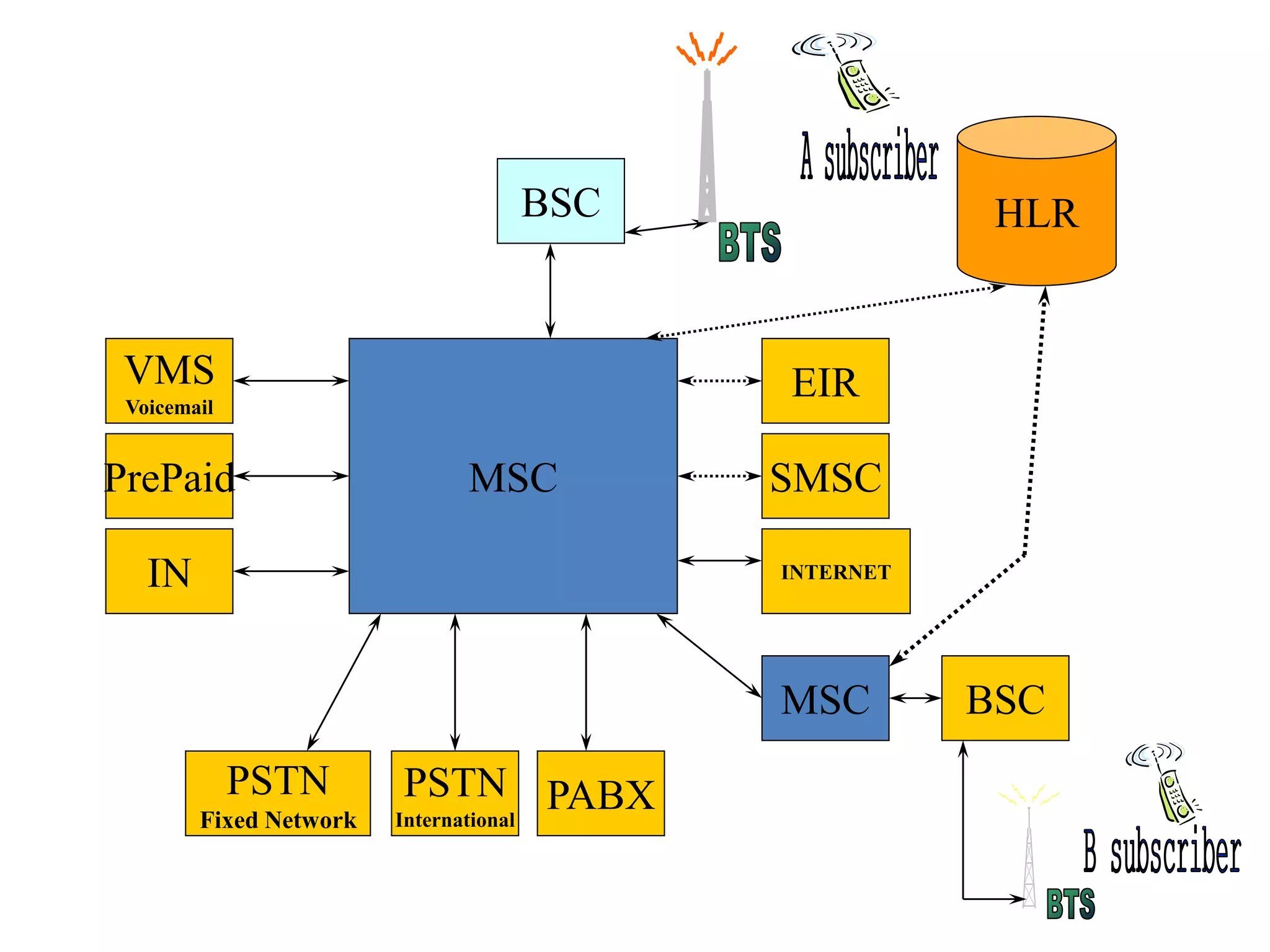
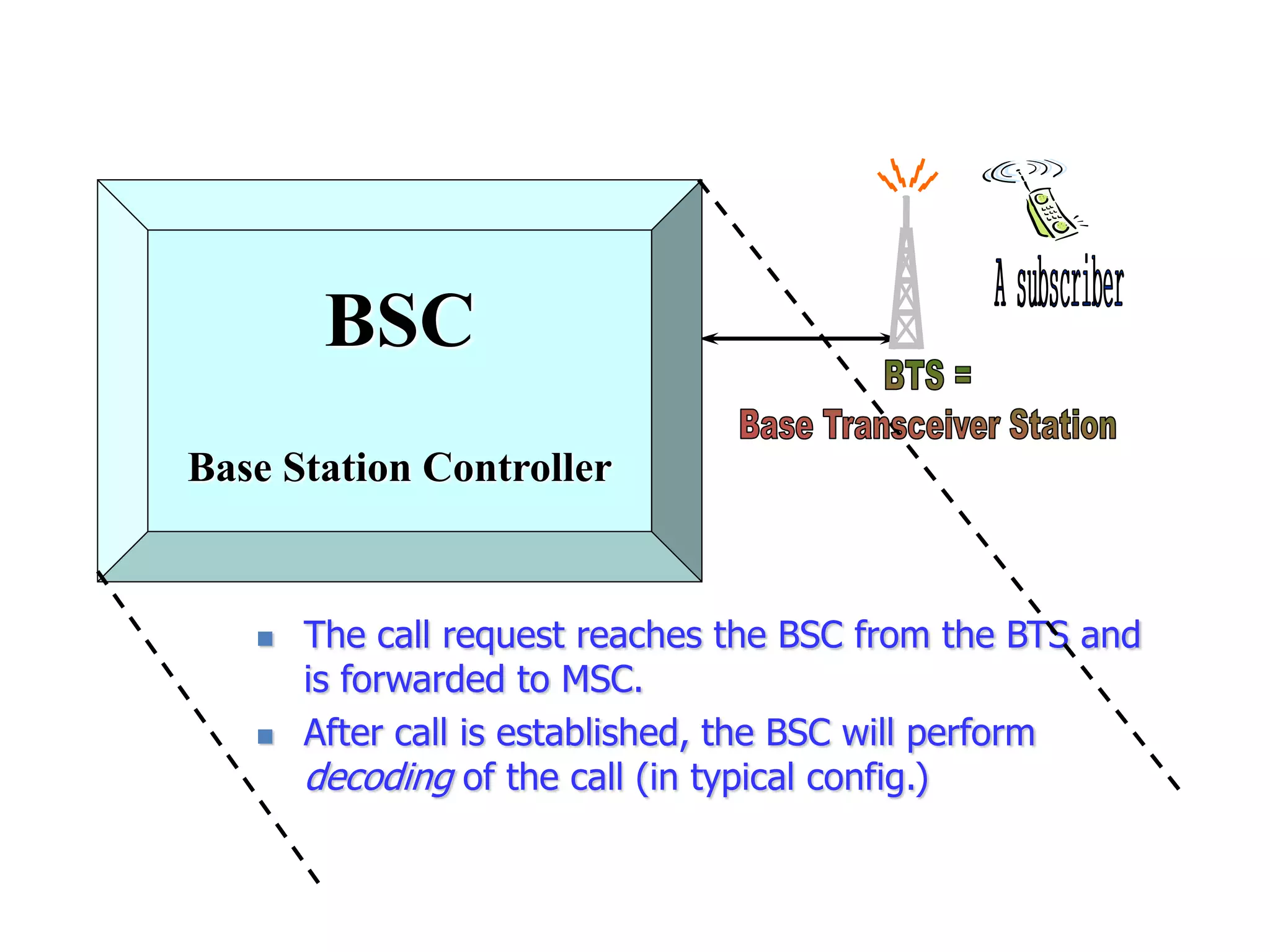
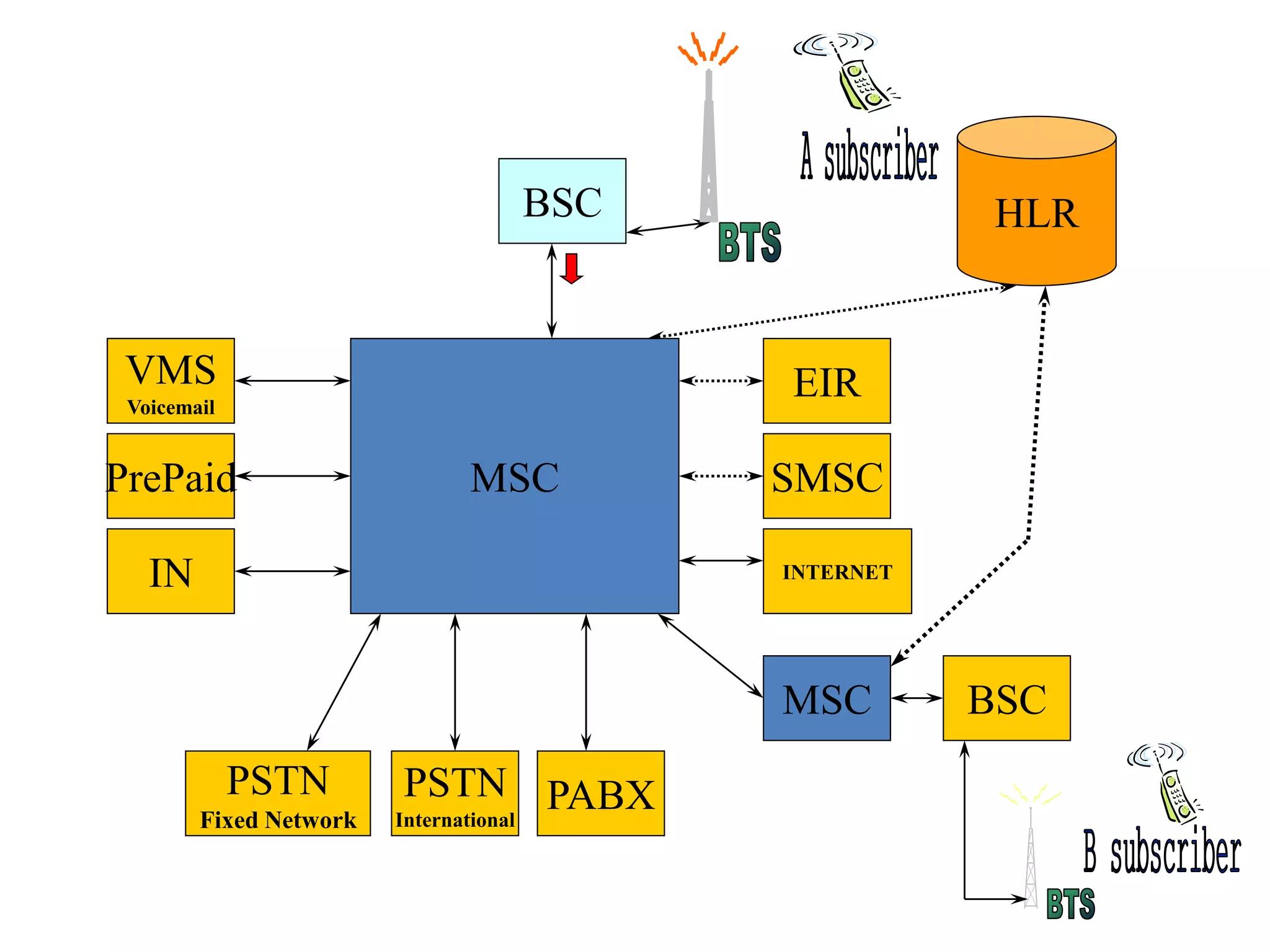
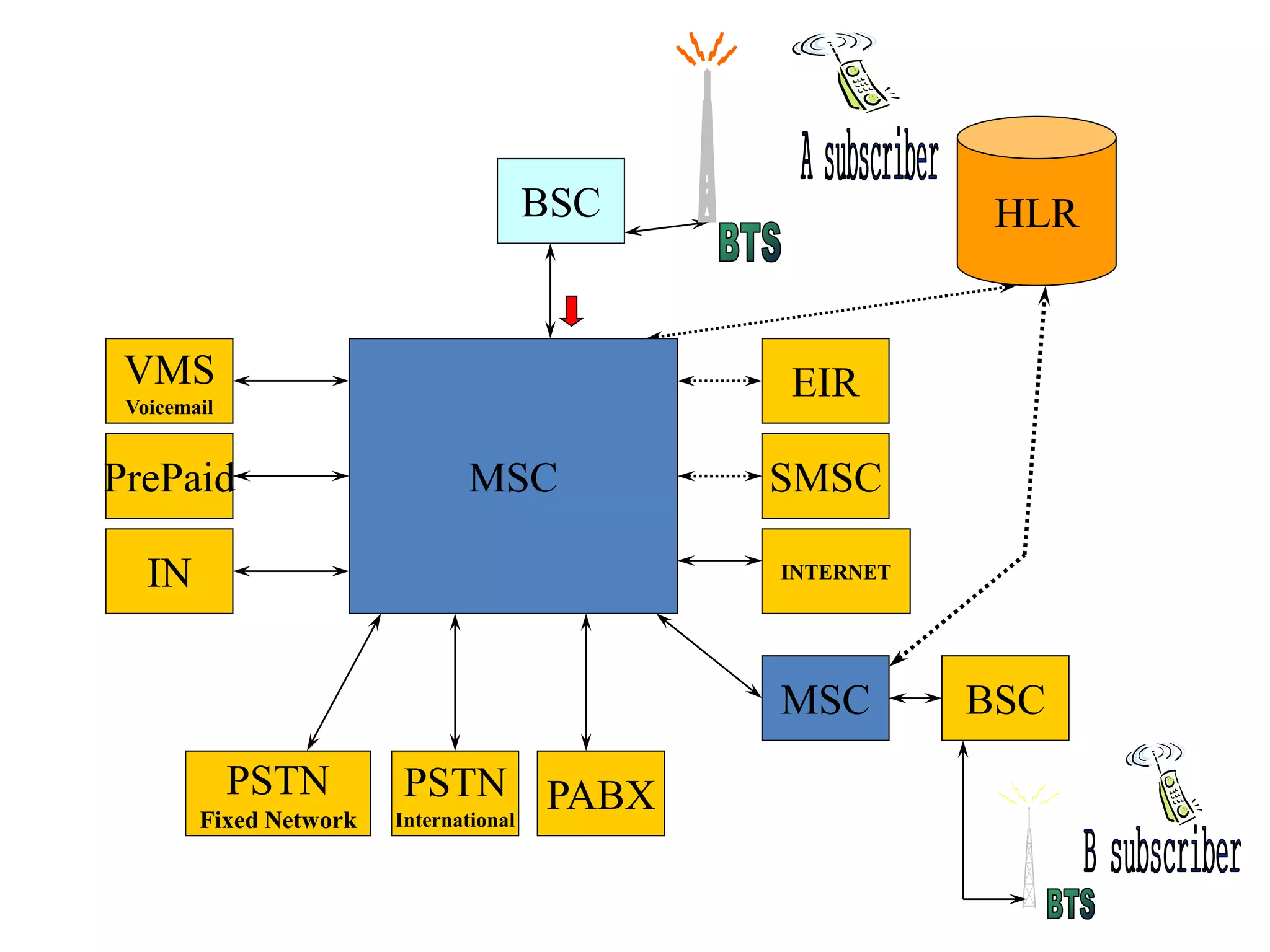
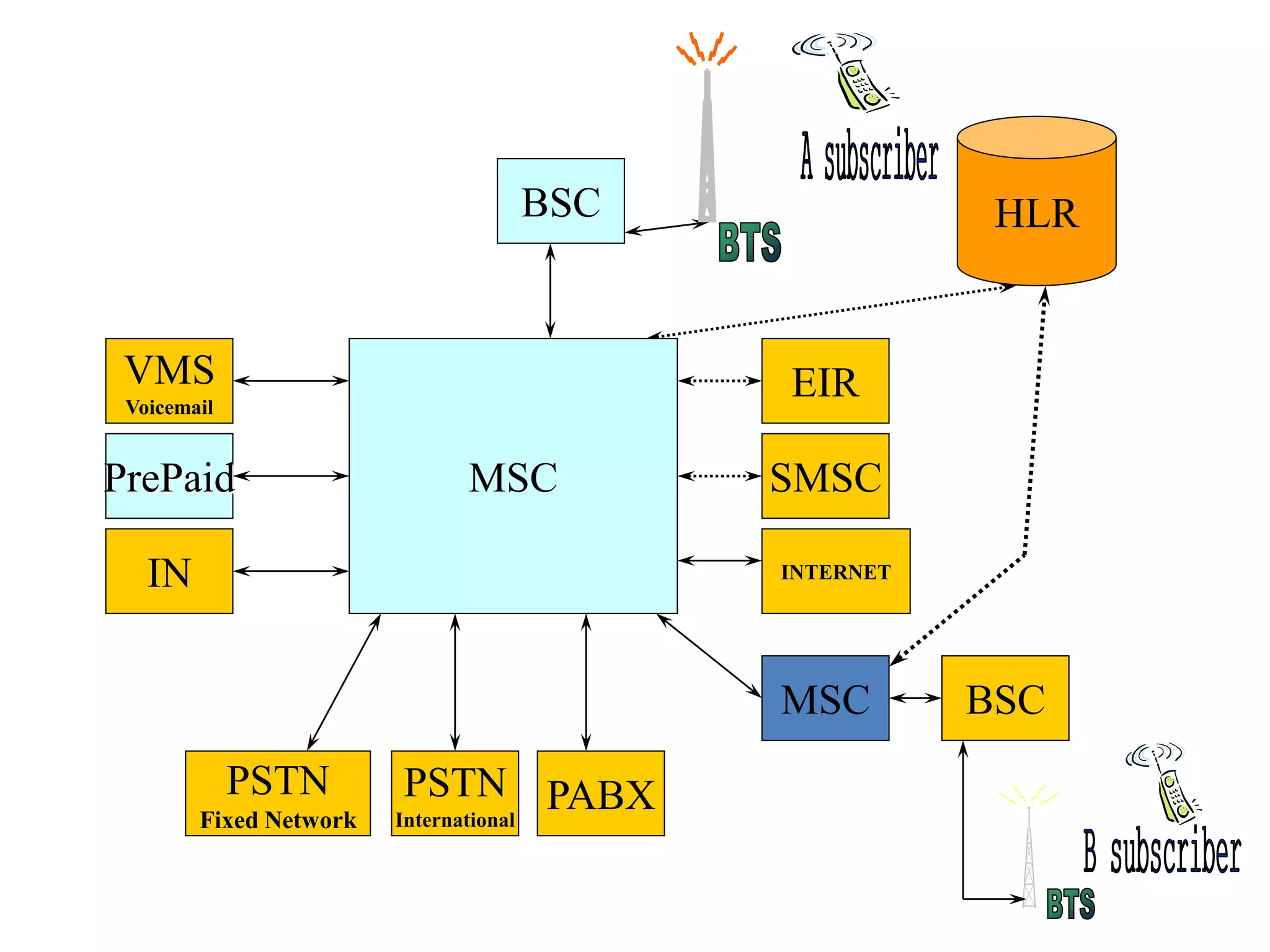
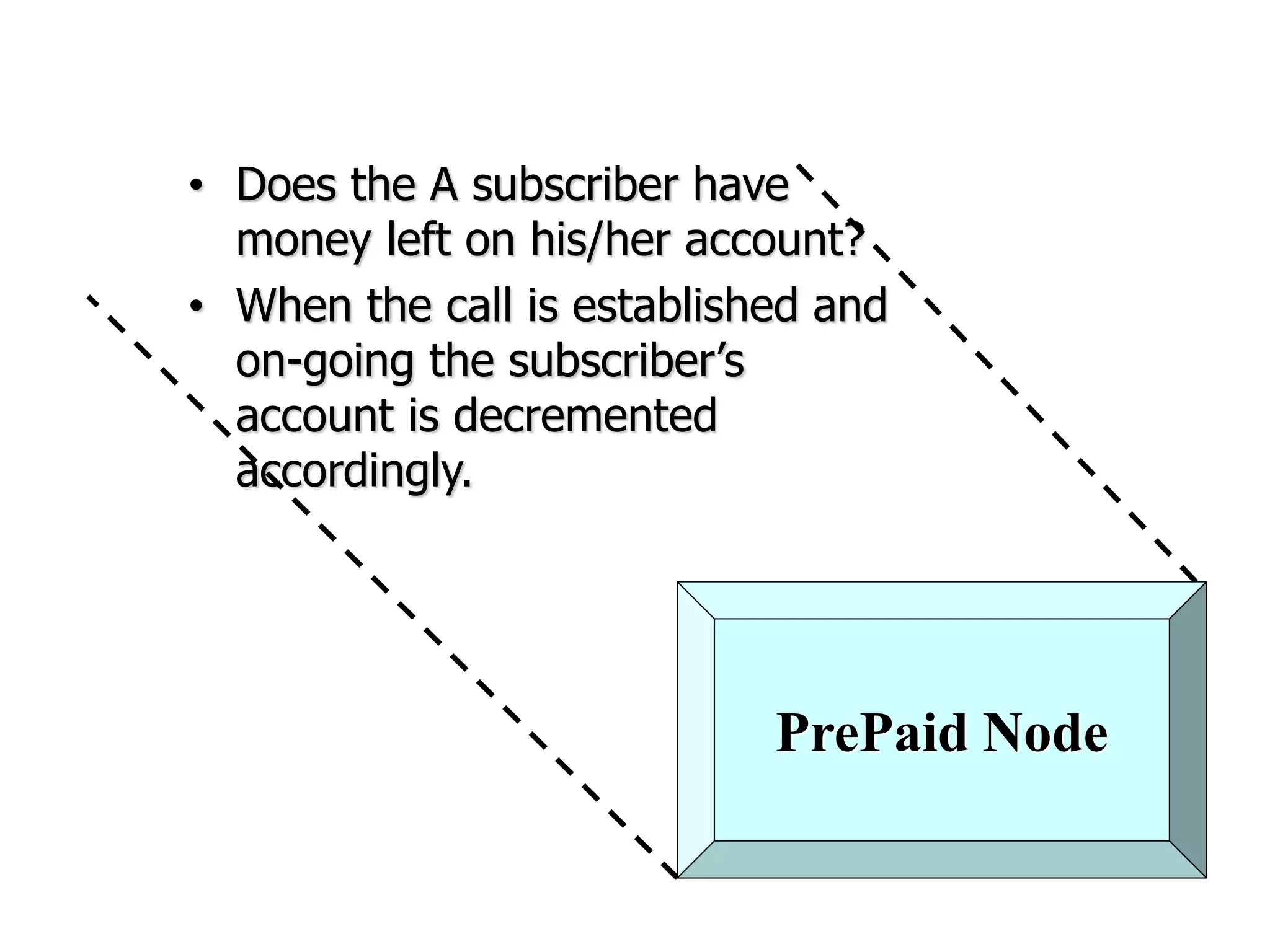
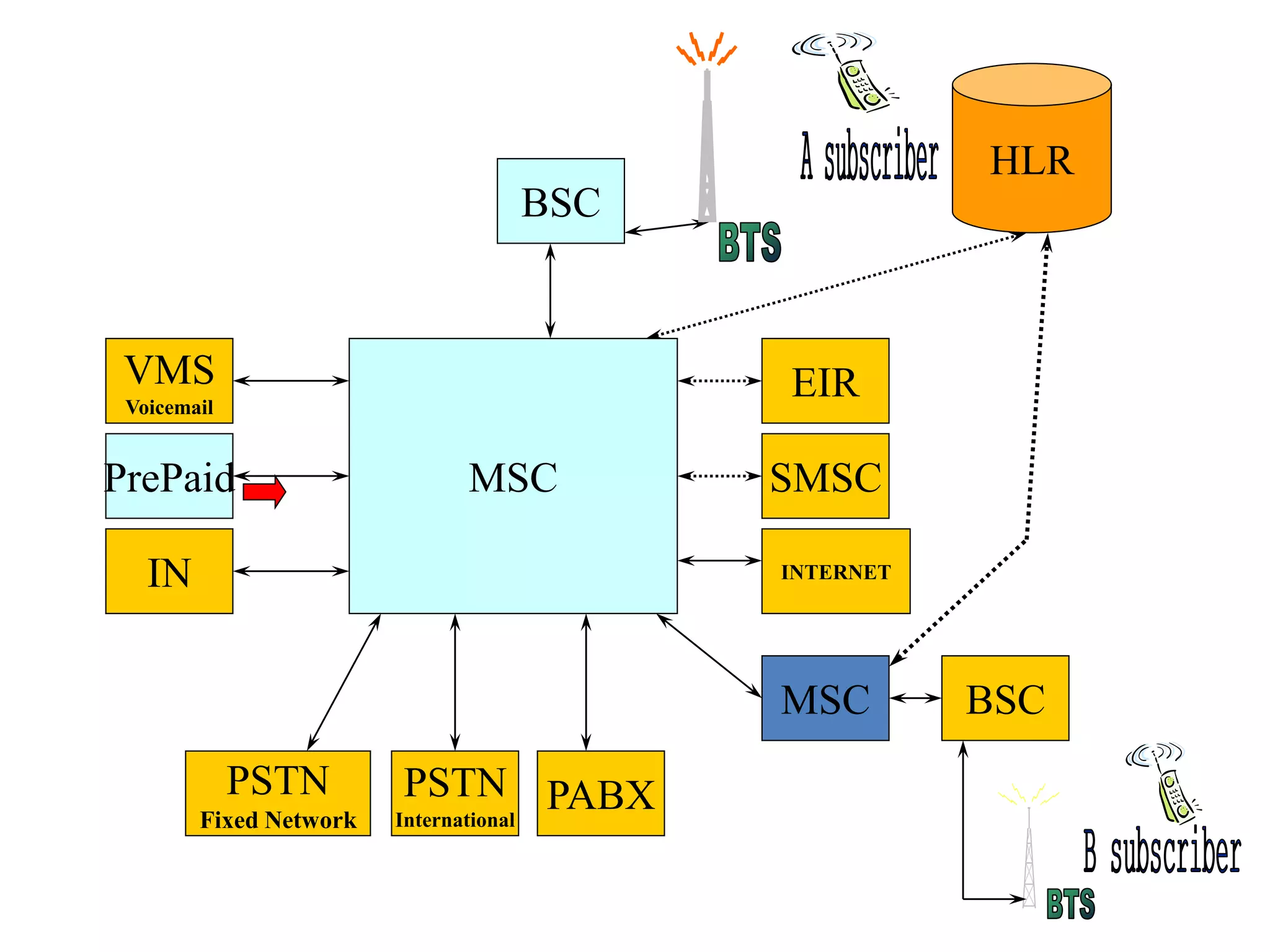
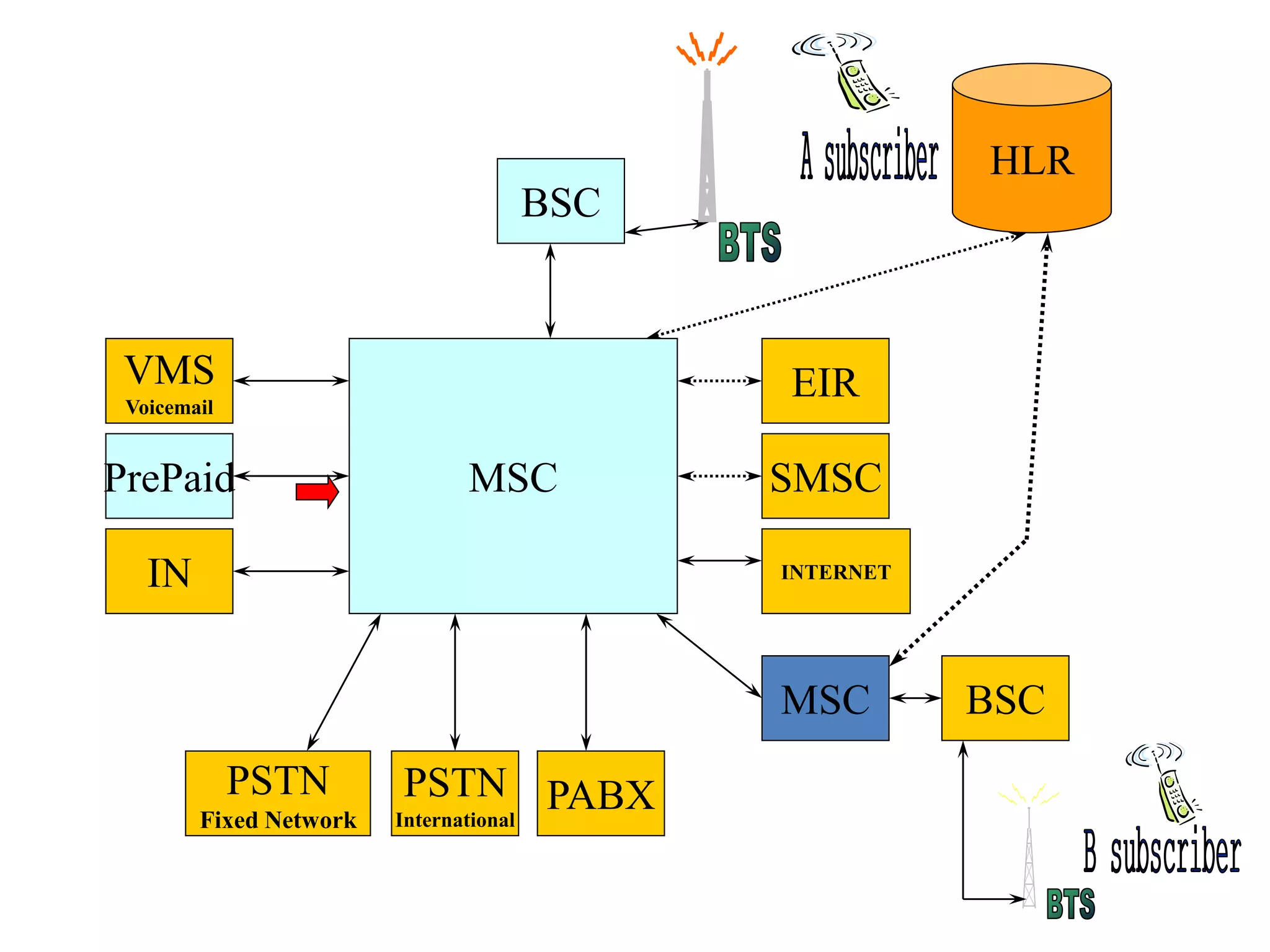
