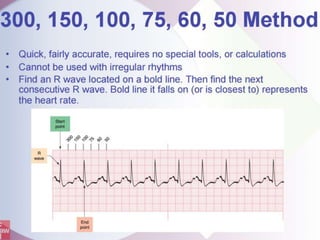
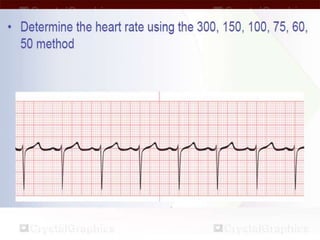
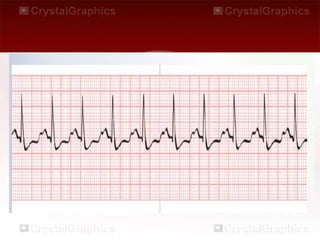
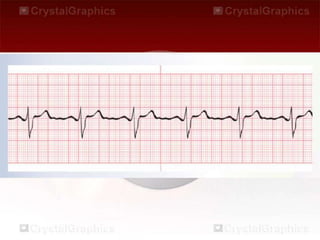
This document provides an overview of basic dysrhythmia interpretation and ECG analysis. It defines key aspects of the ECG waveform including the P wave, PR interval, and QRS complex. It describes methods for calculating heart rate and outlines the characteristics of normal sinus rhythm as well as various arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, premature ventricular contractions, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and different types of AV blocks. The document emphasizes the importance of consistently analyzing the ECG for rate, rhythm, P wave properties, and interval durations.