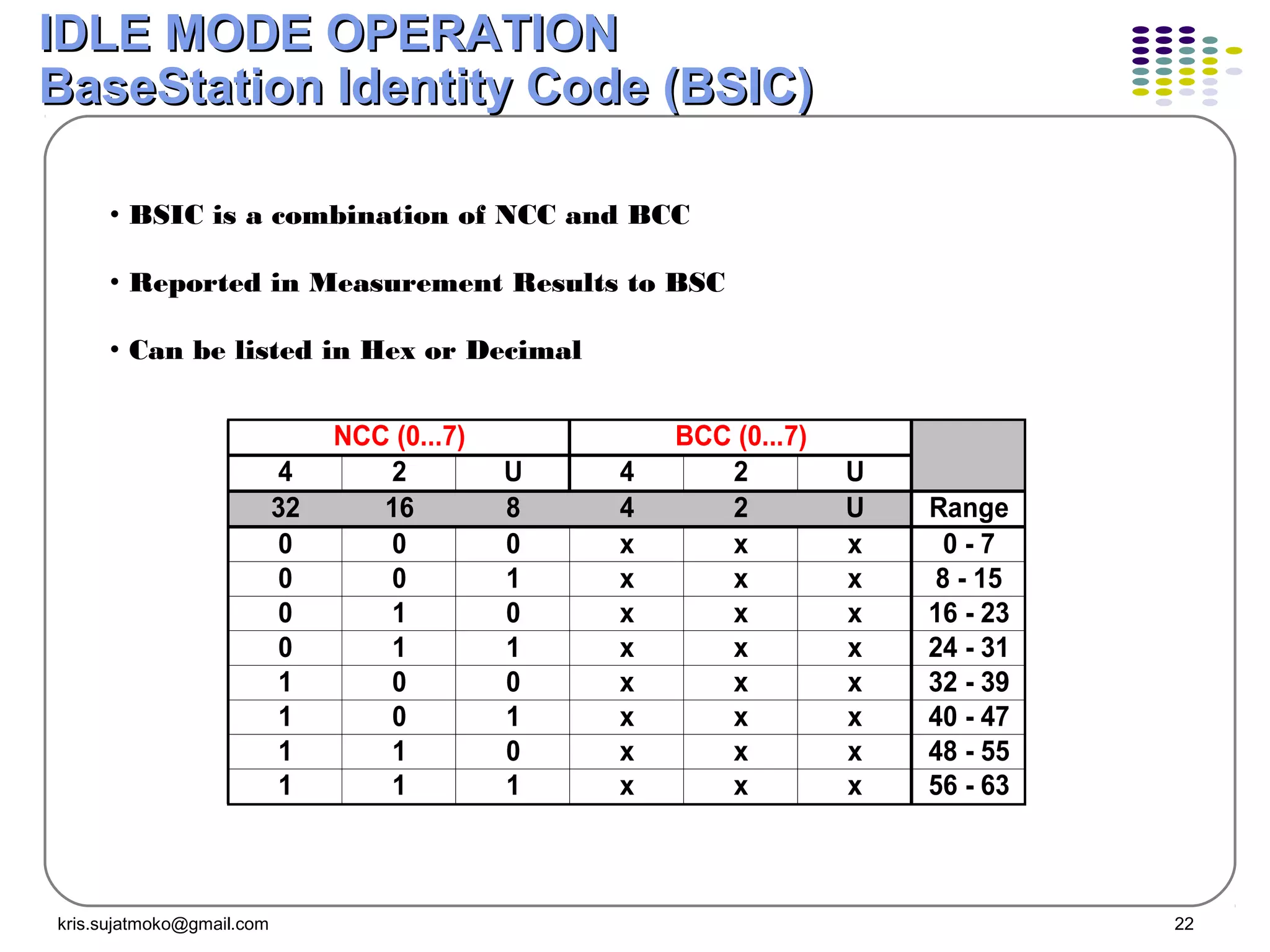
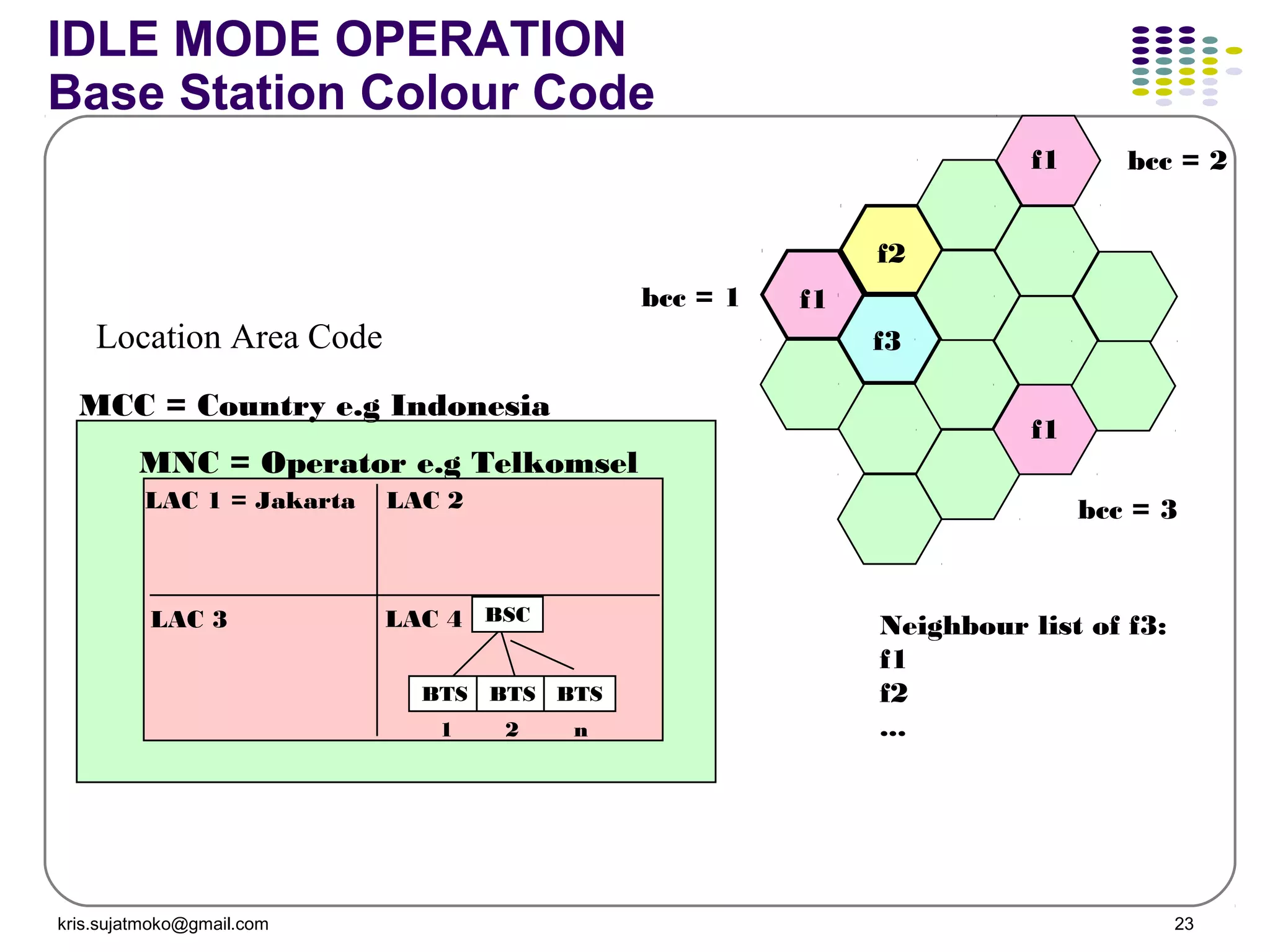
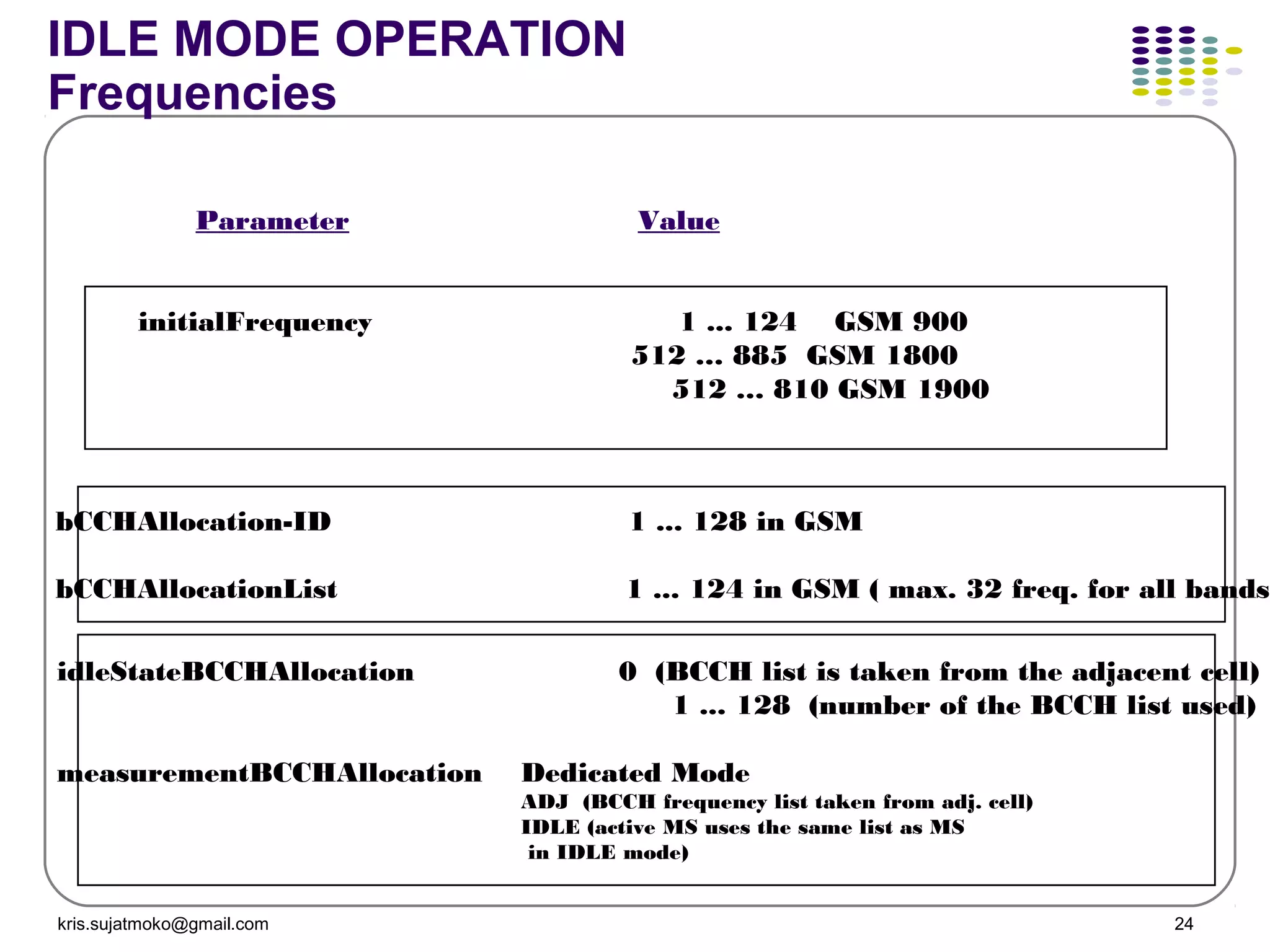
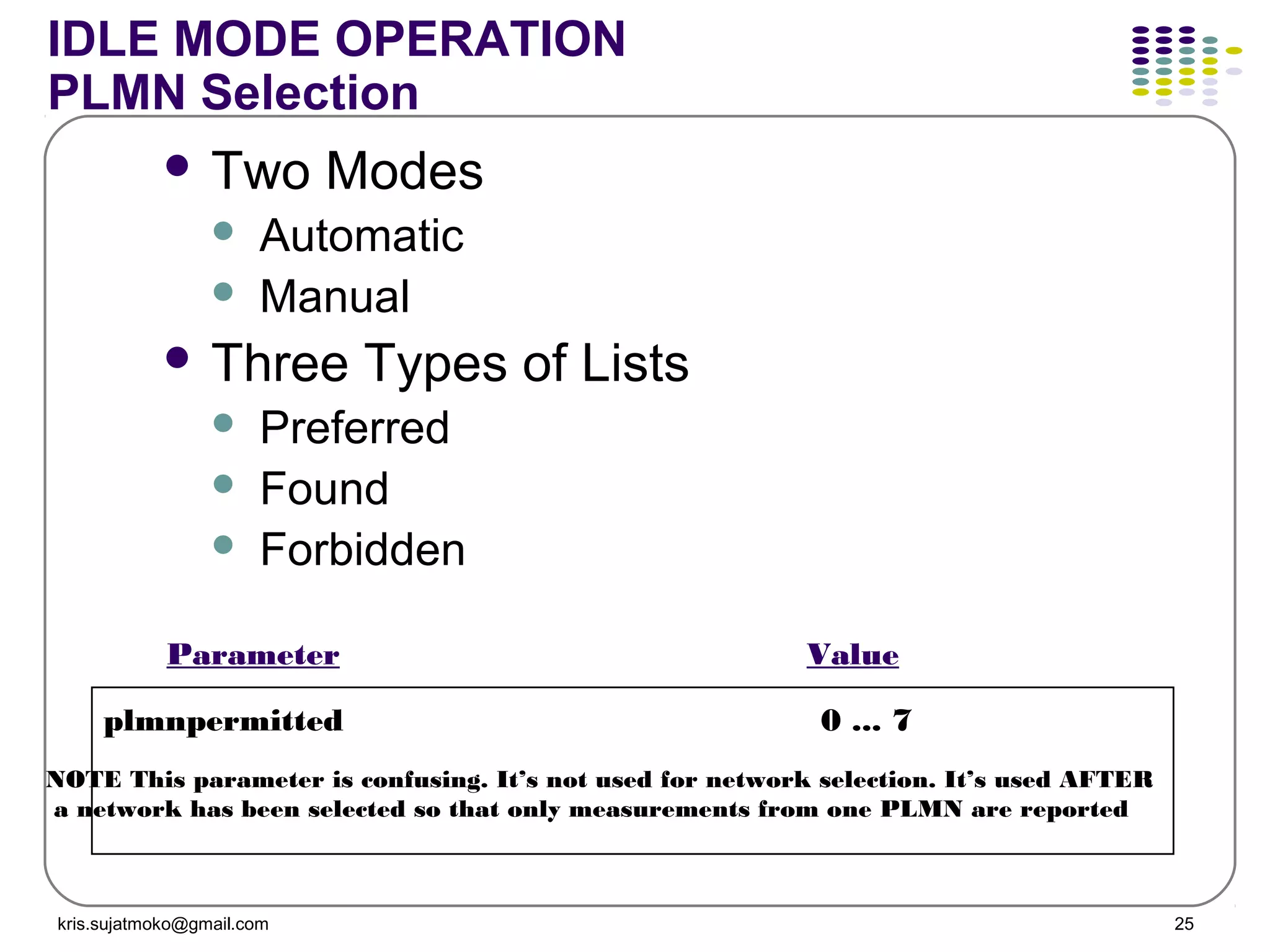