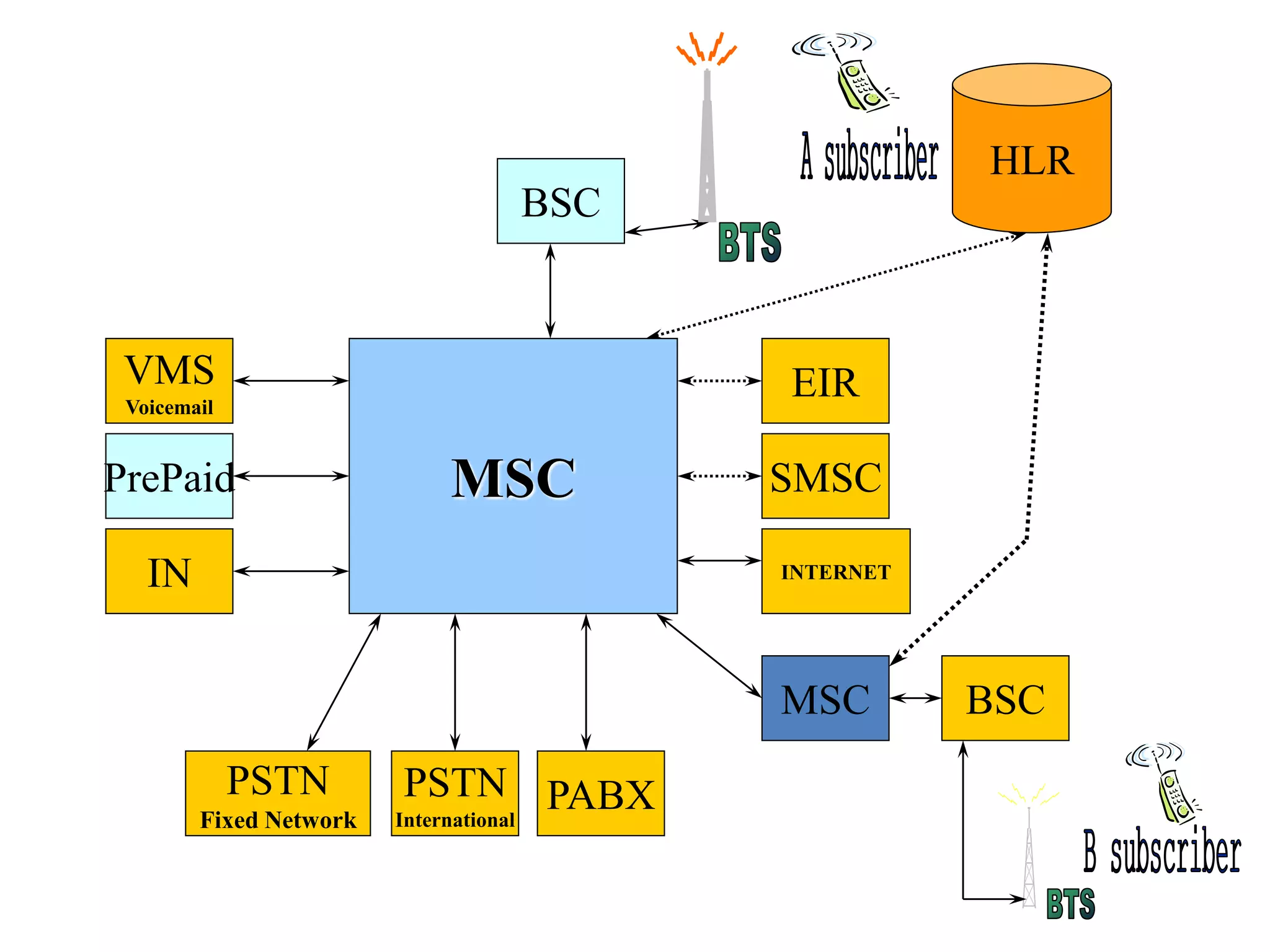
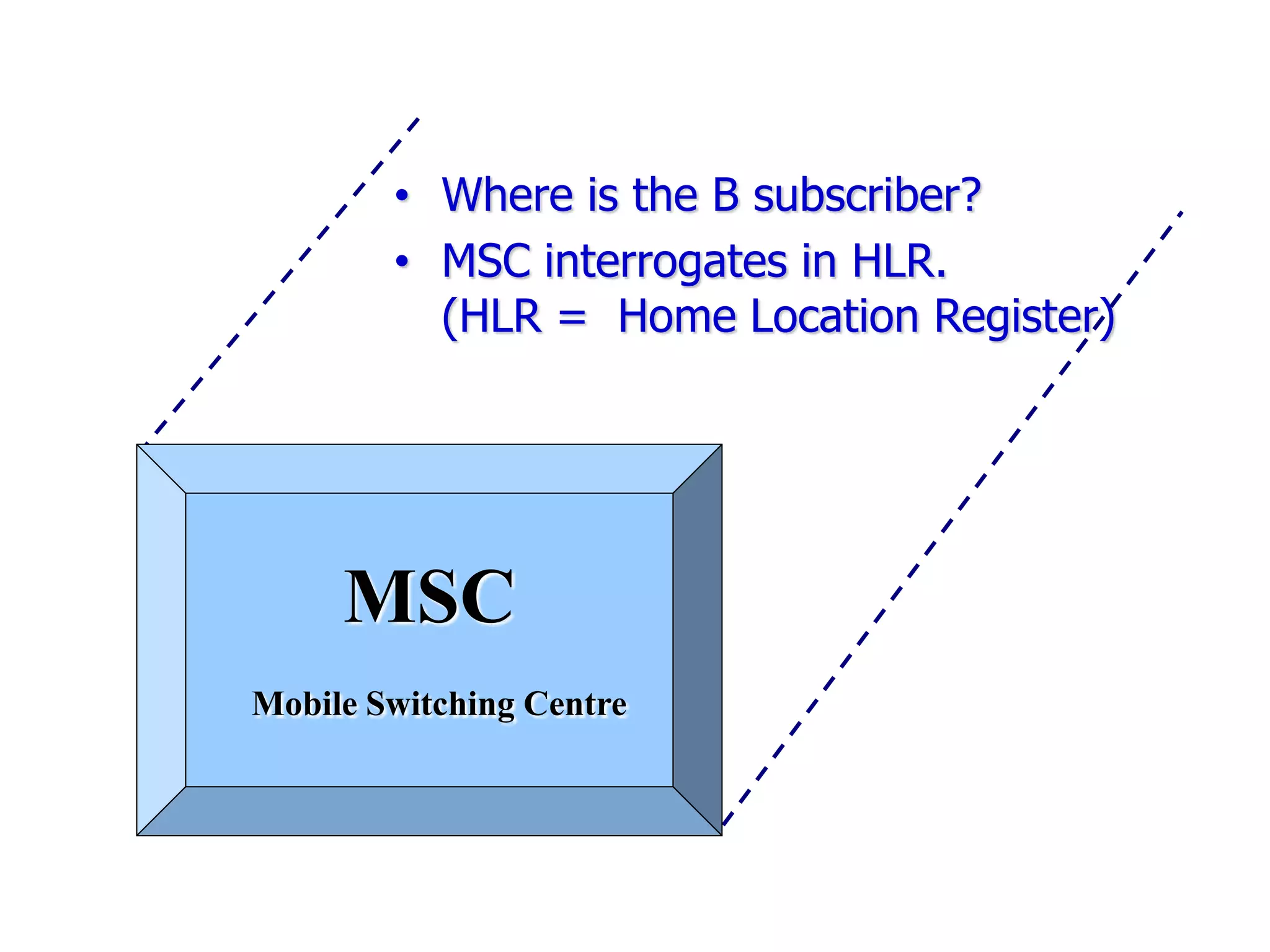
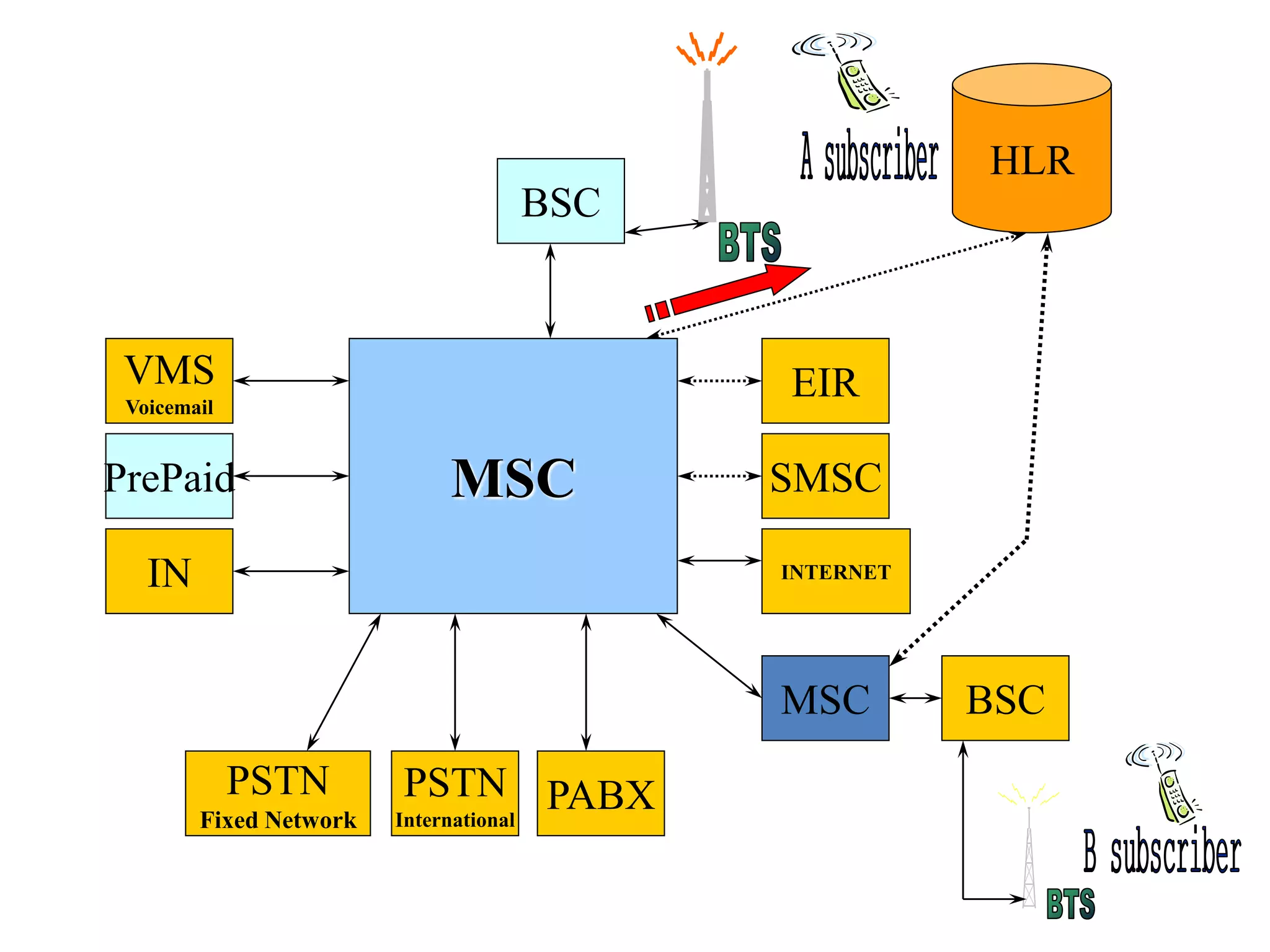
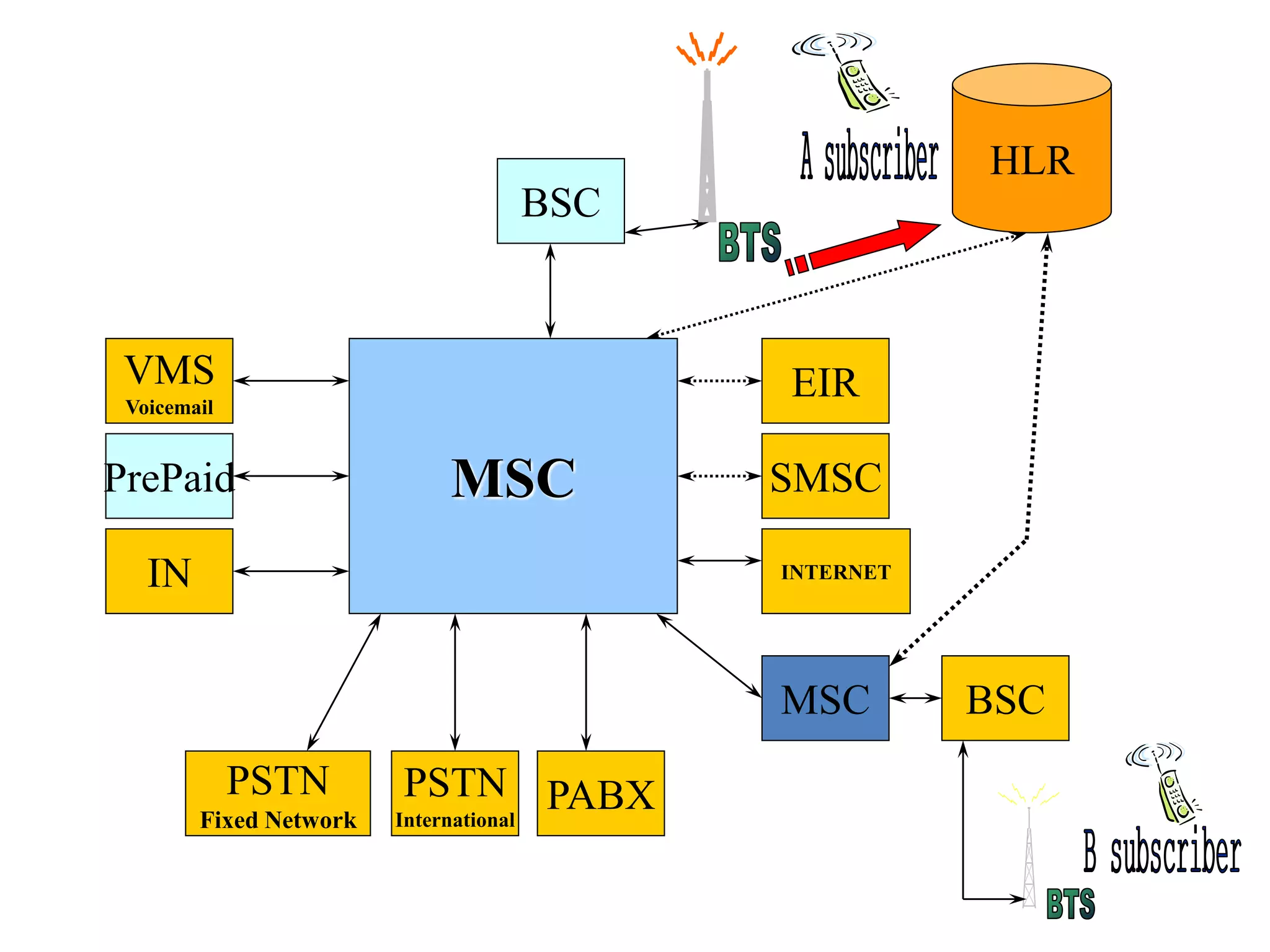
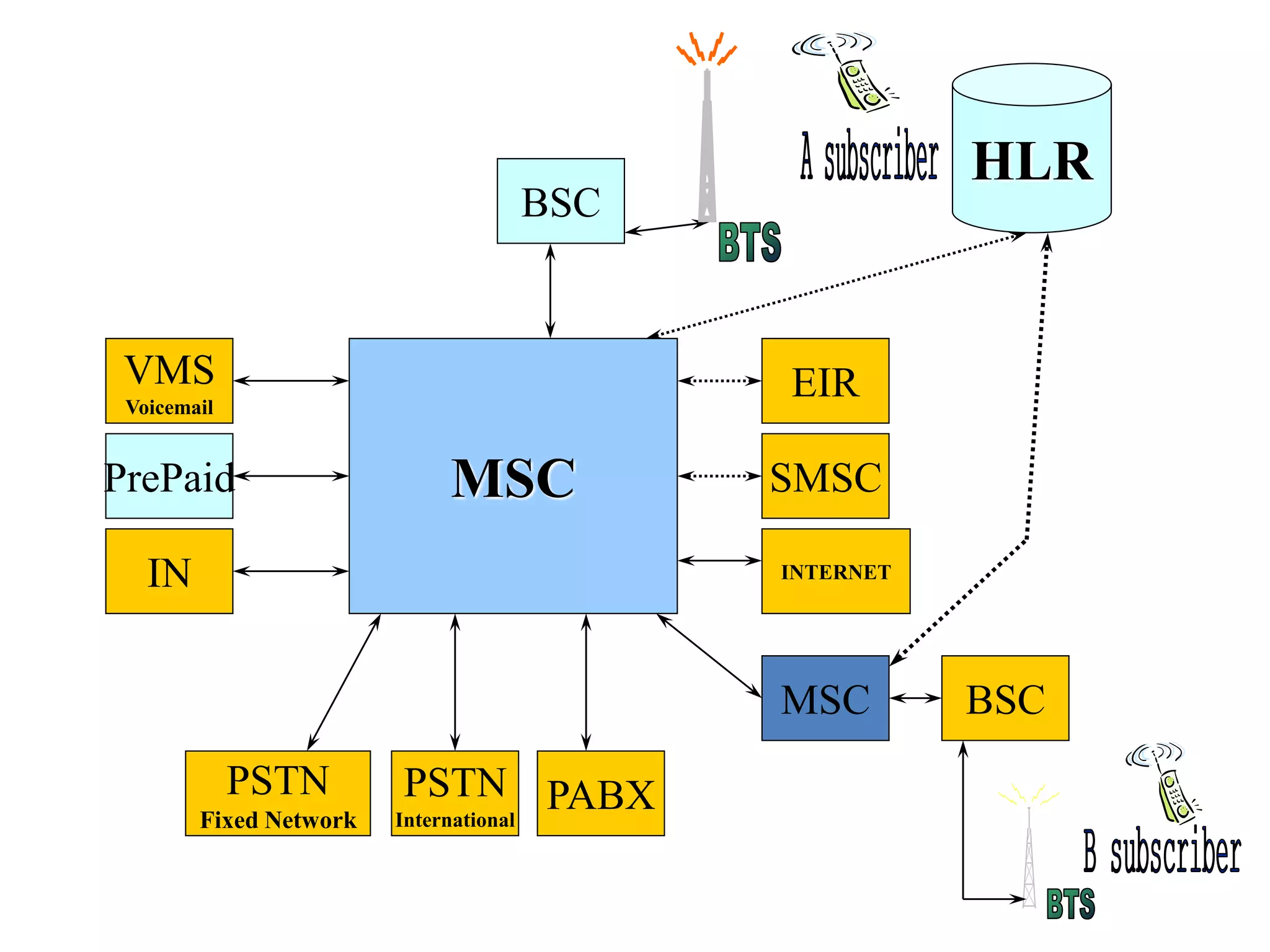
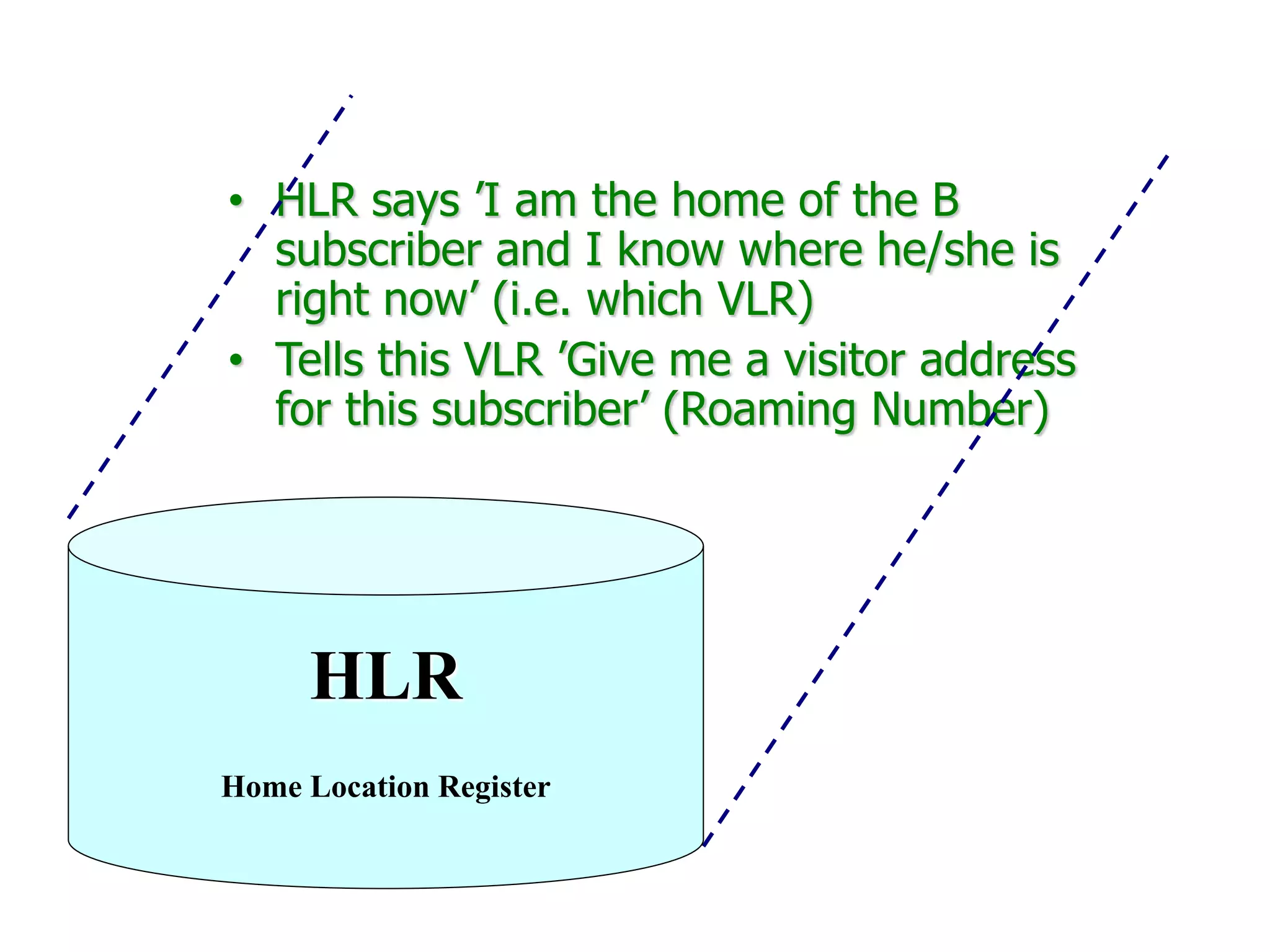
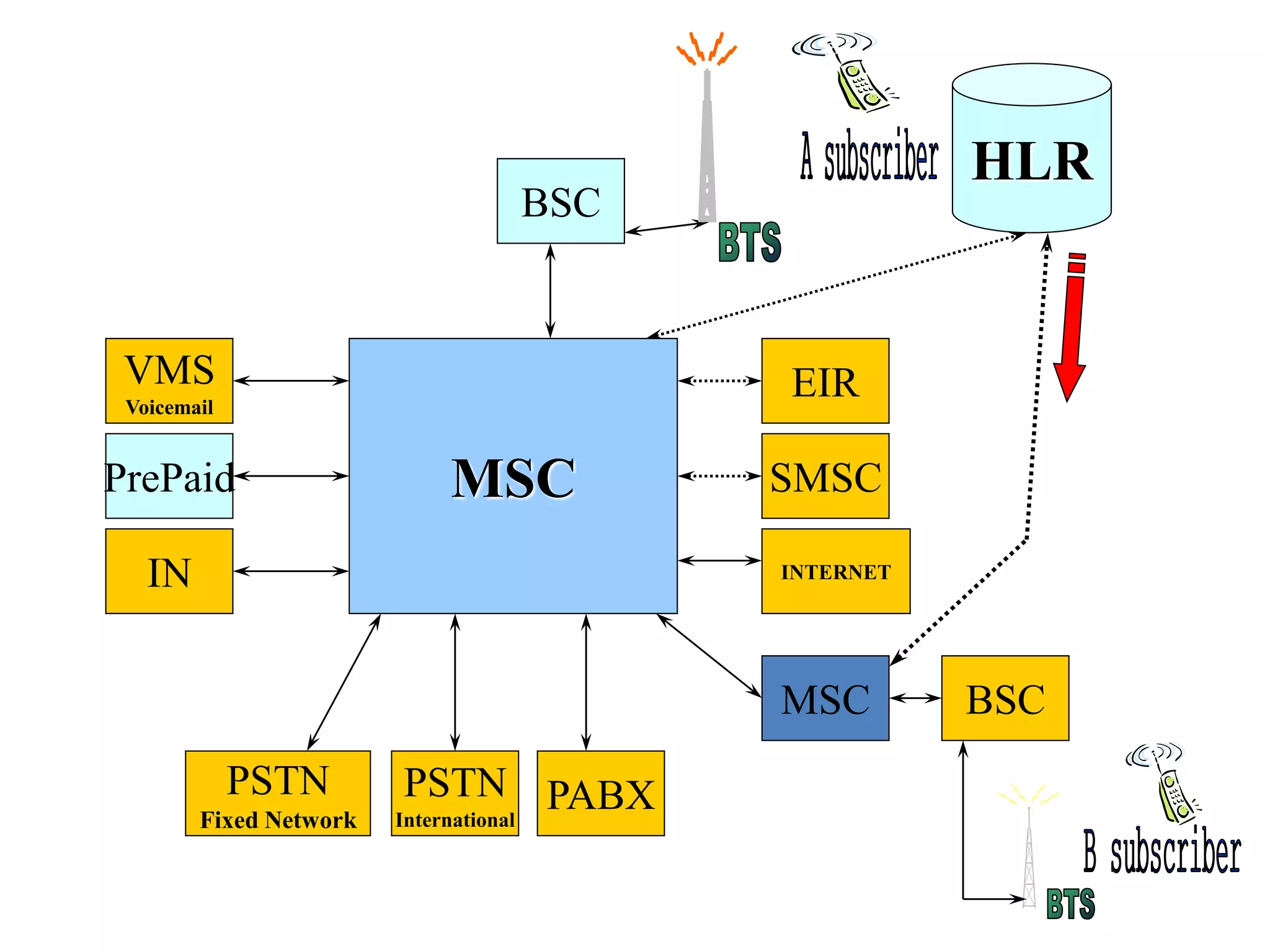
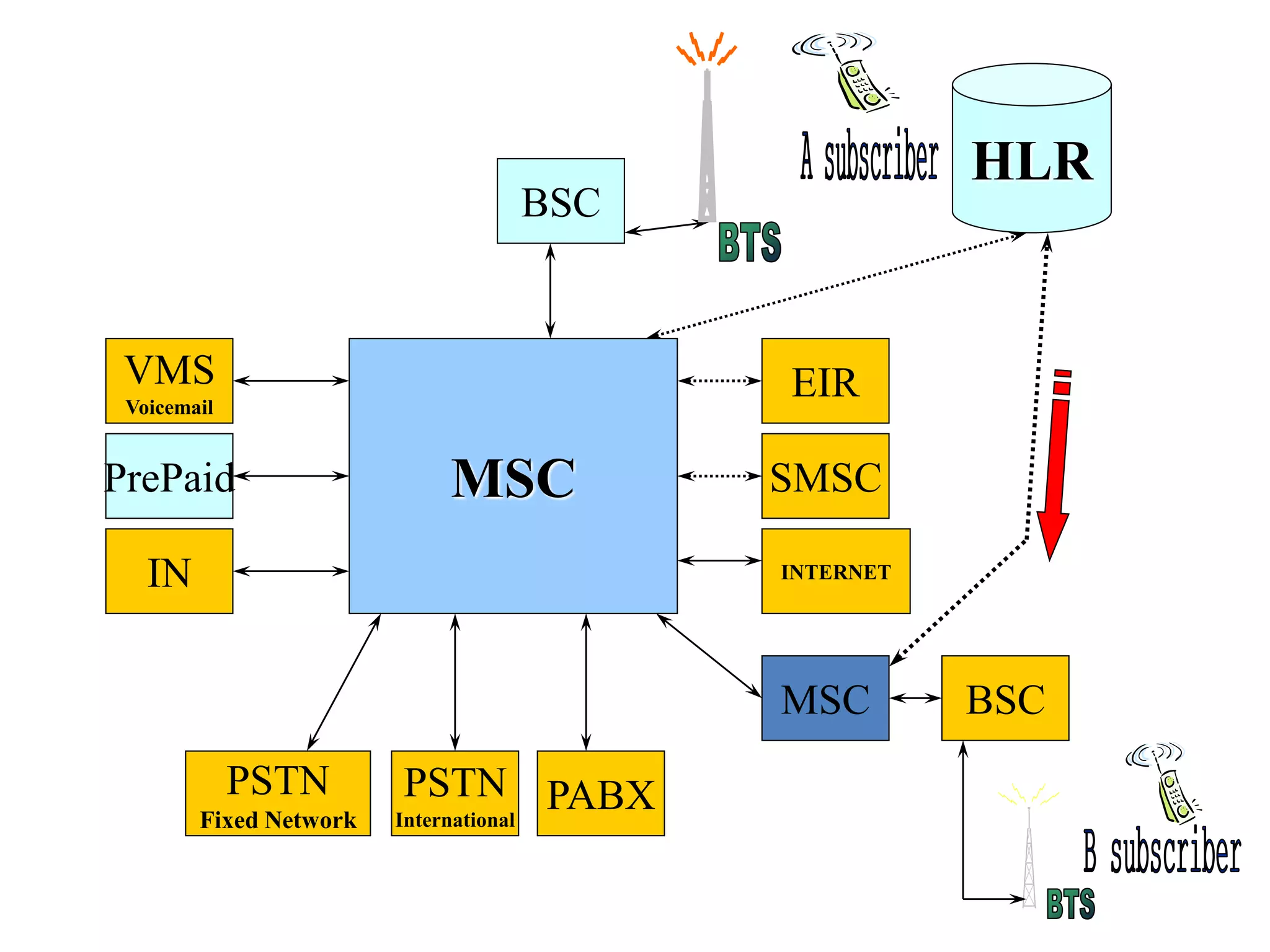
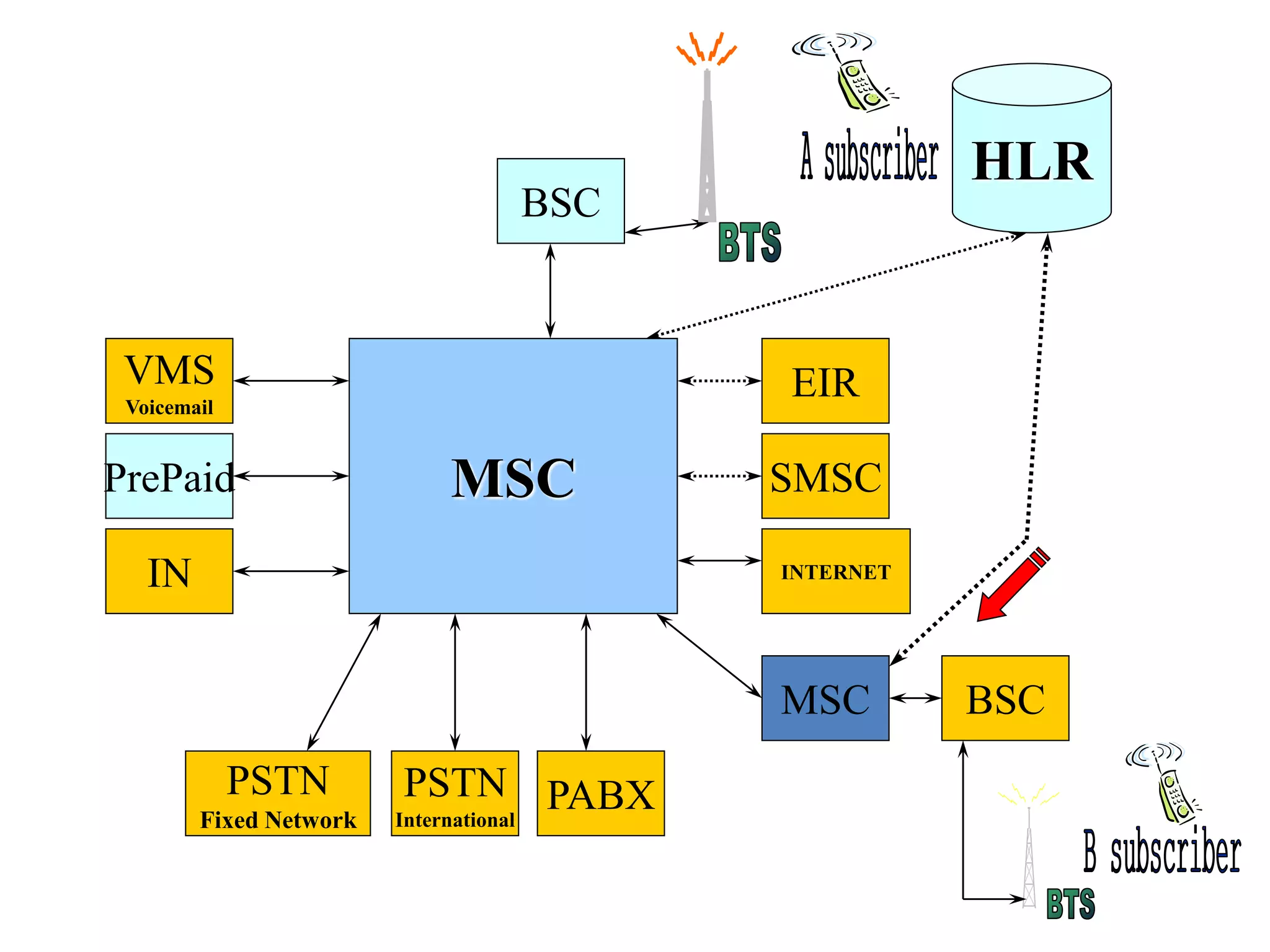