The document discusses GSM-GPRS network operations including:
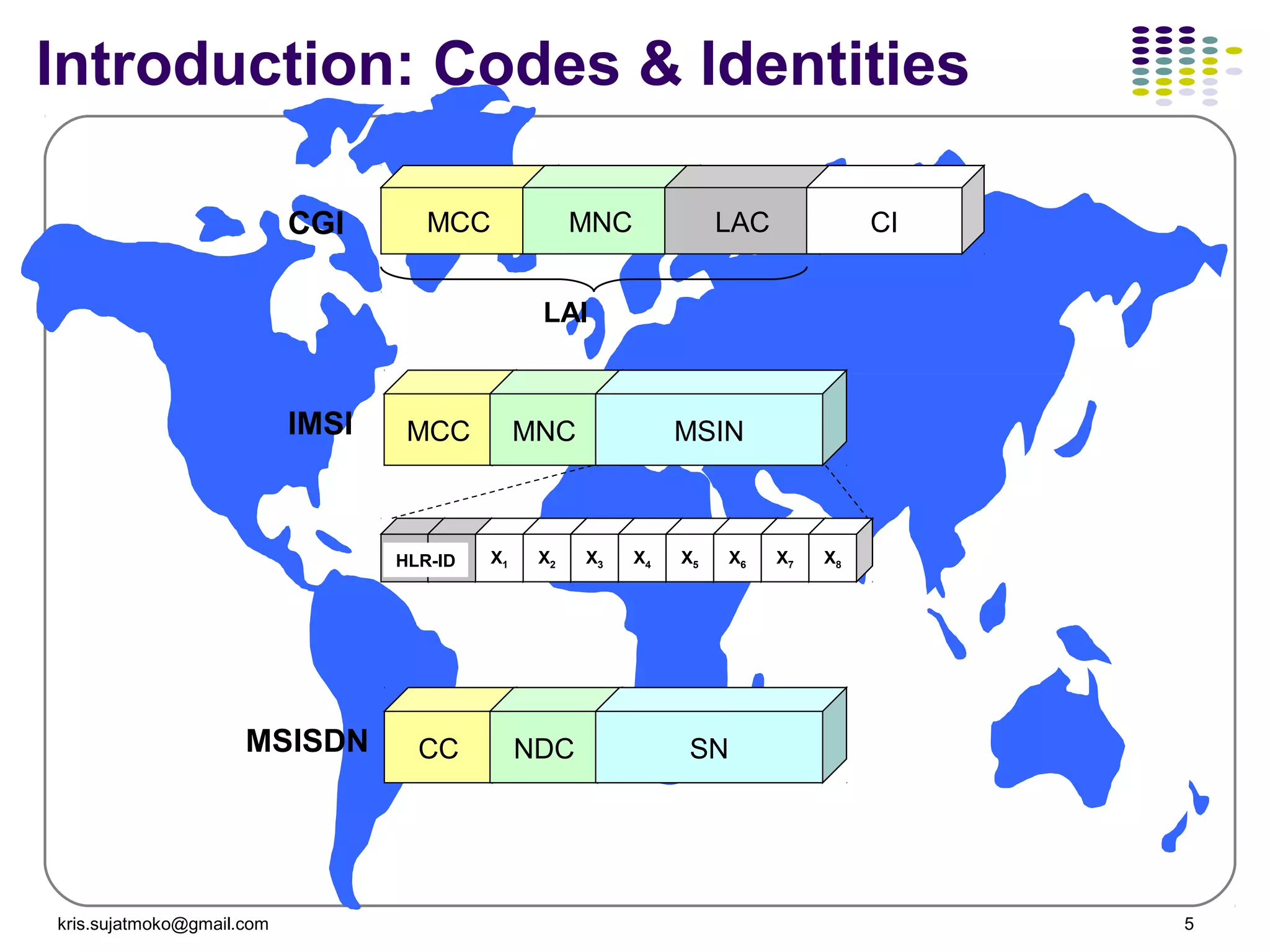
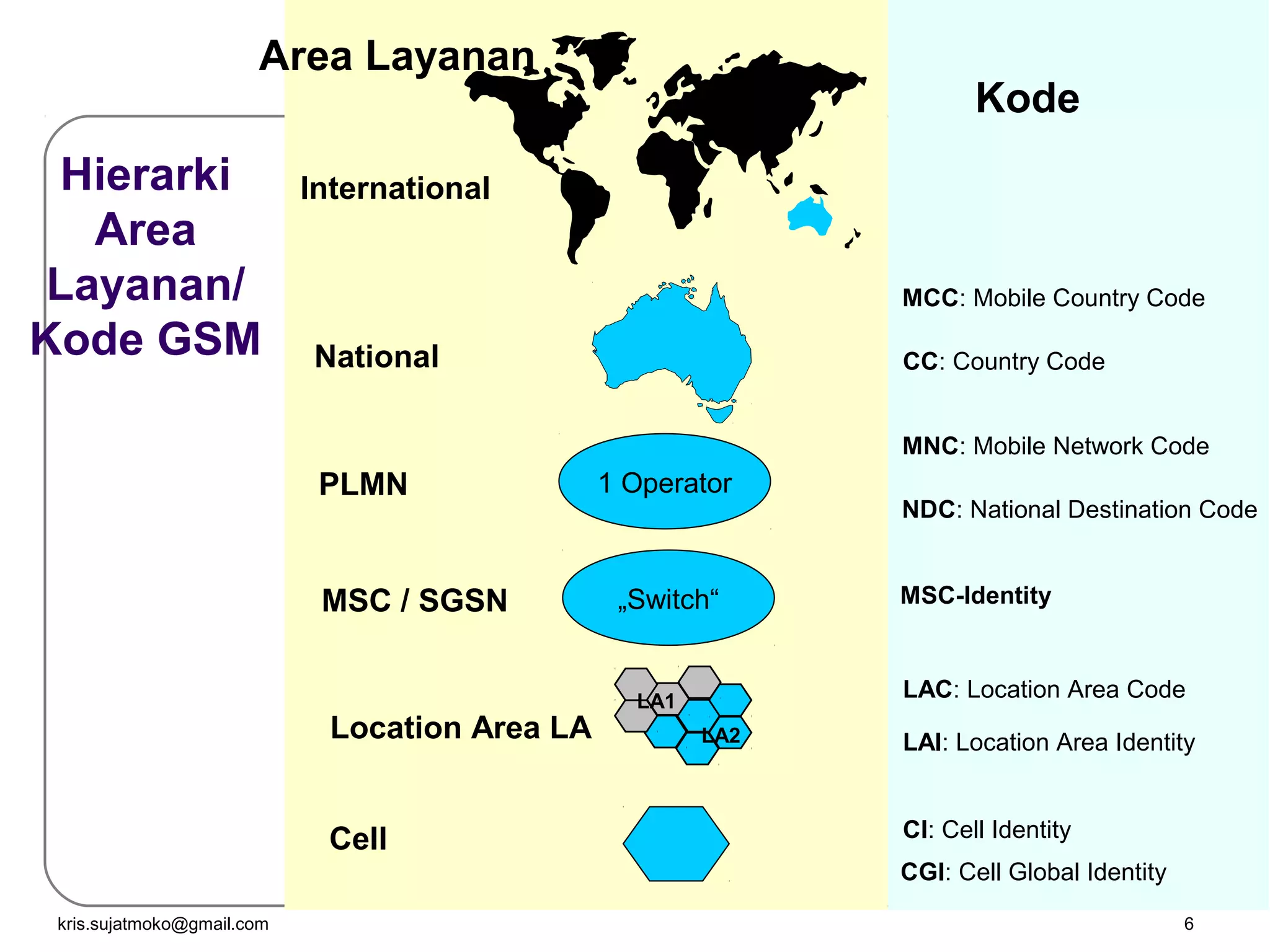