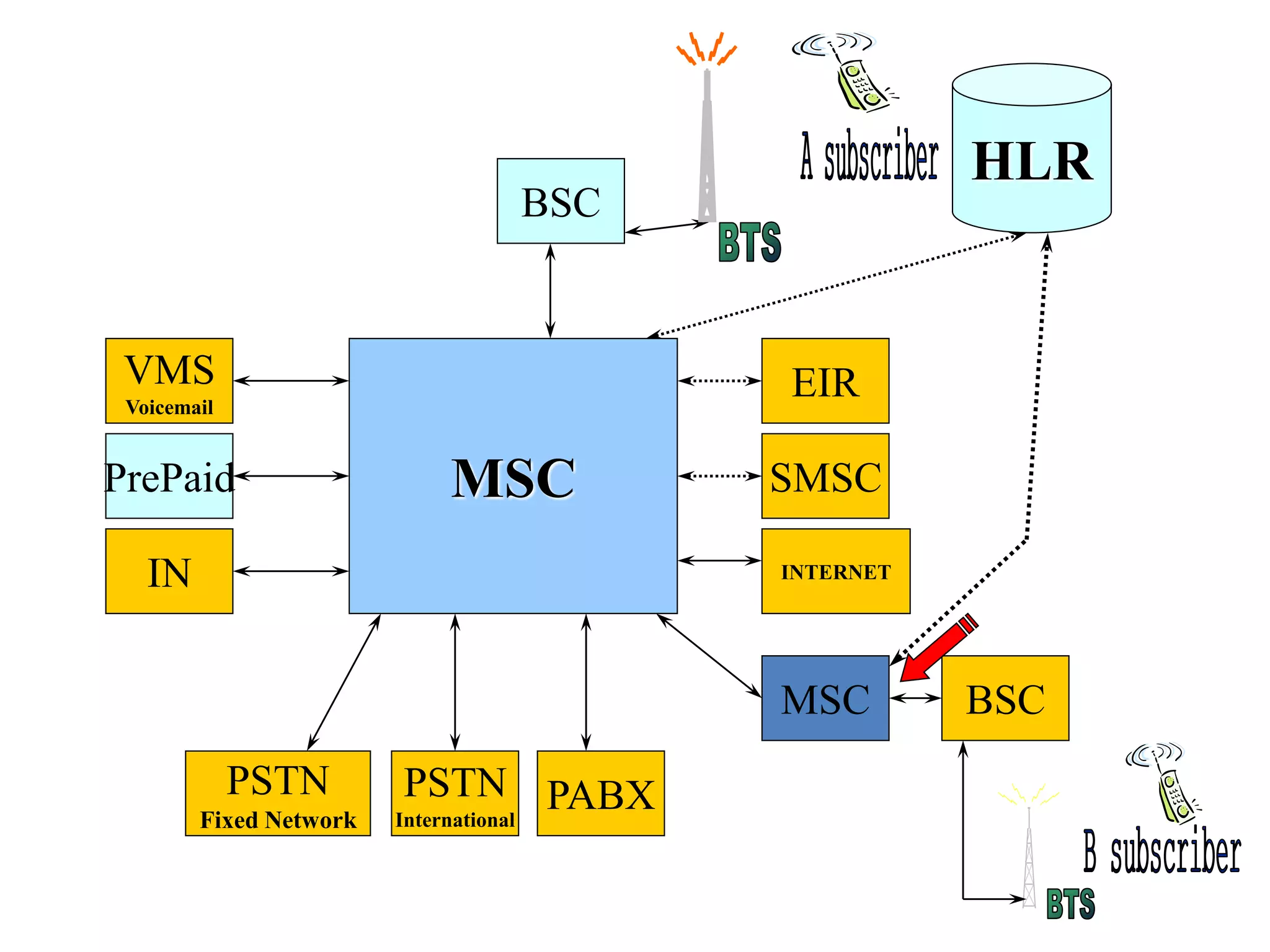
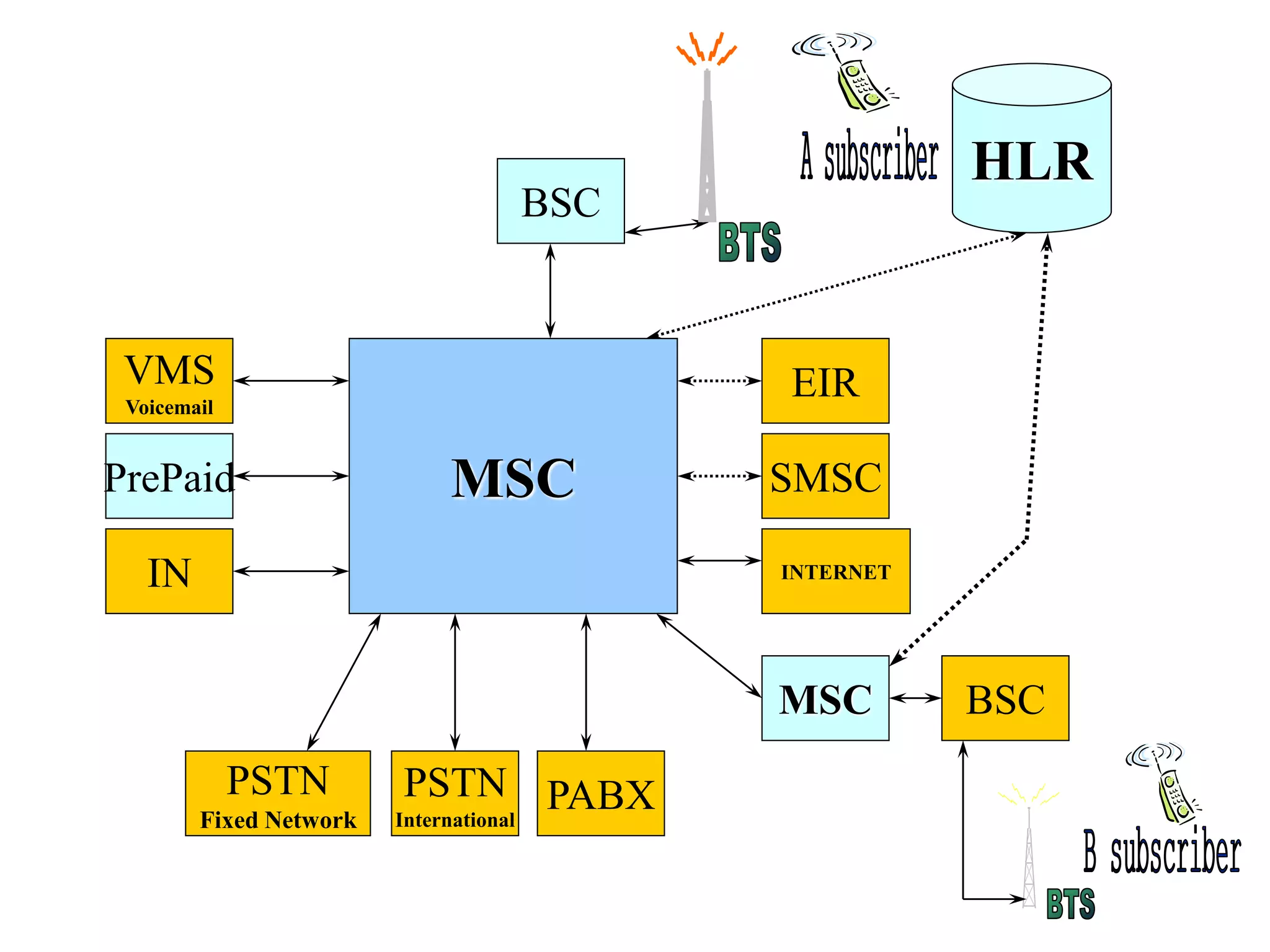
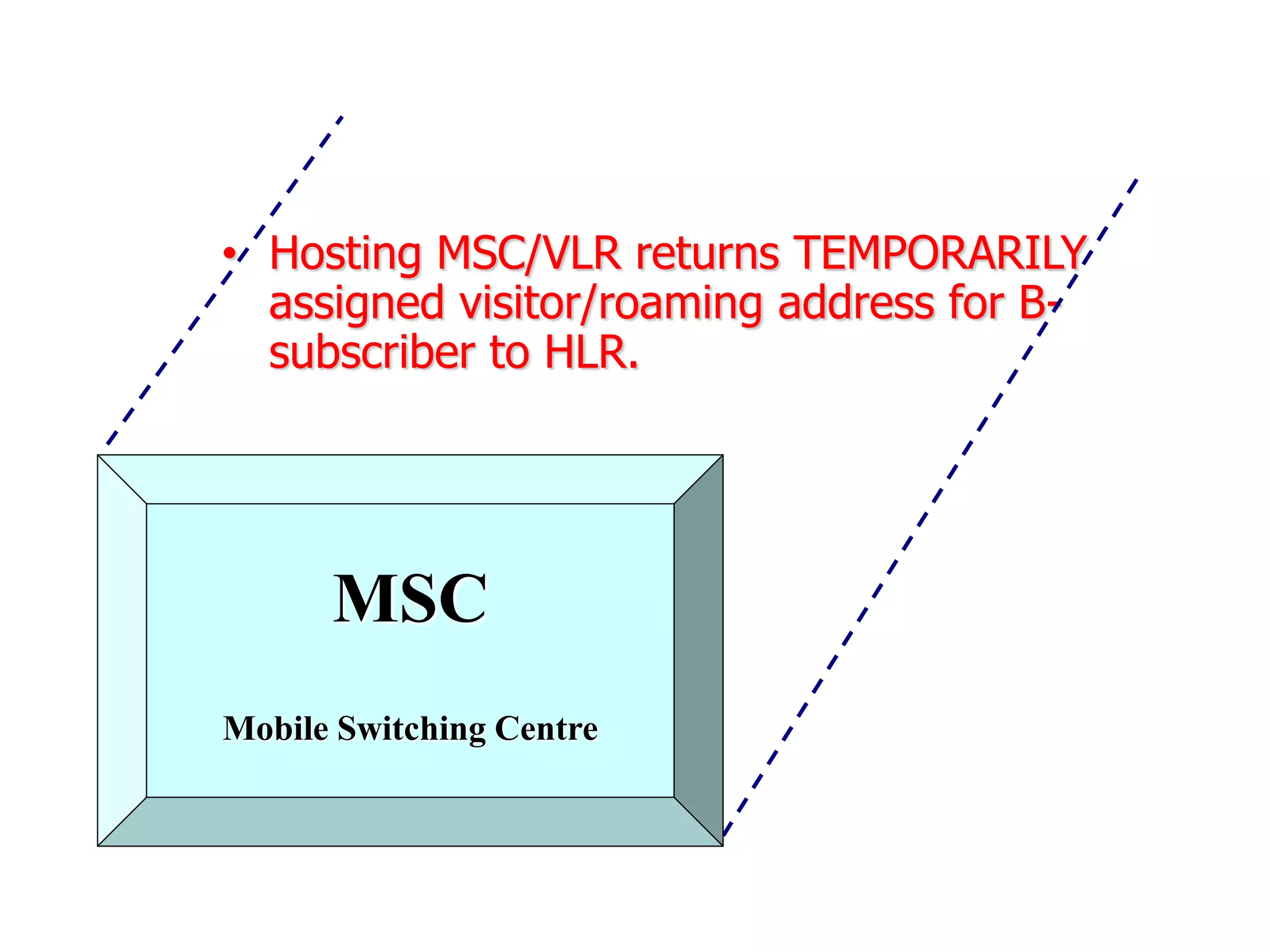
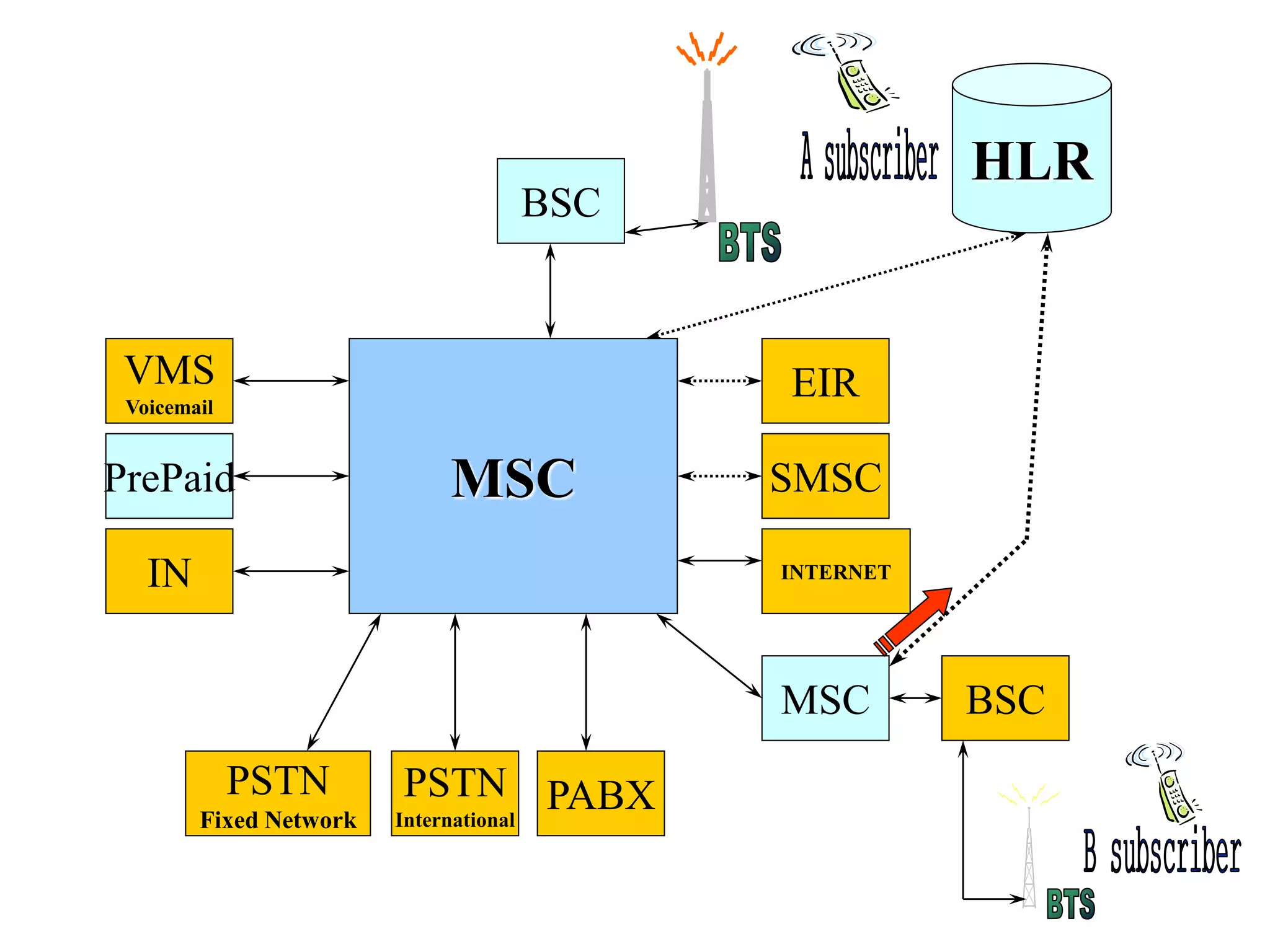
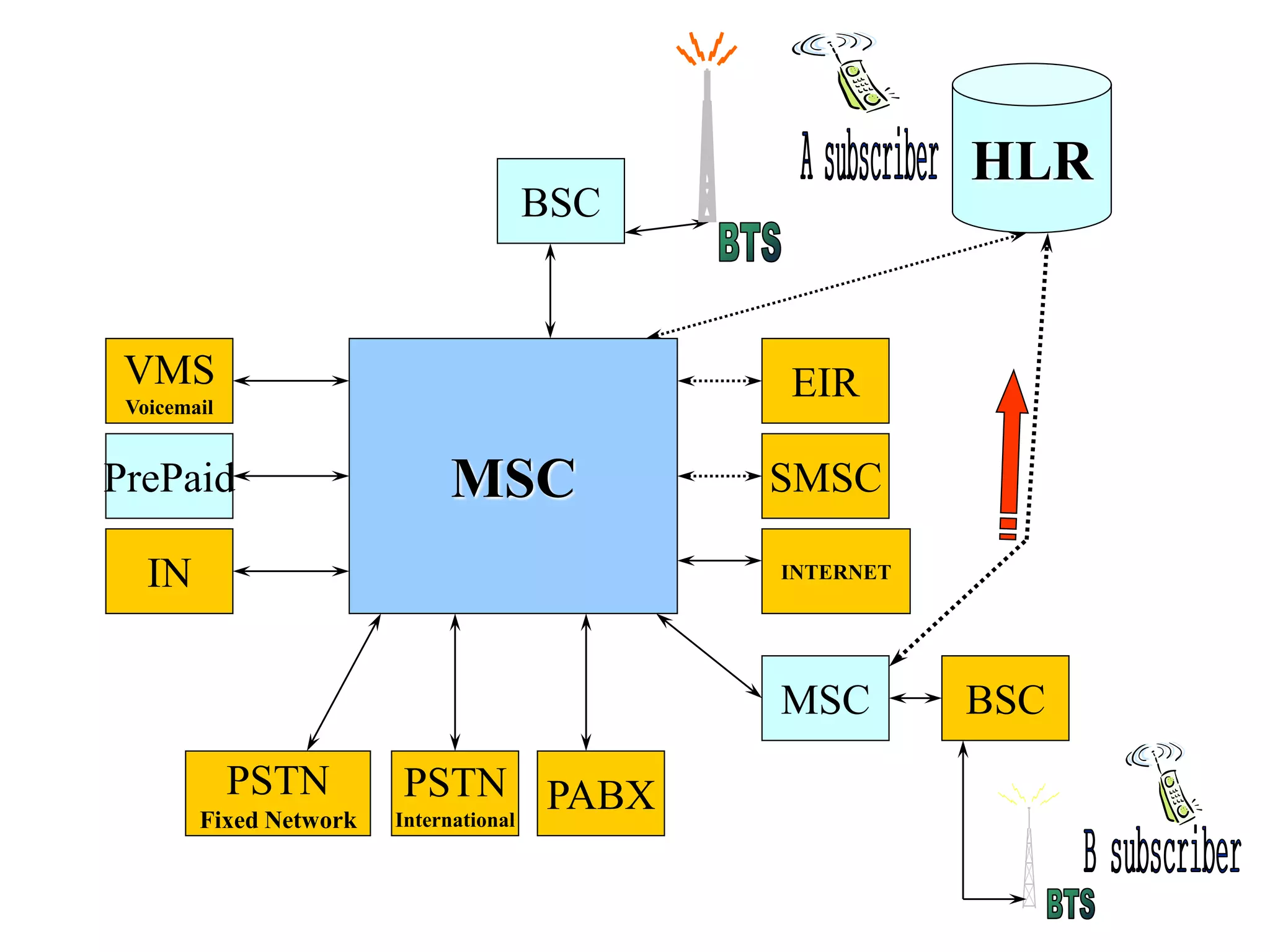
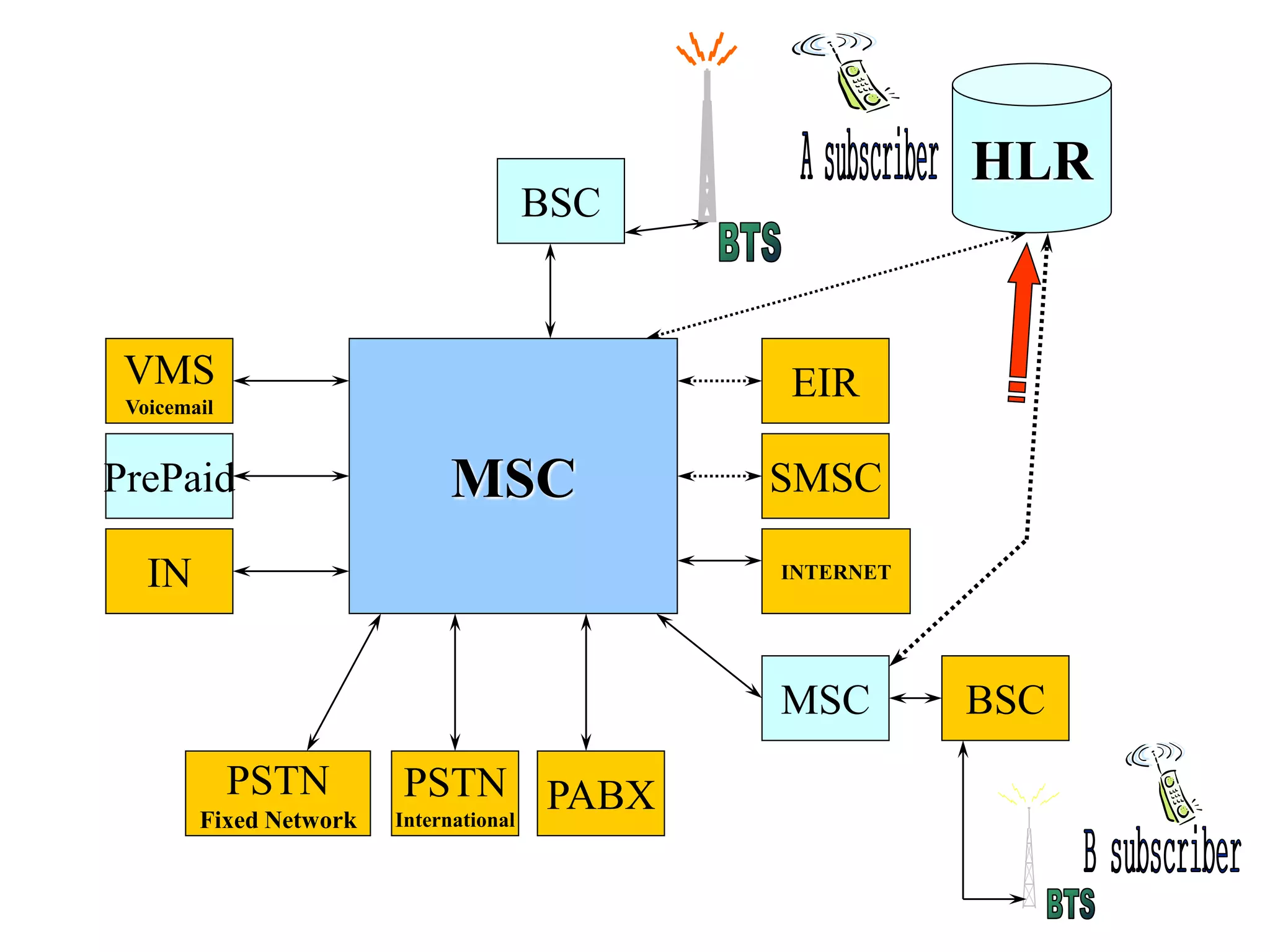
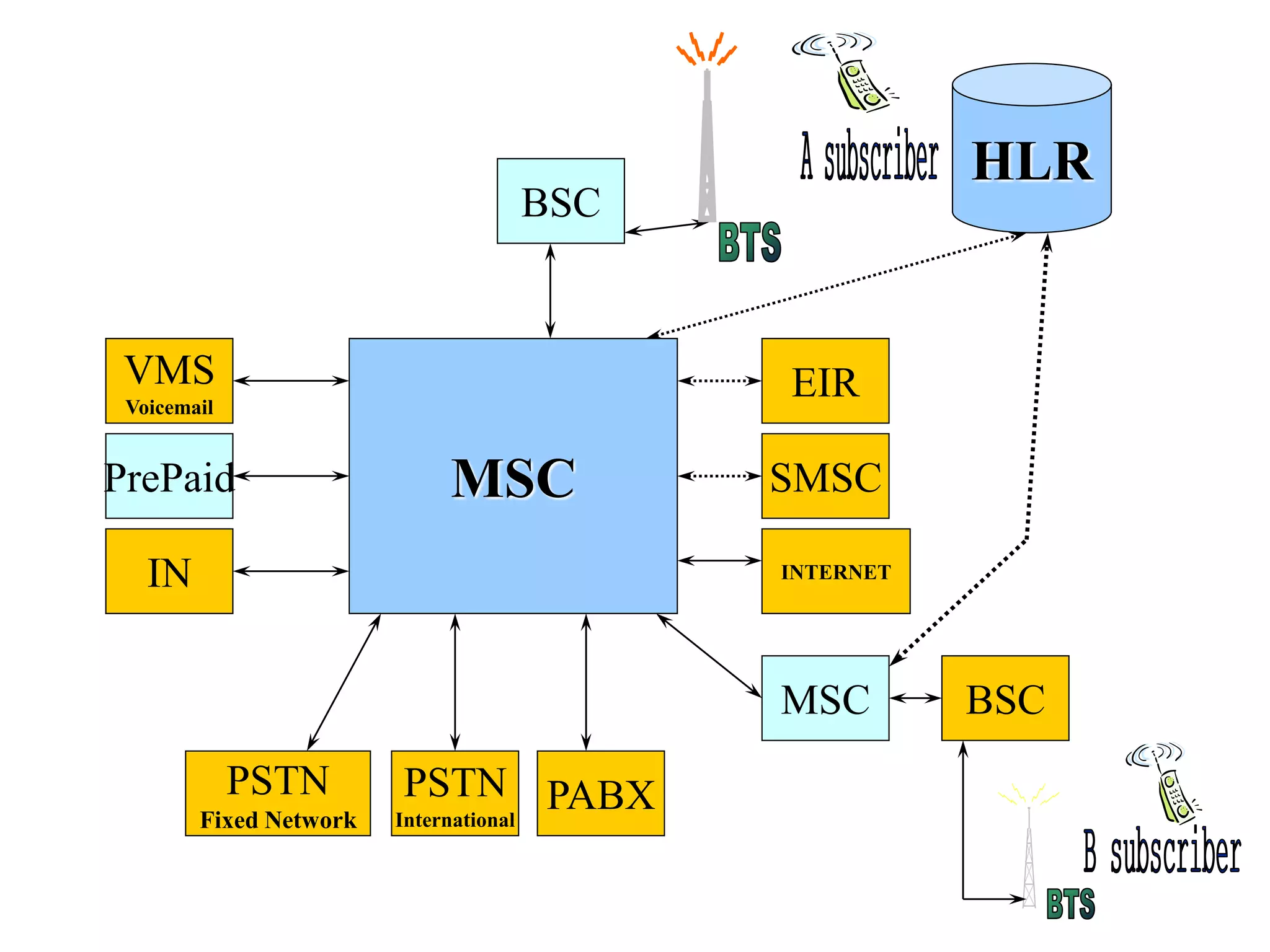
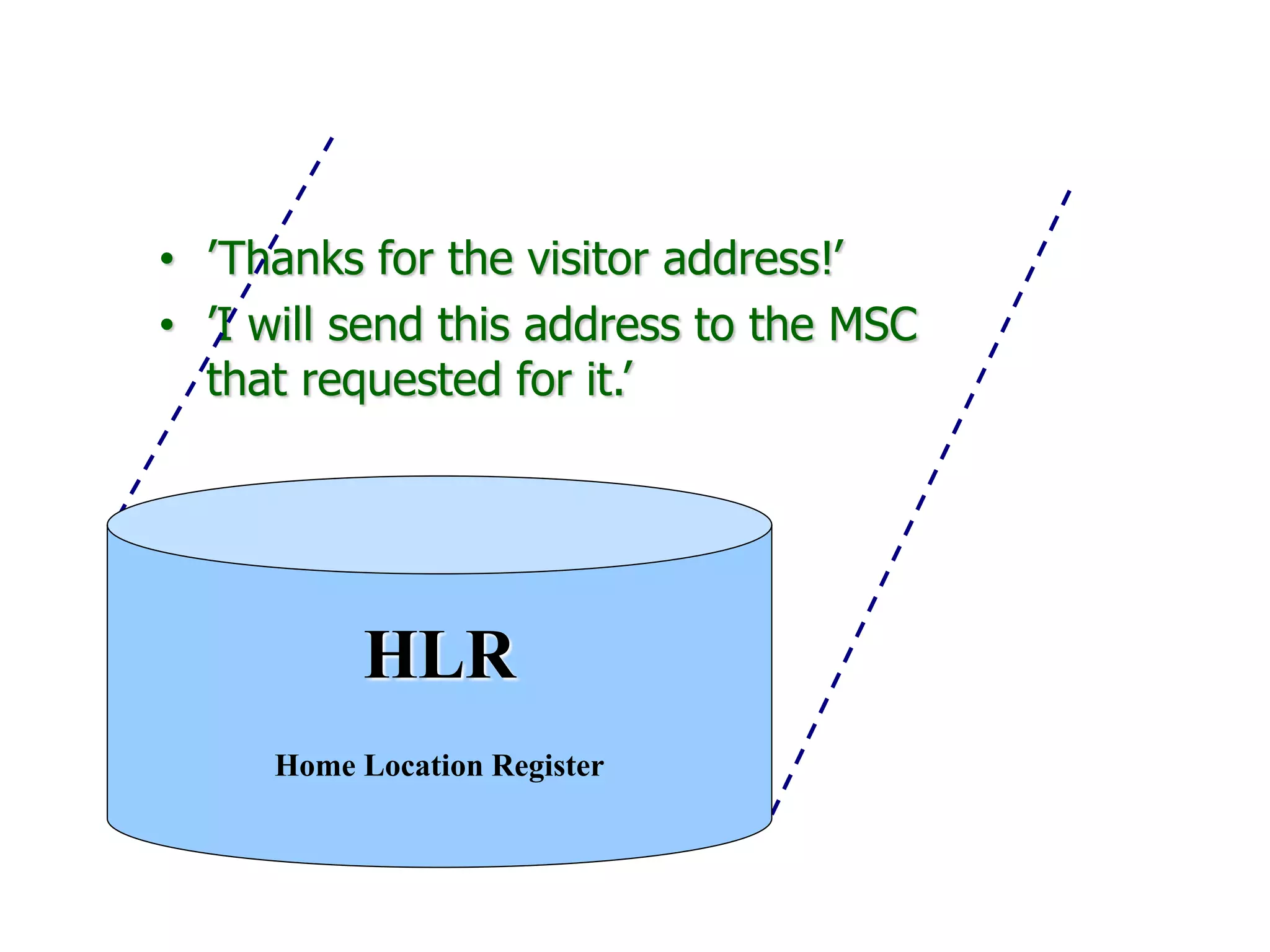
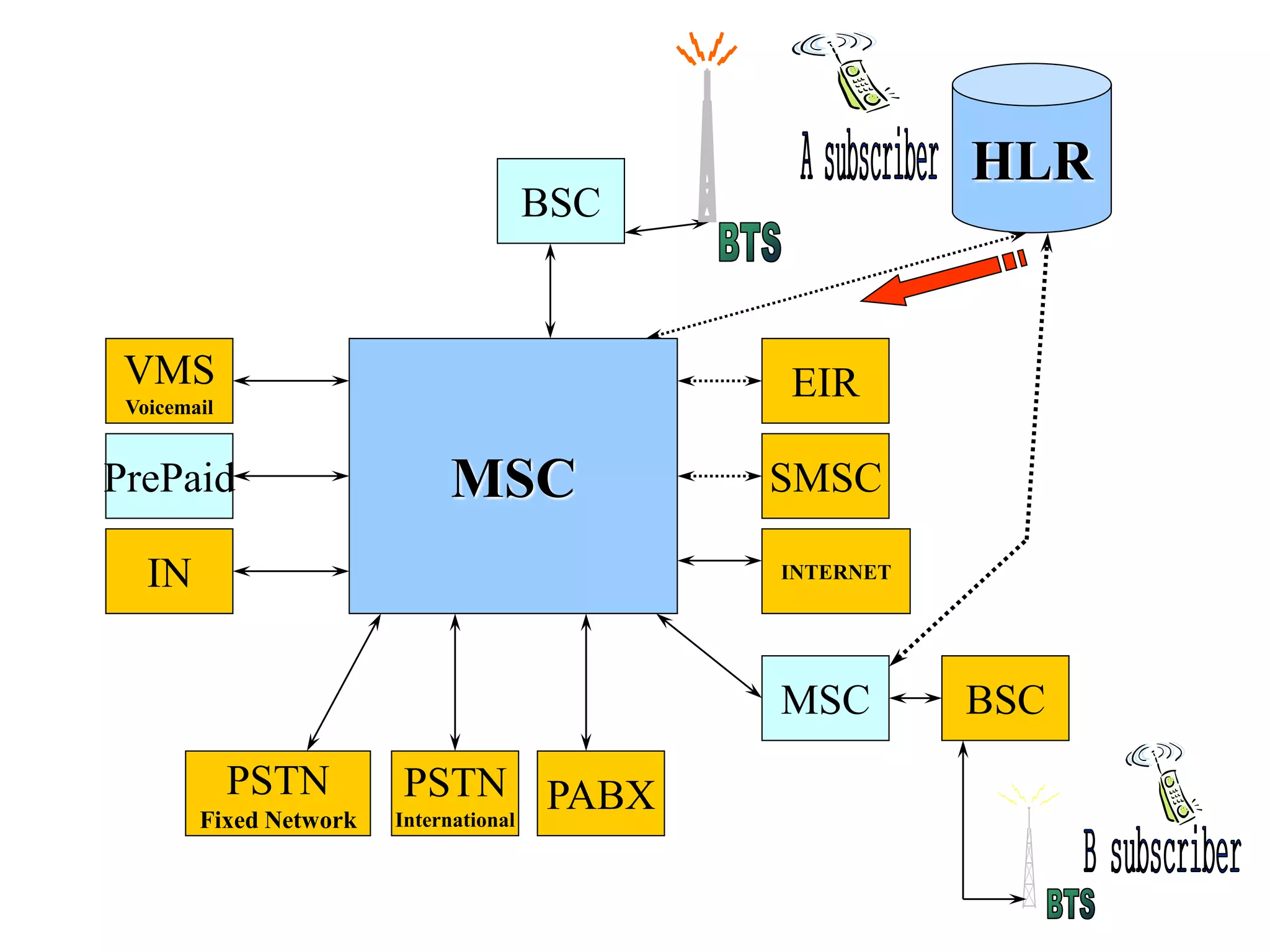
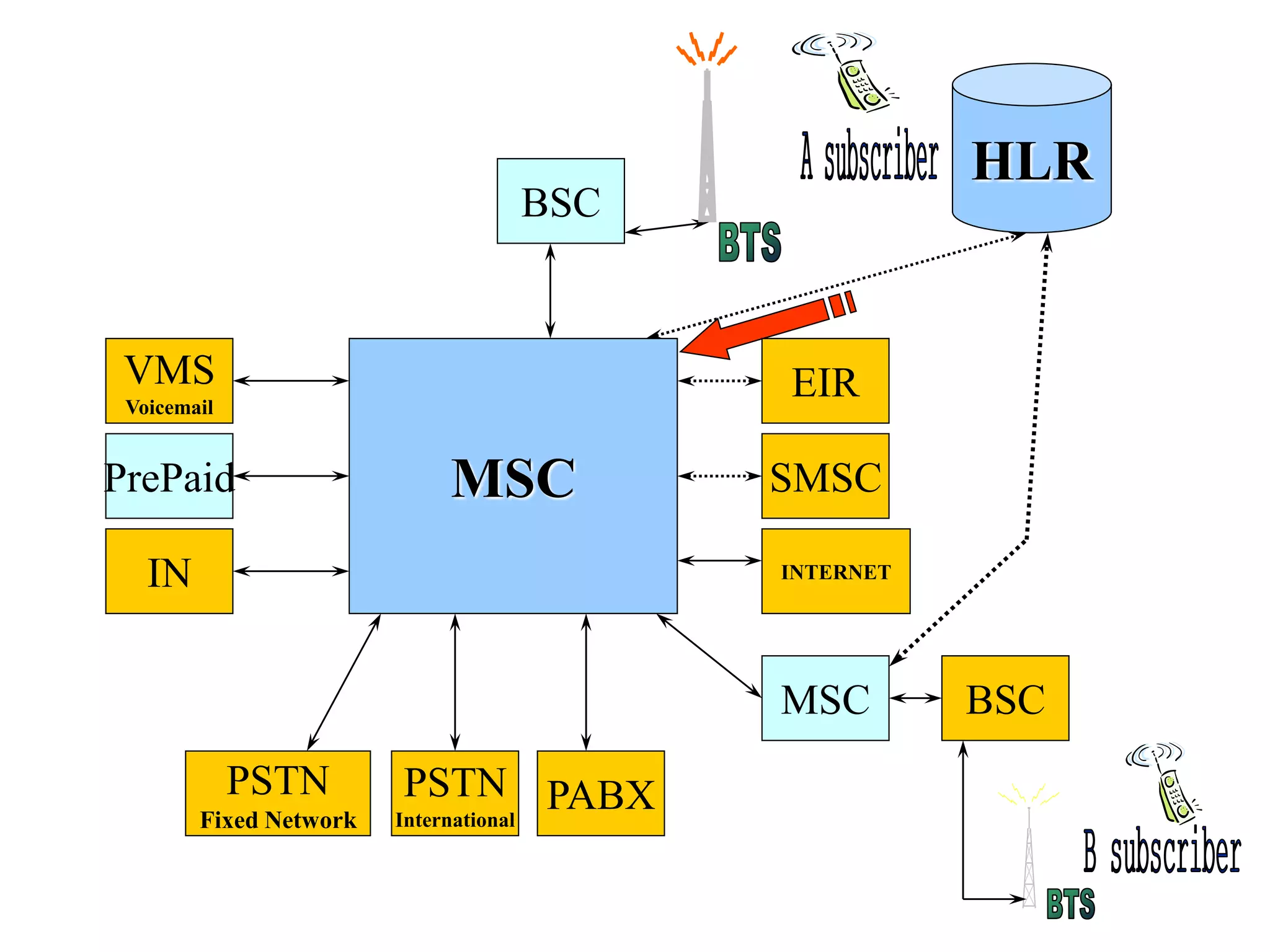
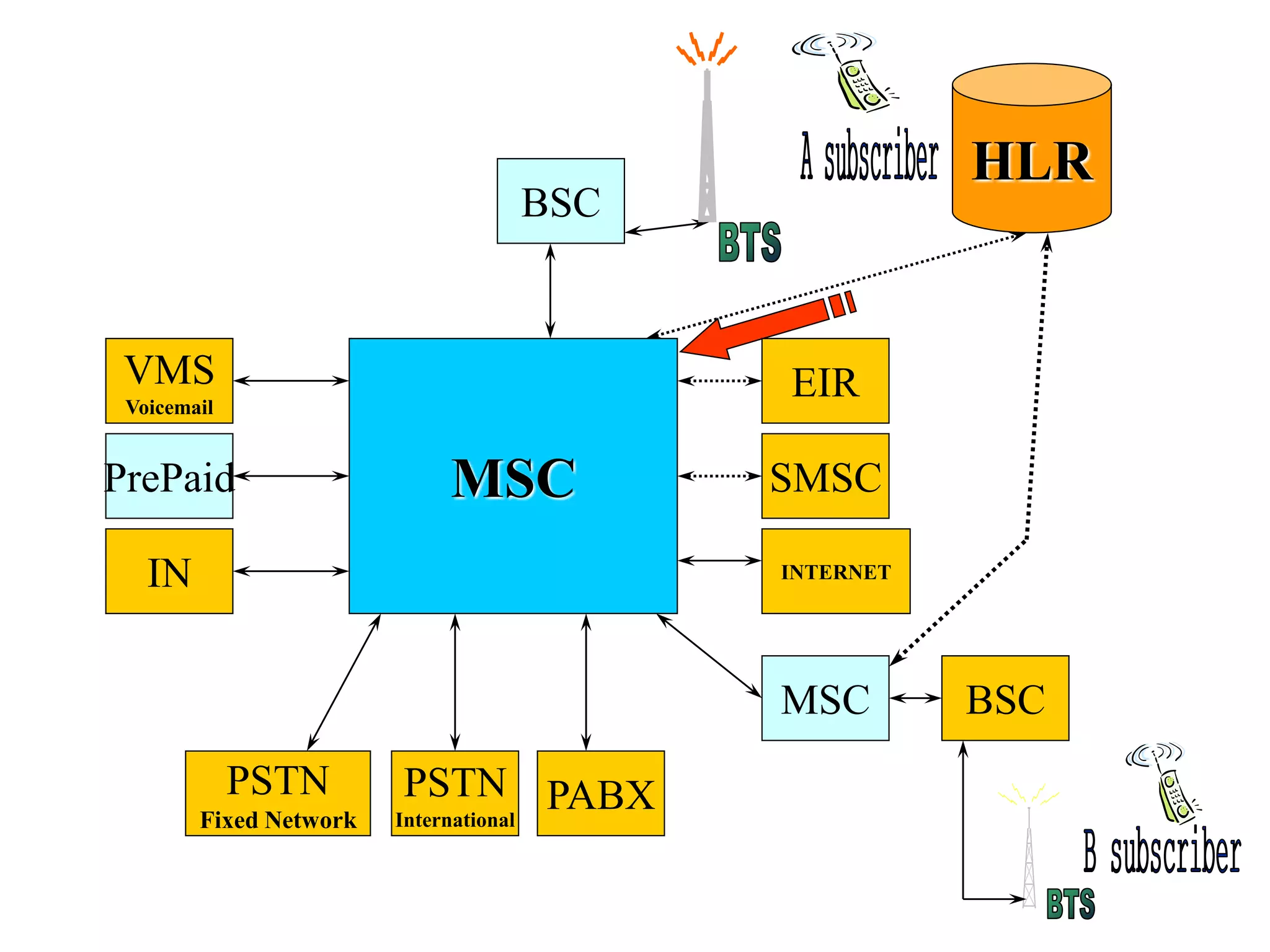
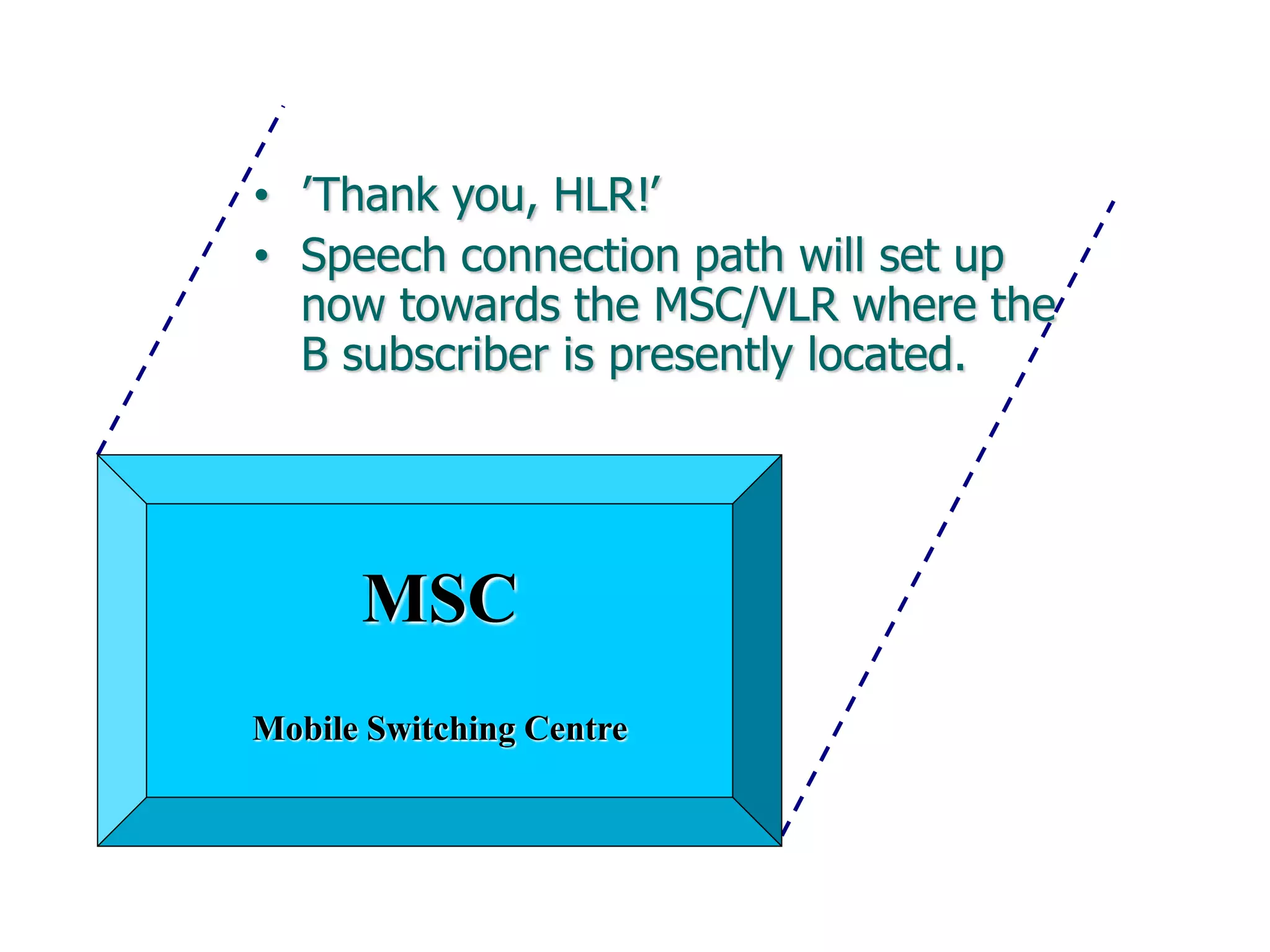
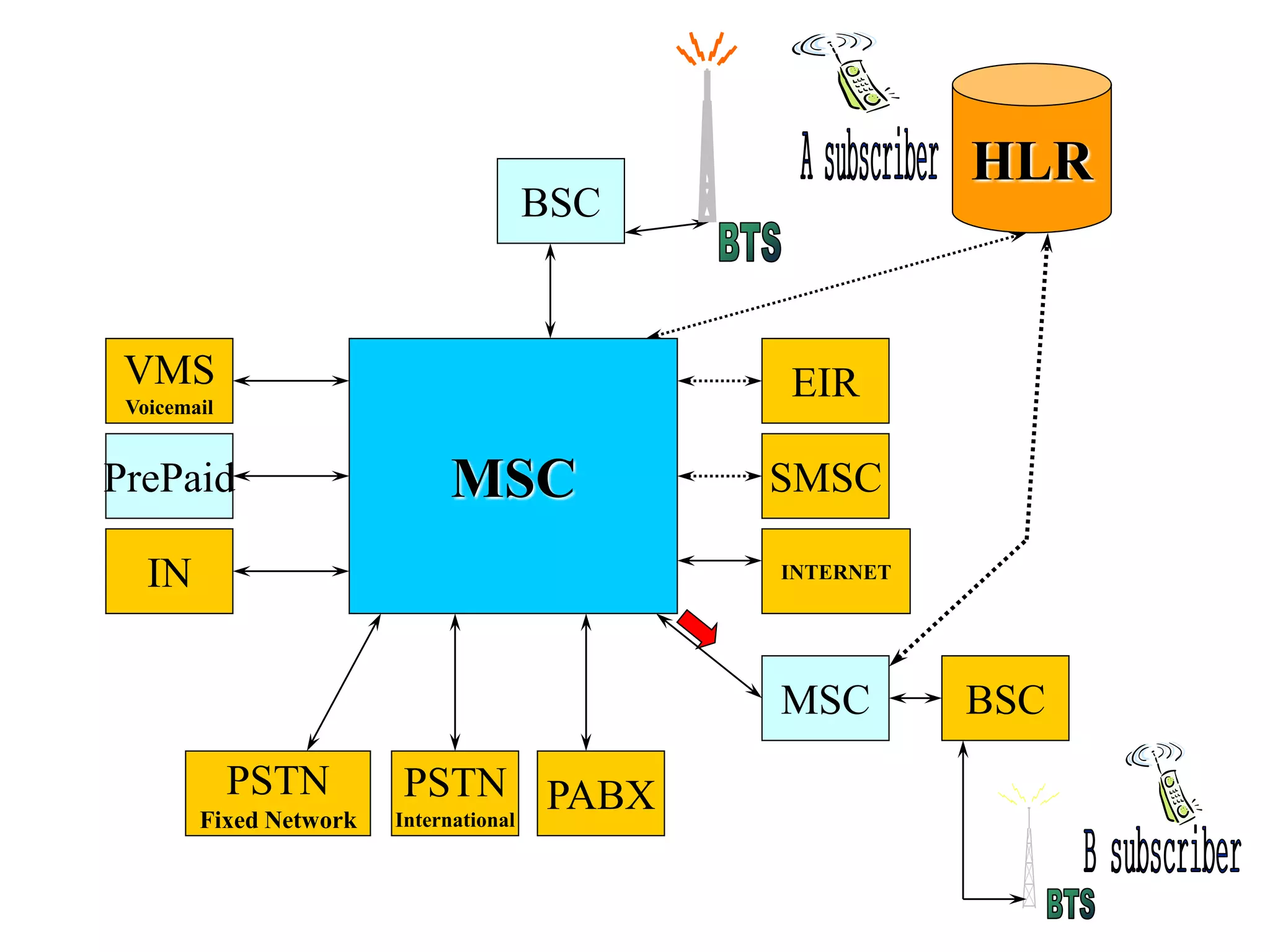
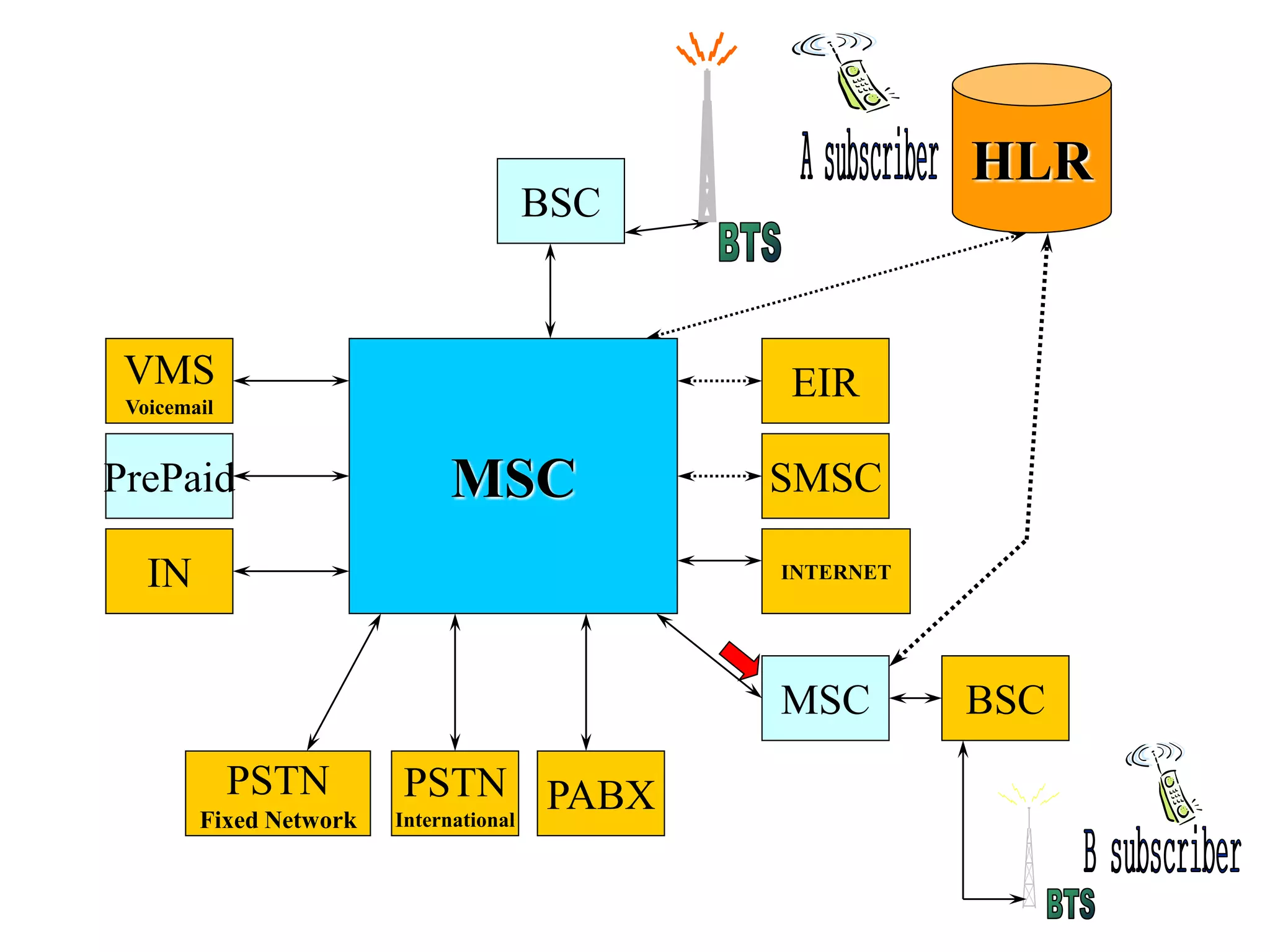
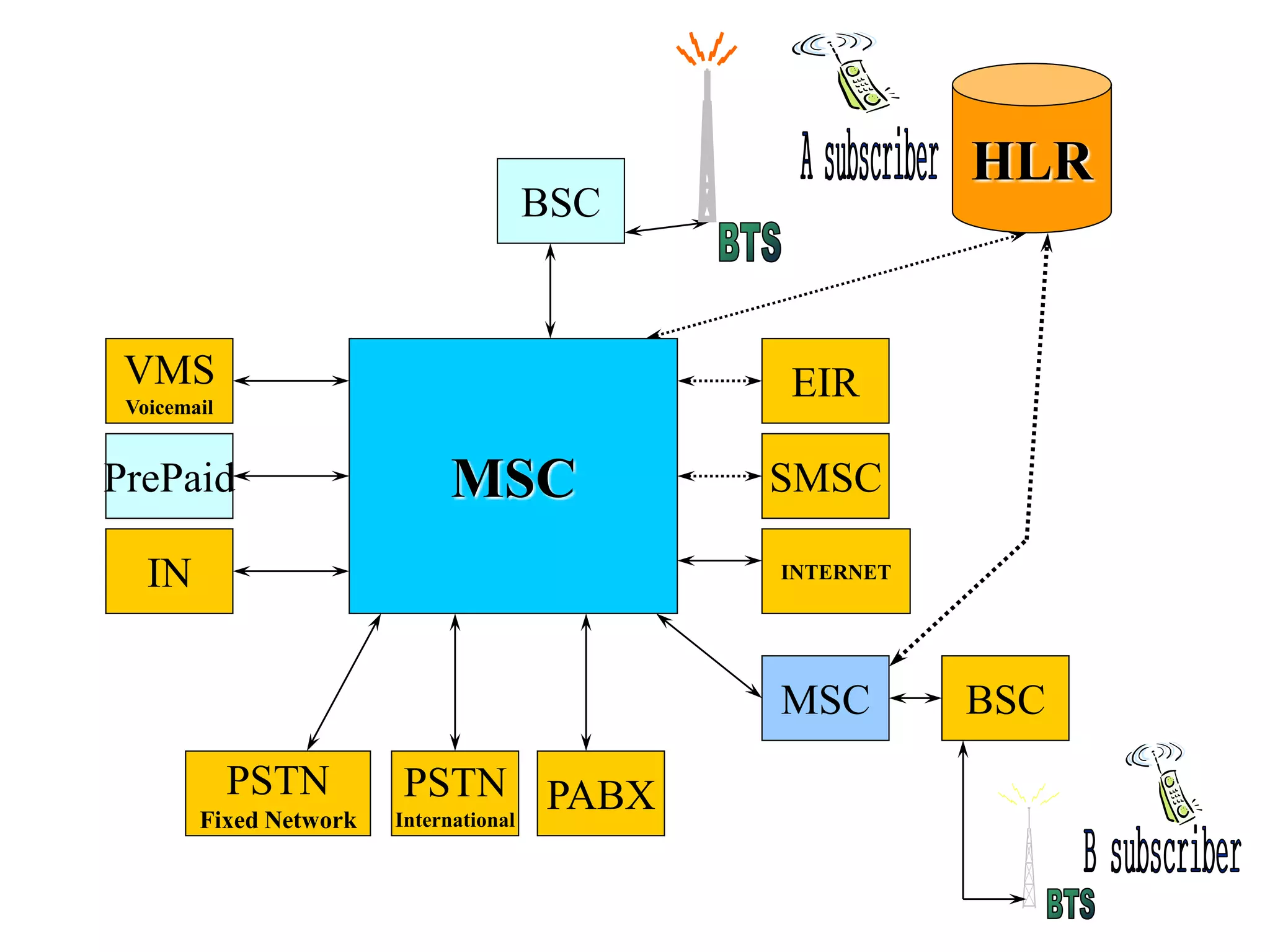
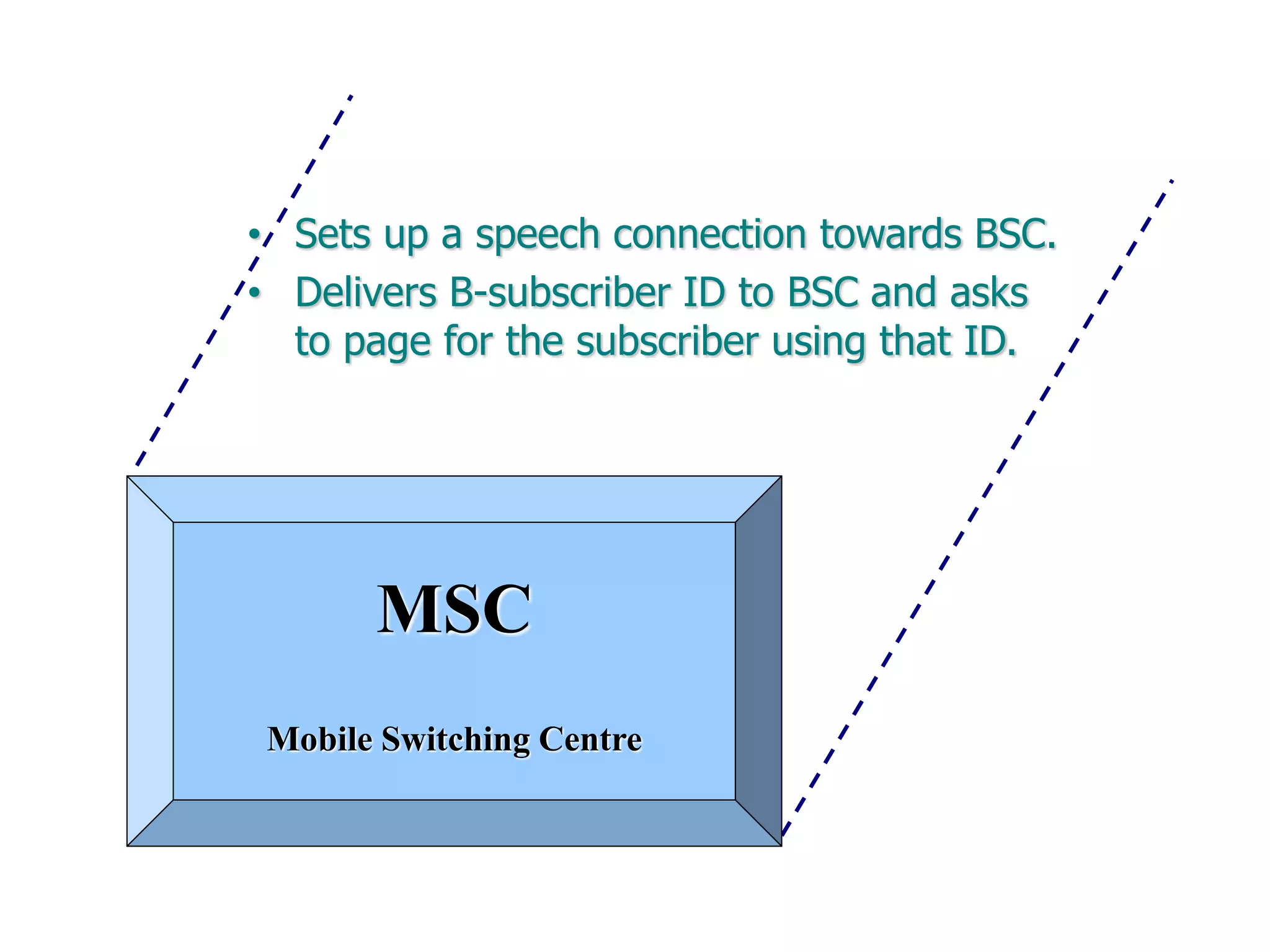
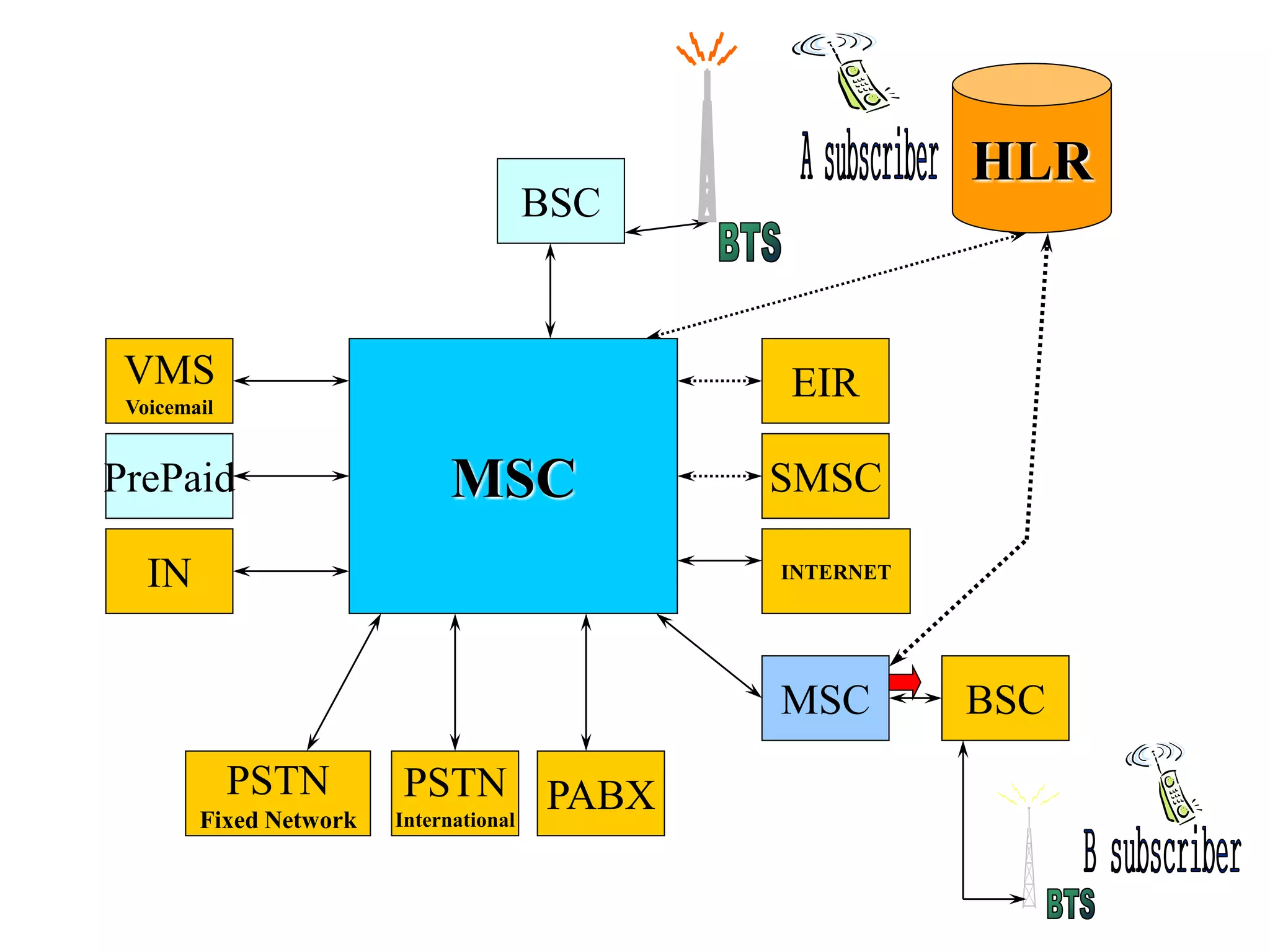