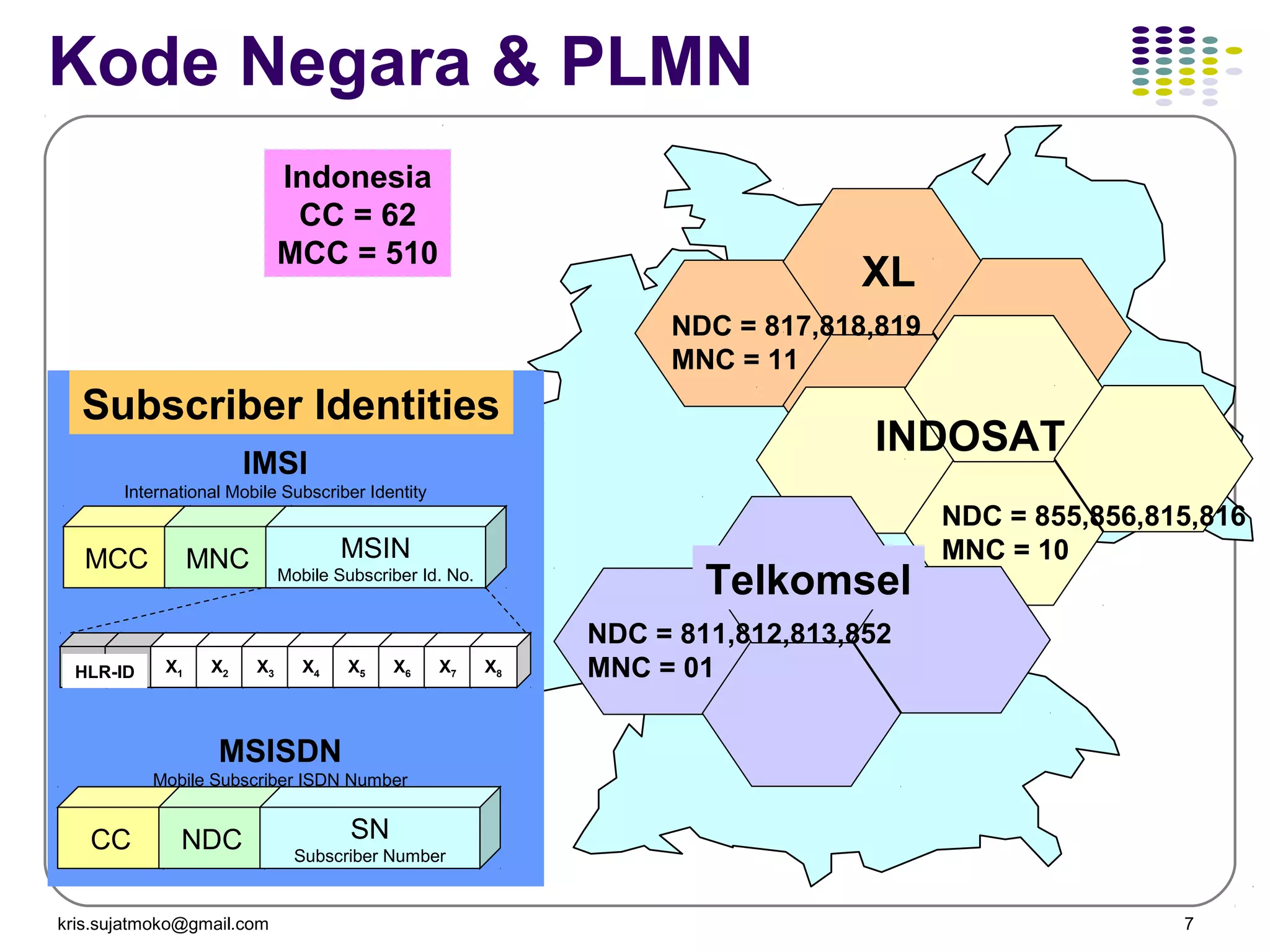
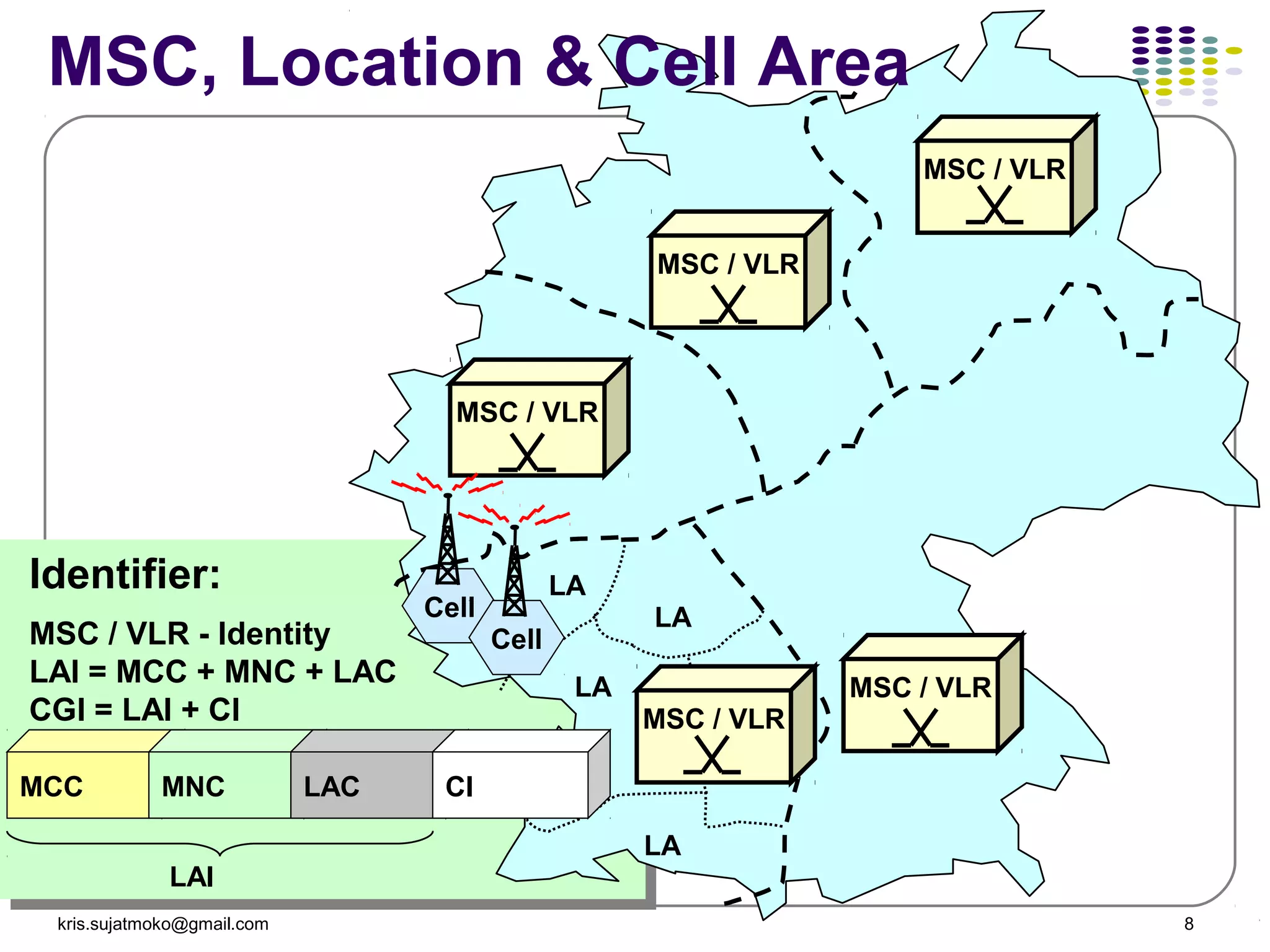
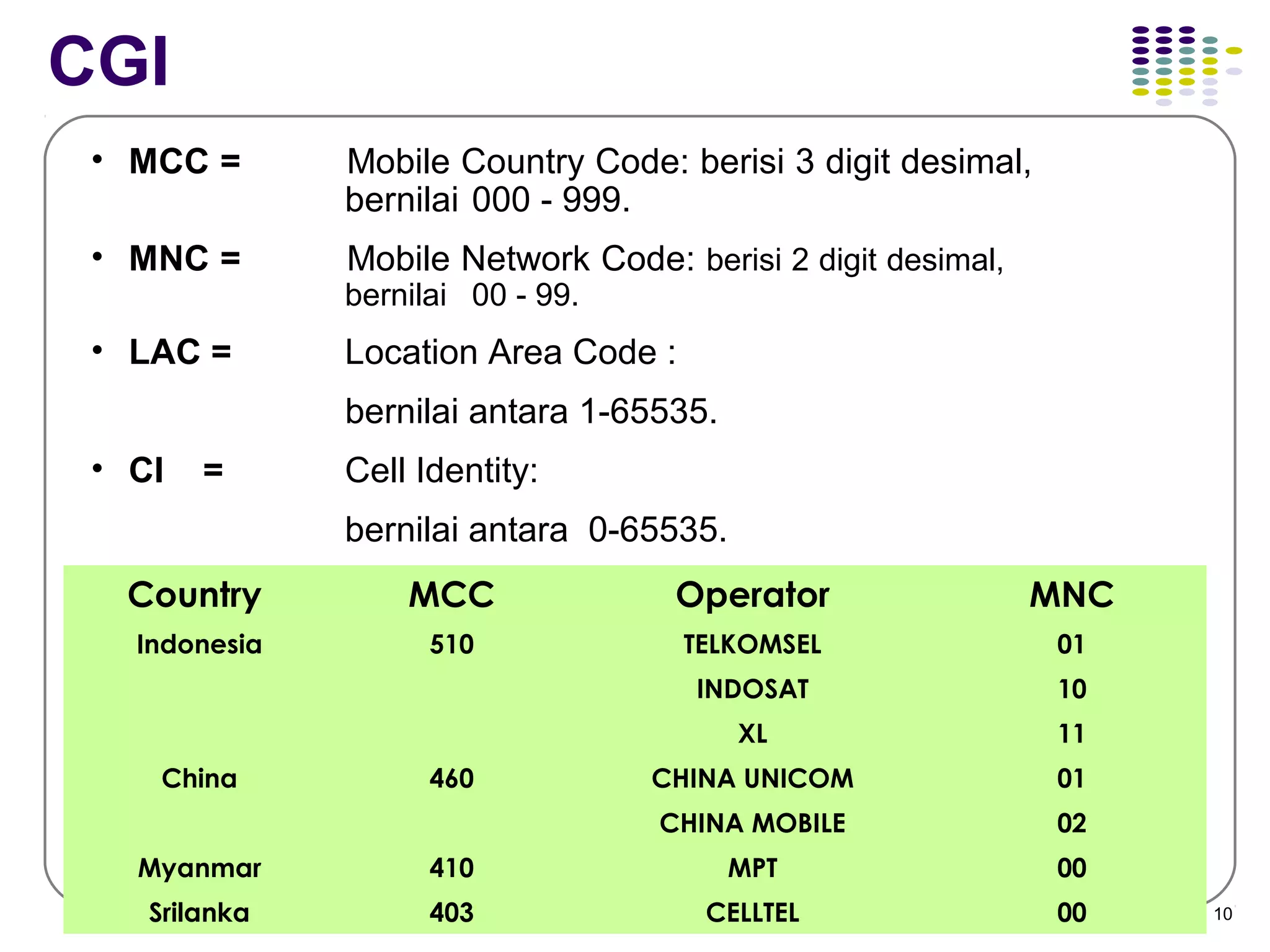
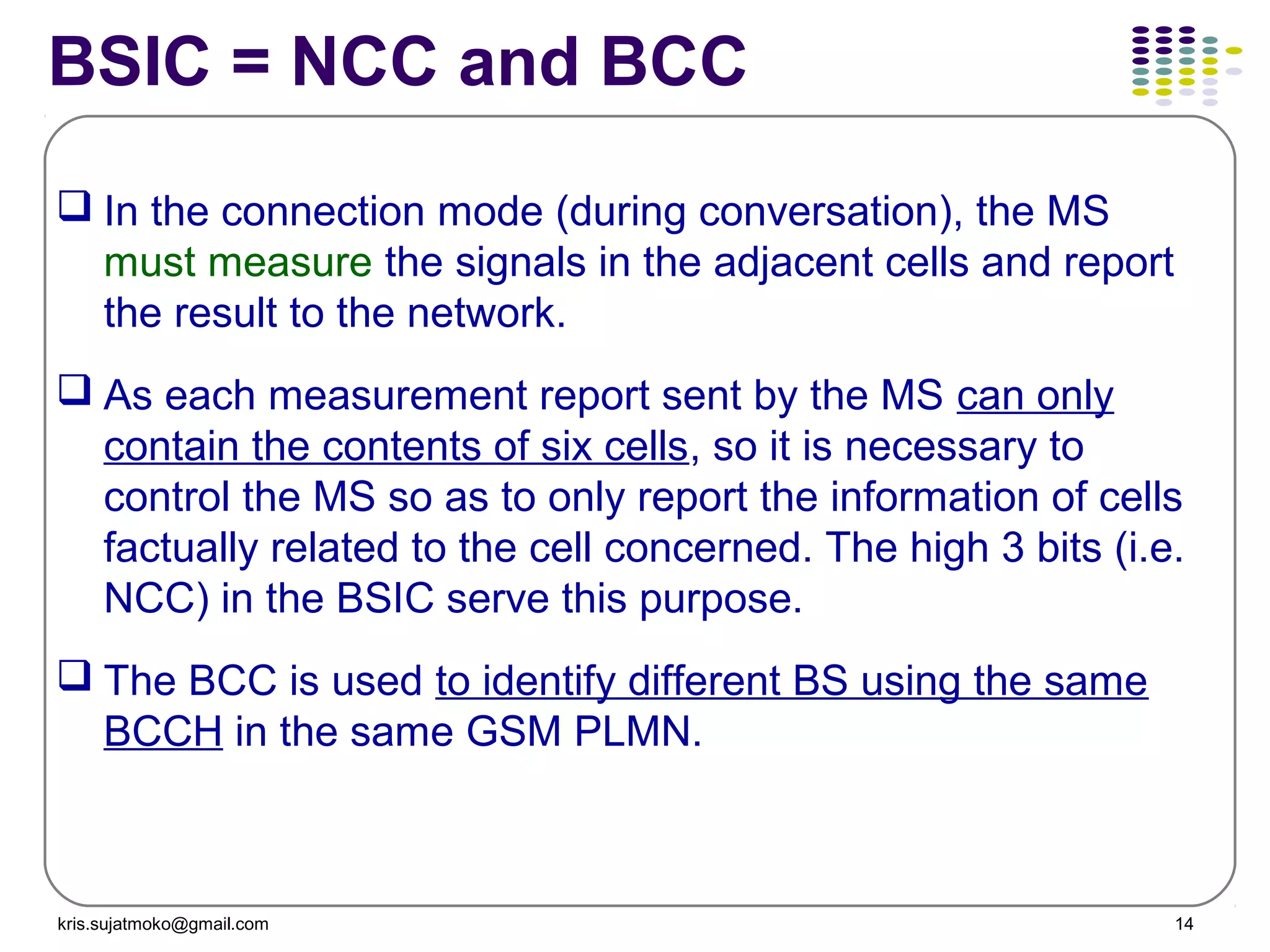
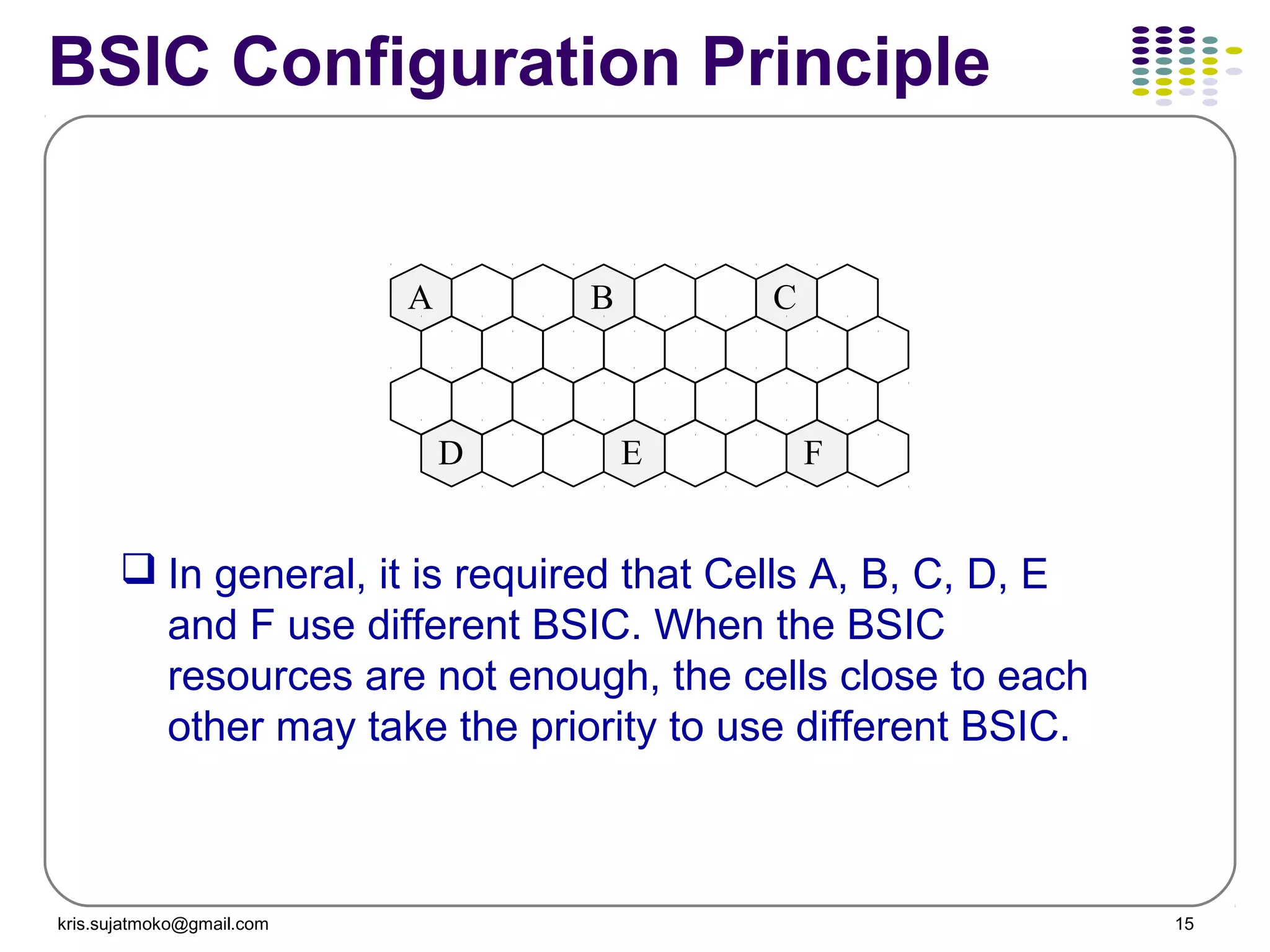
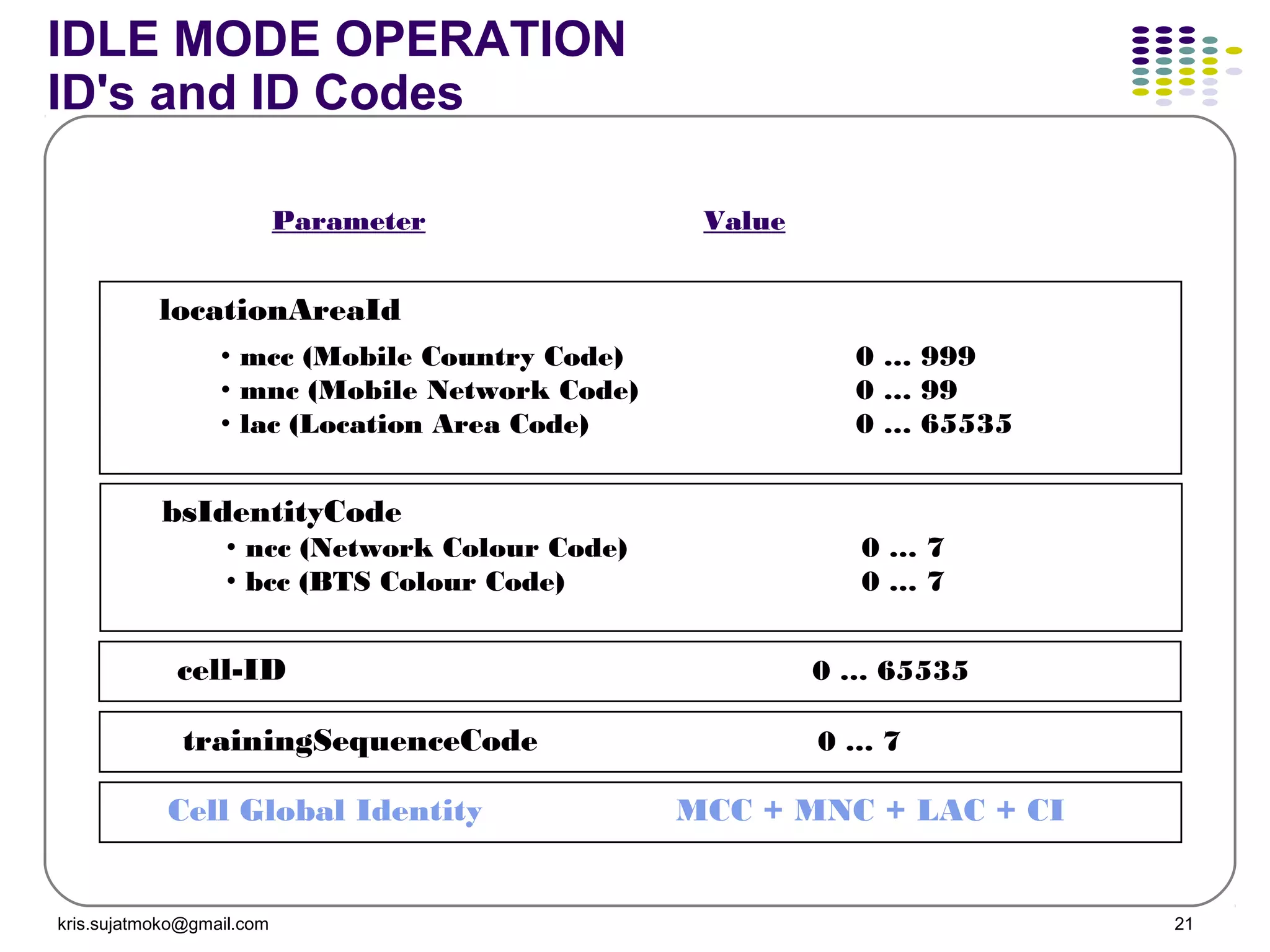
1. Network identity parameters