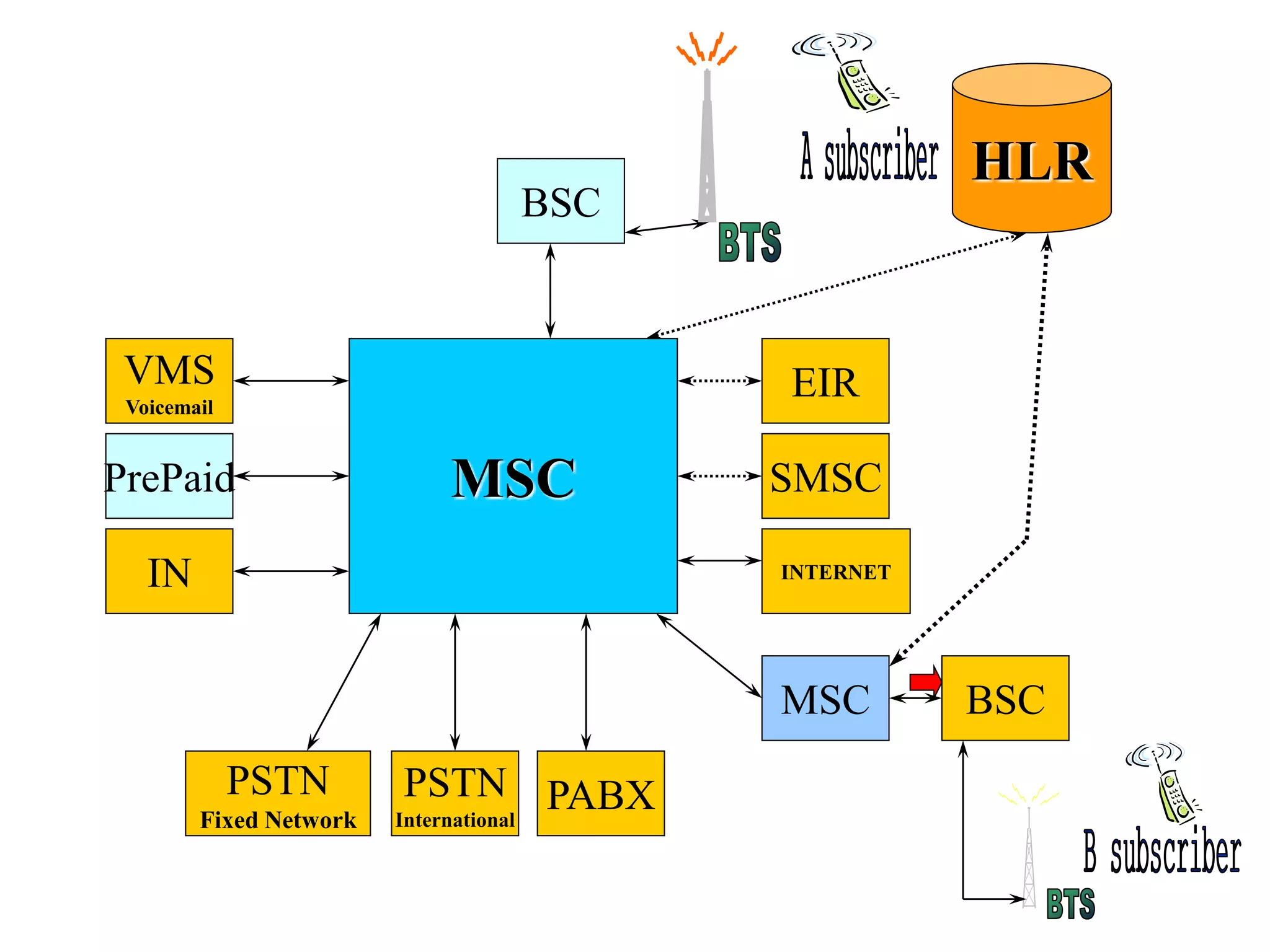
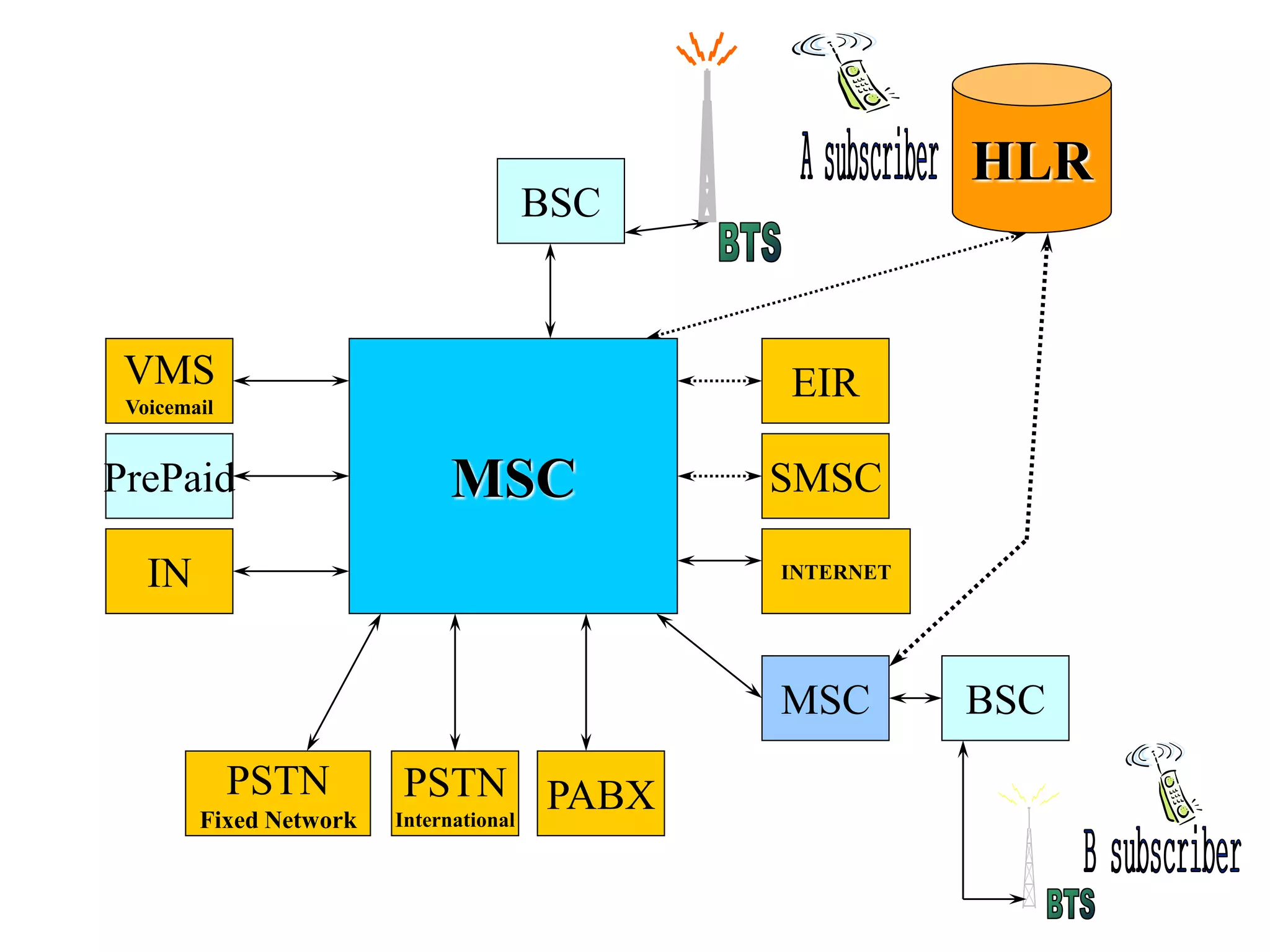
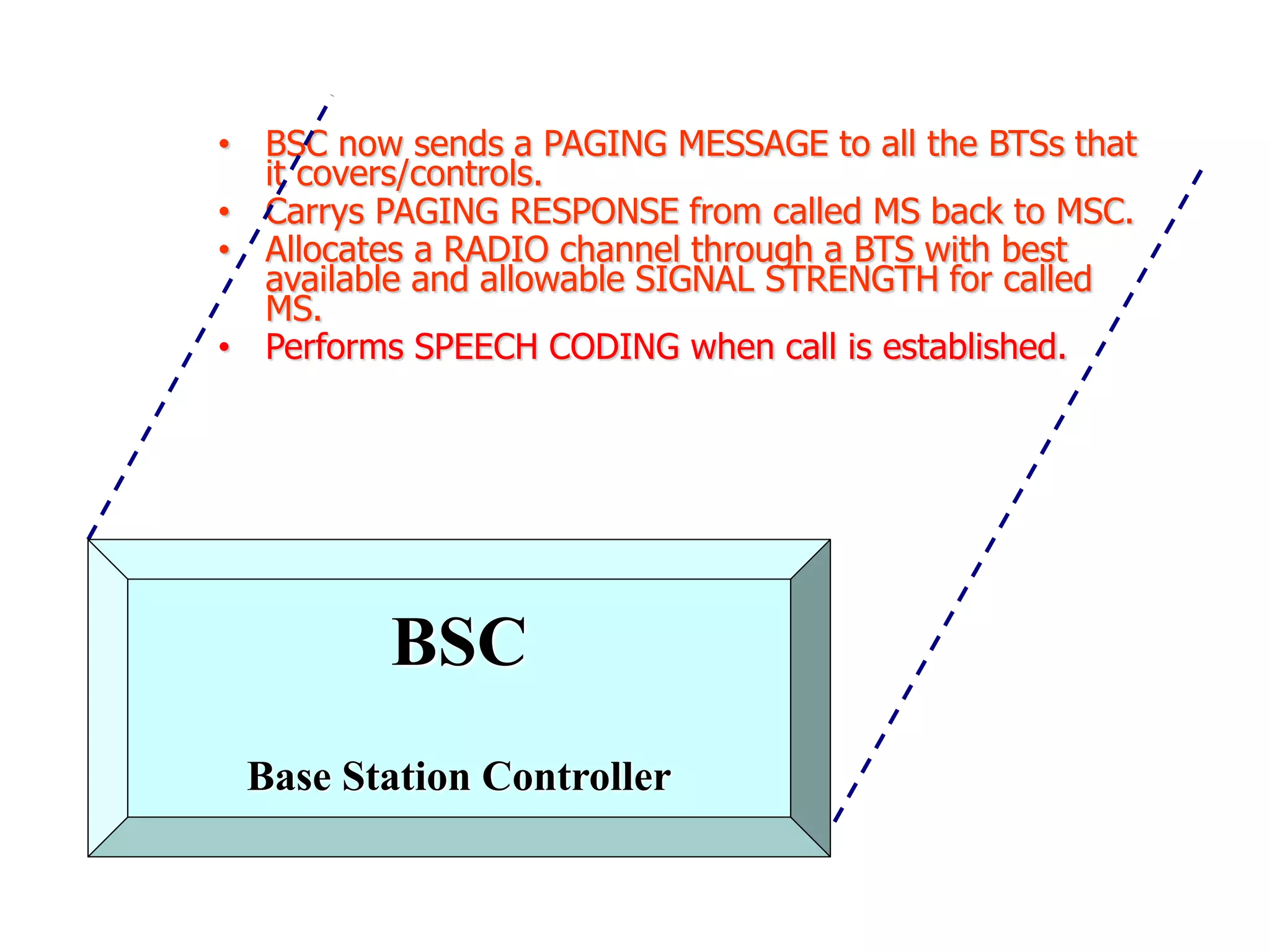
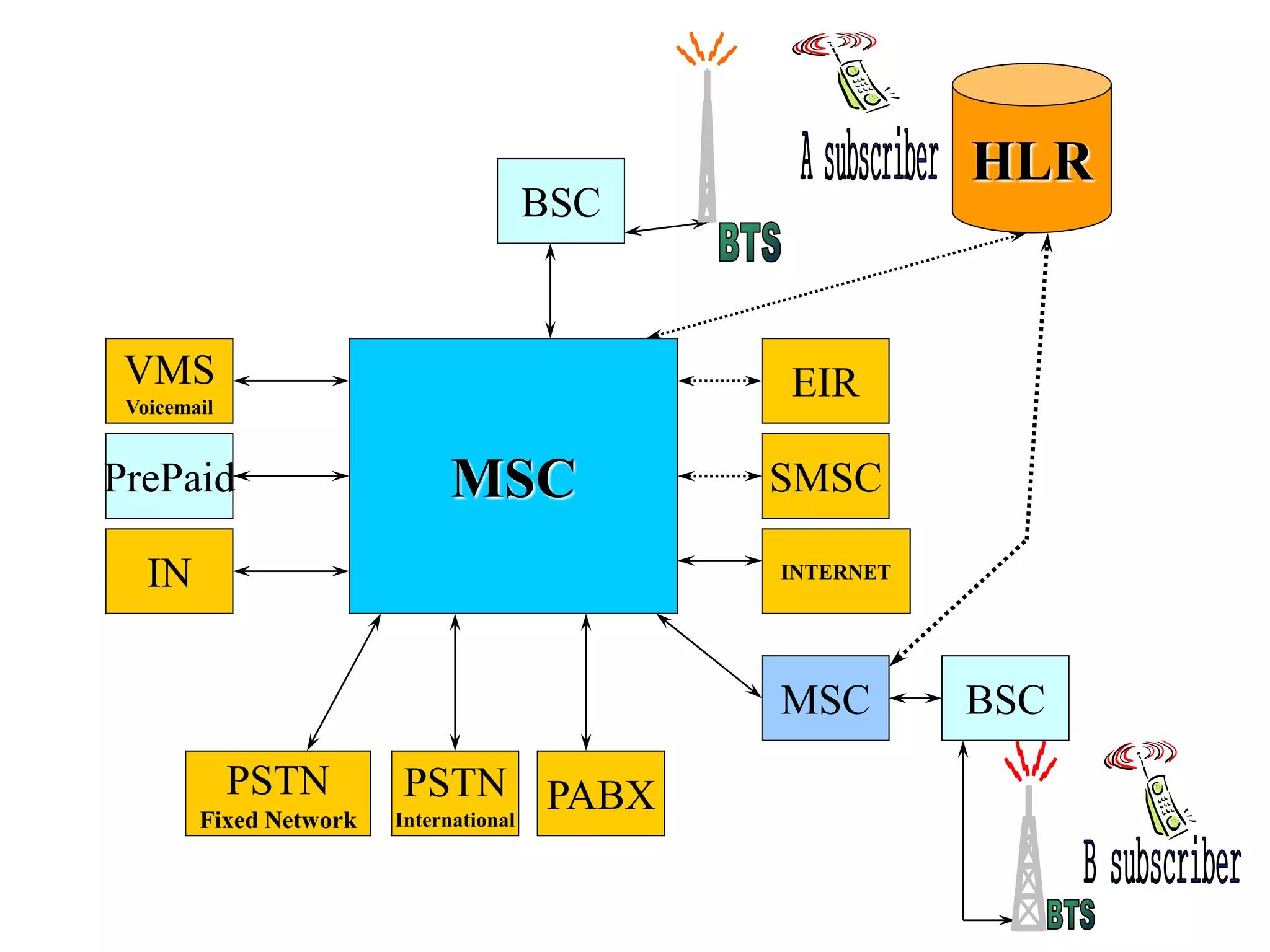
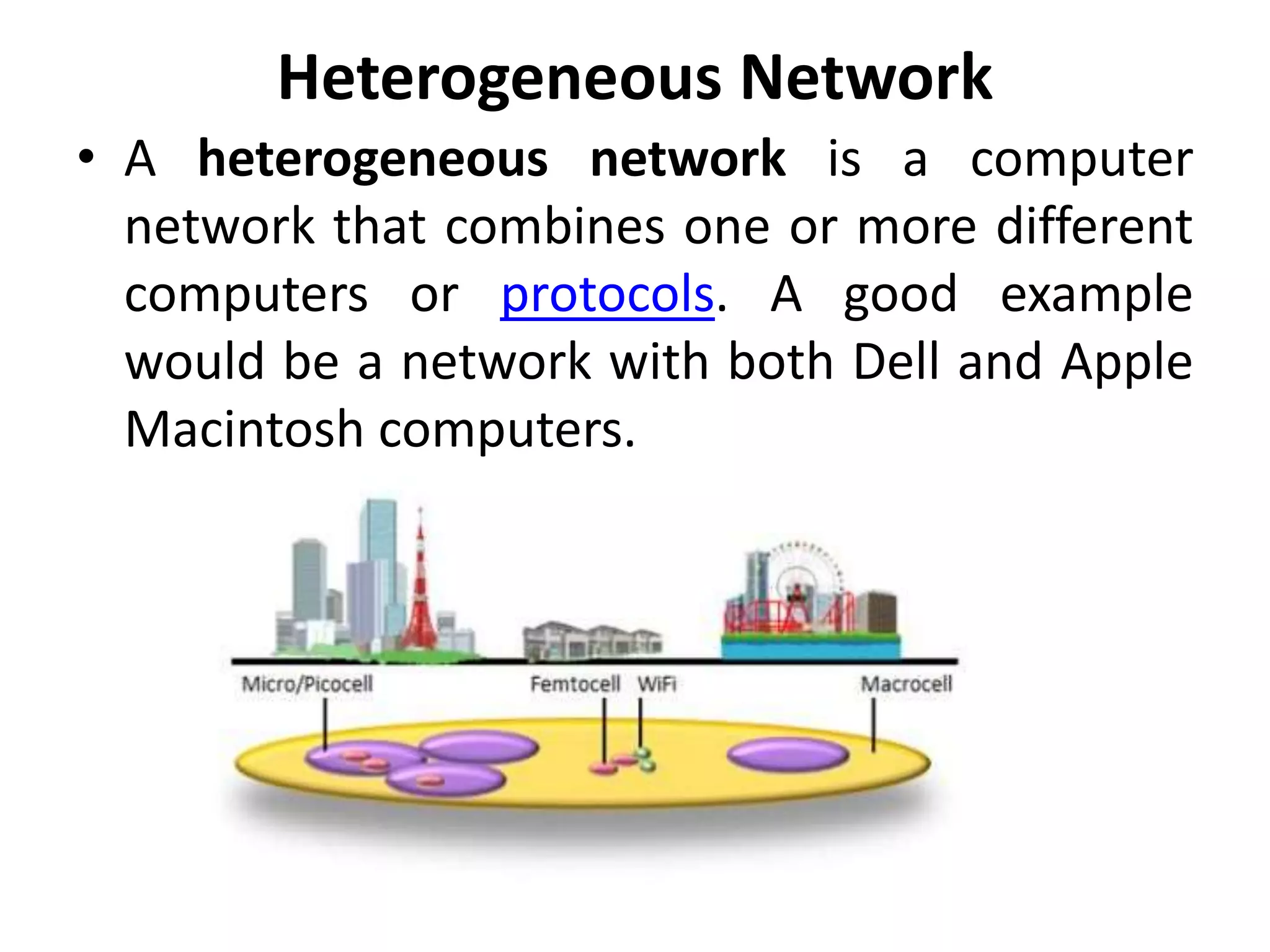
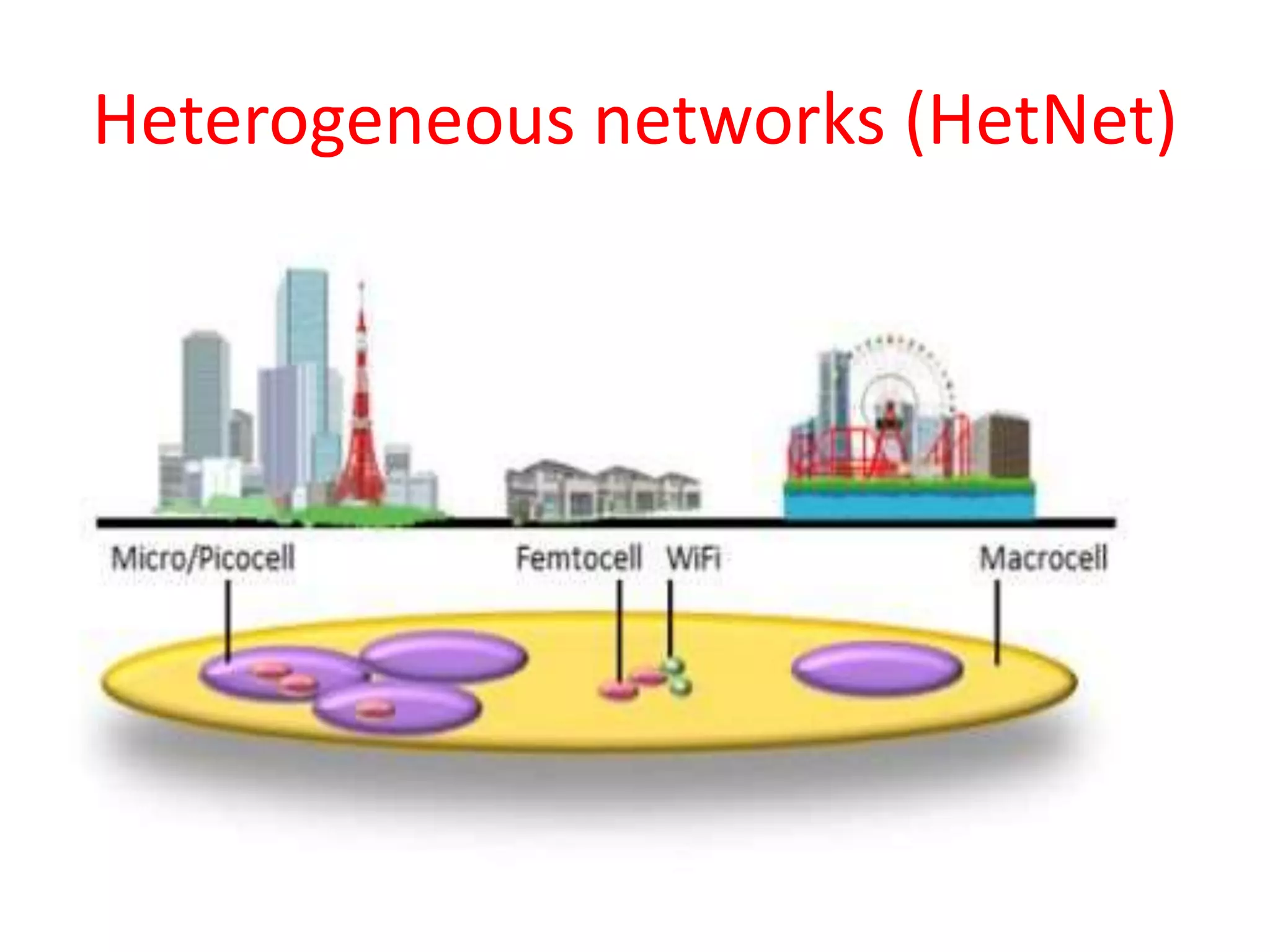
The document explains the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous networks, with homogeneous networks consisting of similar configurations and protocols, such as Microsoft Windows over TCP/IP, while heterogeneous networks integrate multiple different systems and protocols. It elaborates on the challenges that heterogeneous networks face, including security, compatibility, cost, and complexity issues, and discusses the relevant technologies like GSM and small cells. It emphasizes the necessity for proper training and configuration management to successfully manage these complex networks.


![Small cell
• Small cells[1] are low-powered radio access nodes
that operate in licensed and unlicensed spectrum
that have a range of 10 meters to 1 or 2
kilometers.
• They are "small" compared to a mobile macrocell,
which may have a range of a few tens of
kilometers. With mobile operators struggling to
support the growth in mobile data traffic,[2]
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-weakbysirtahzaib-180405180208/75/Homogeneous-Homogeneous-Issues-Involve-in-a-Heterogeneous-Network-8-2048.jpg)