such as MCC, MNC, LAC, CI which allow identification of network elements and location of mobile stations.
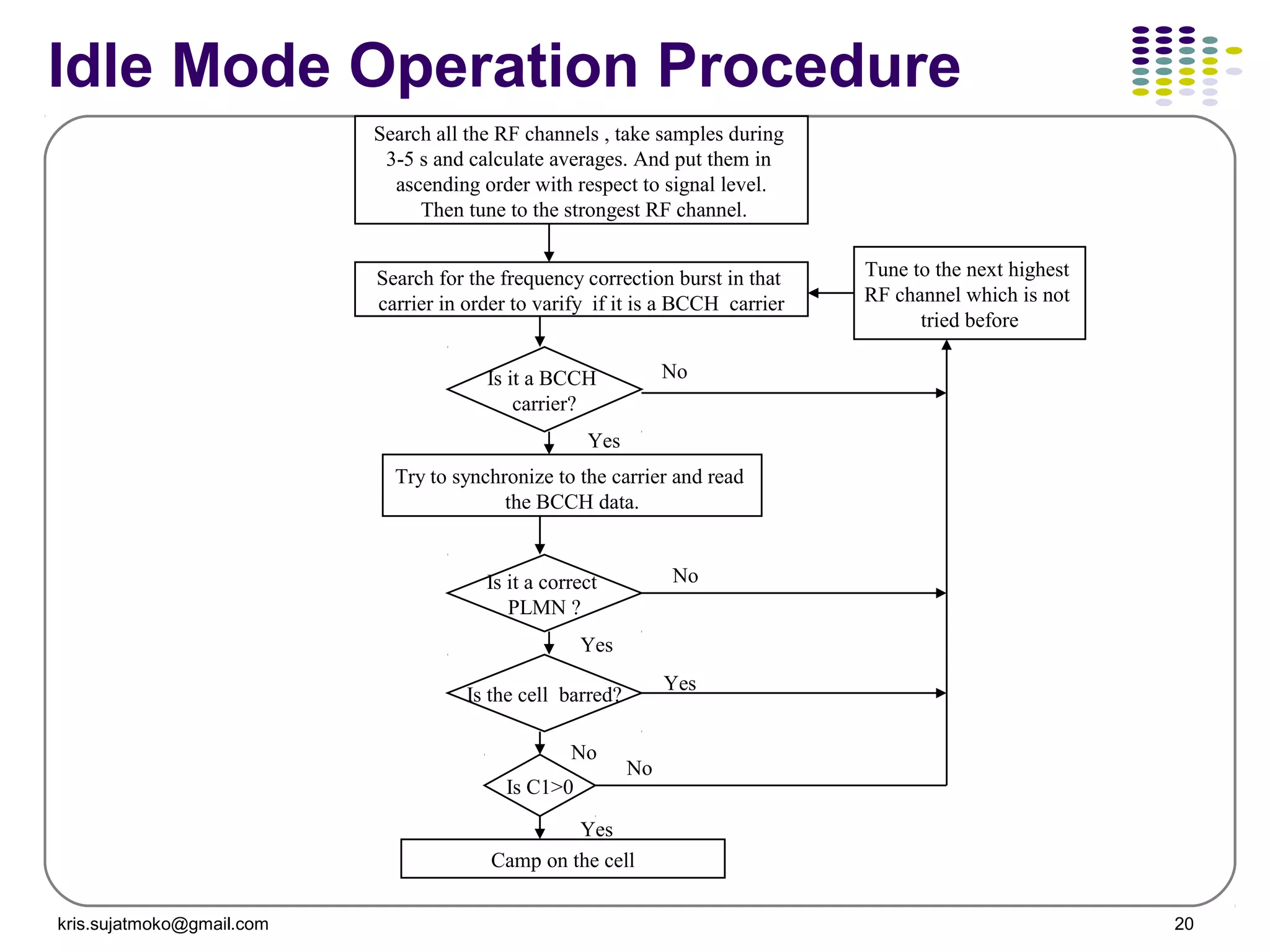
2. Idle mode operations which include cell selection, location updating, and allow mobile stations to receive system information when not in a call.
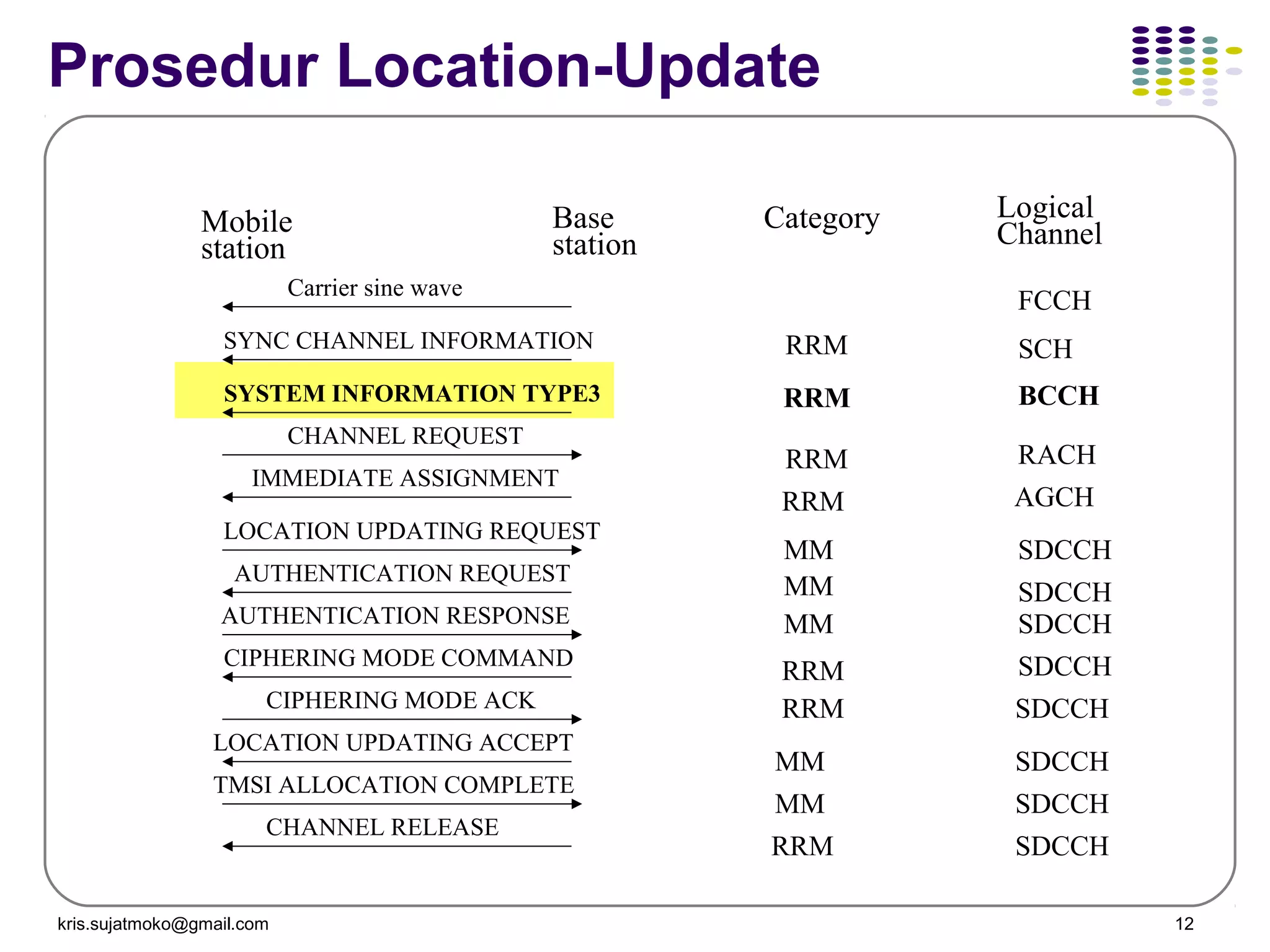
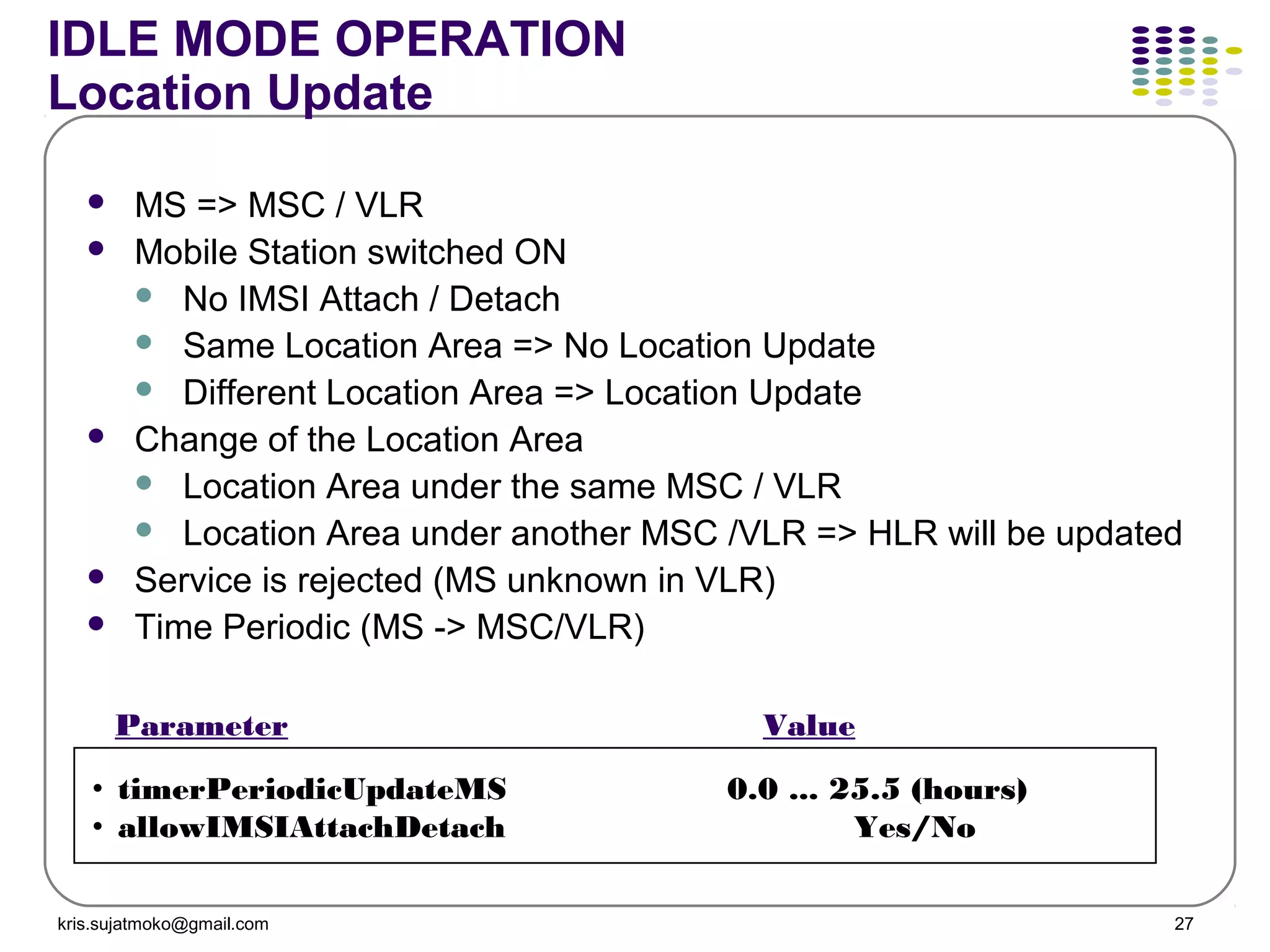
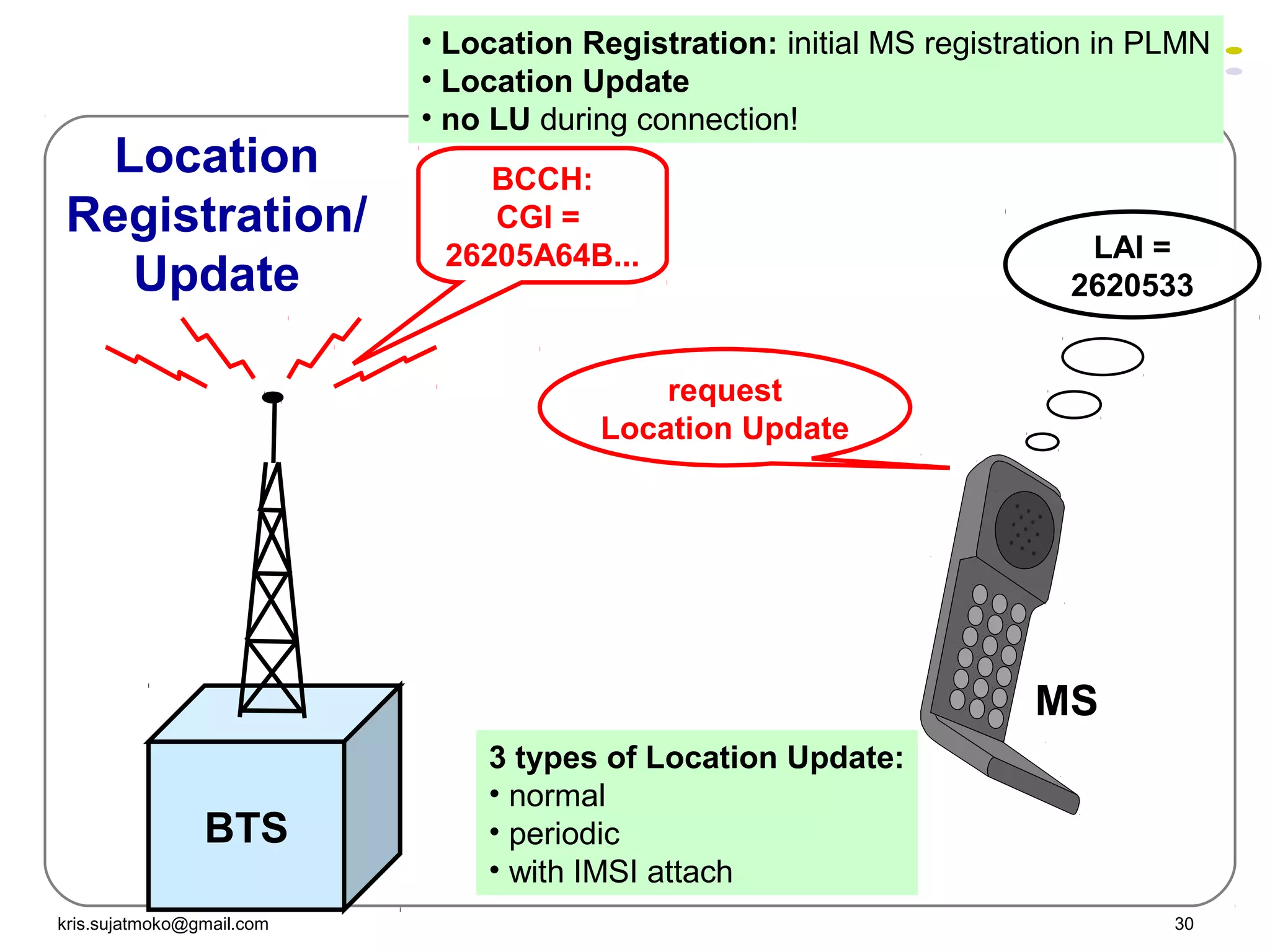
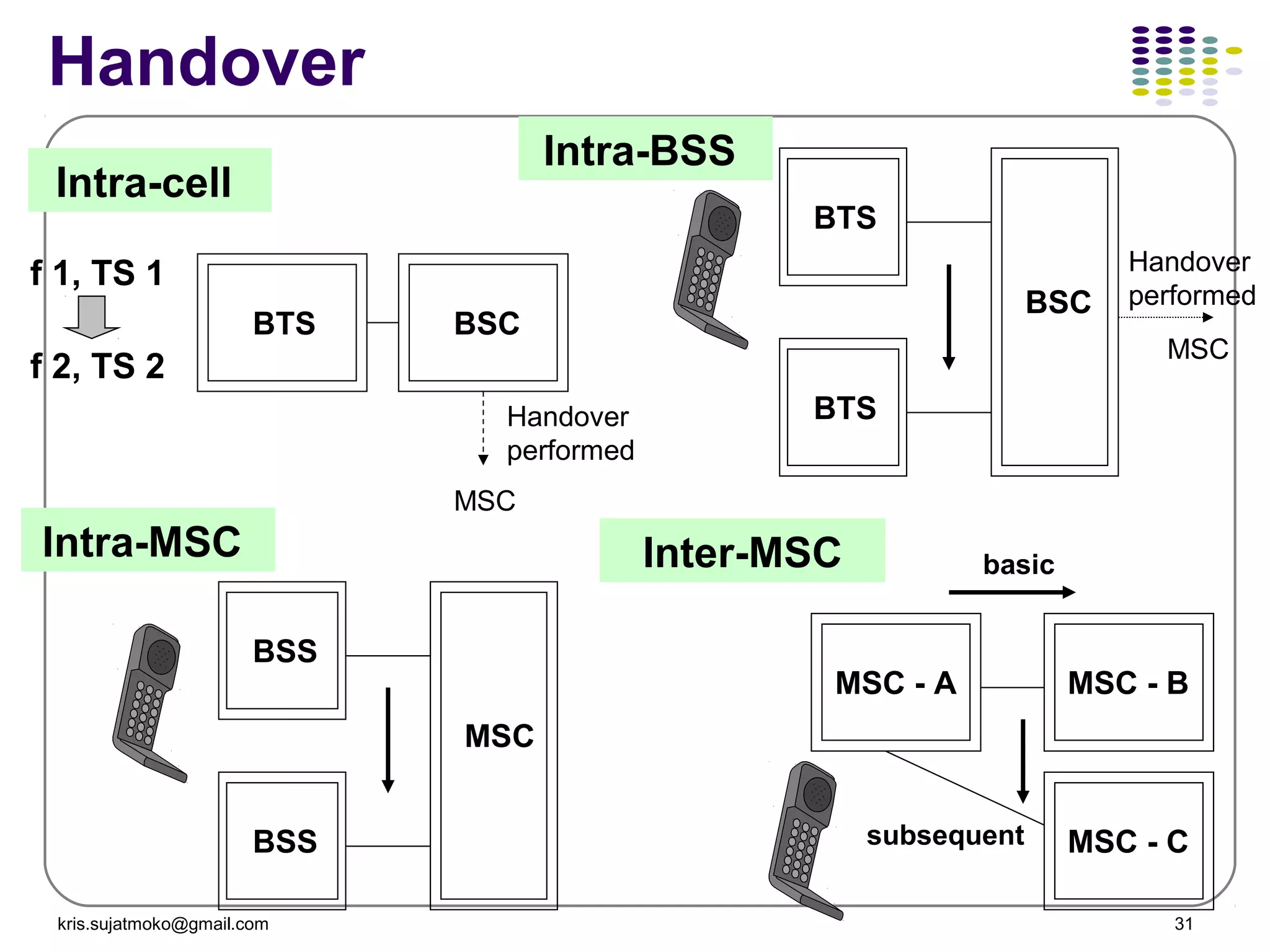
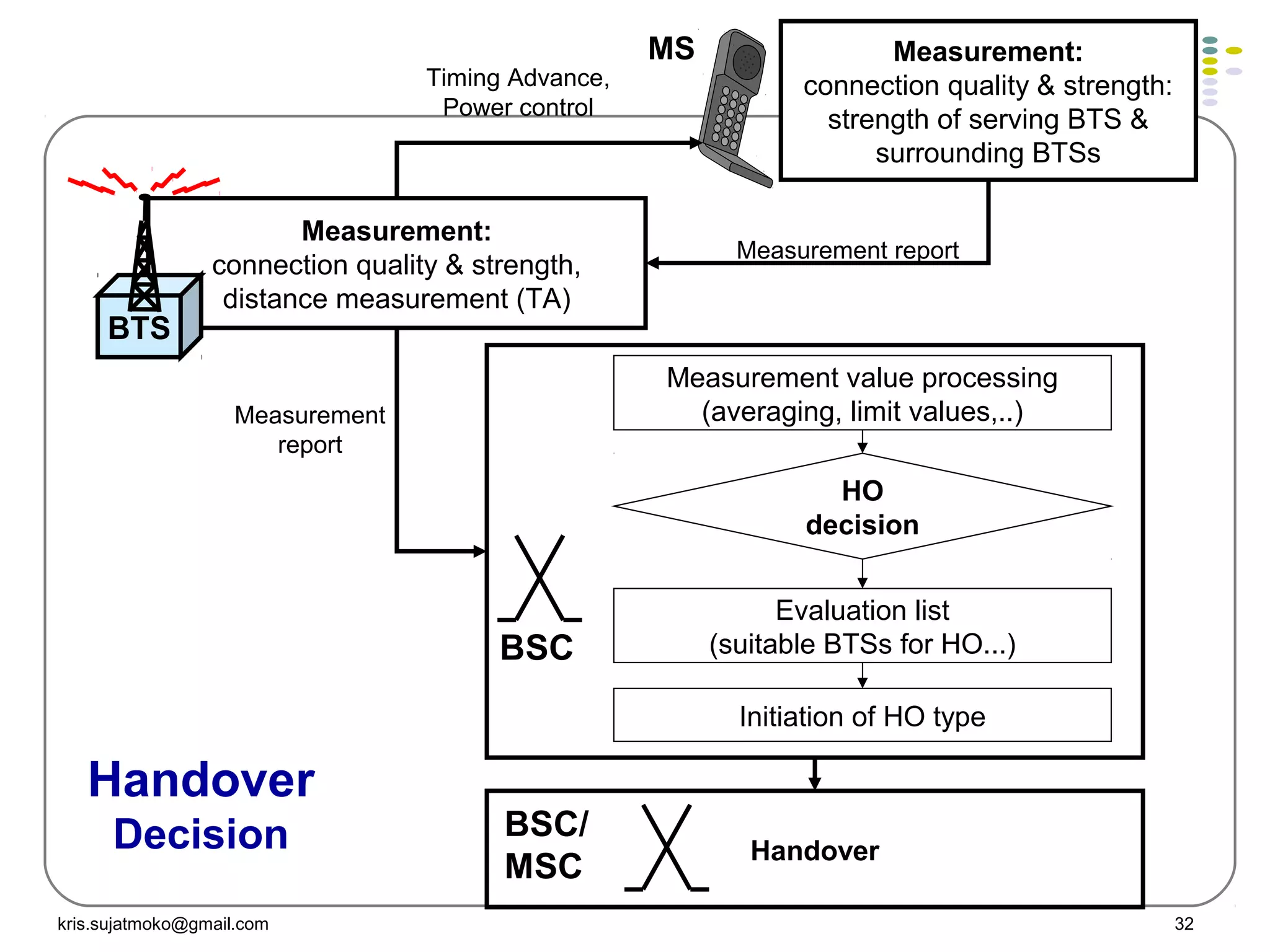
3. Location update and handover procedures which update the network on a mobile station's location area and allow calls to be maintained as a mobile station moves between cells.