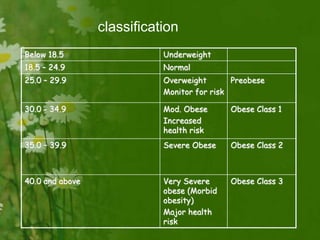
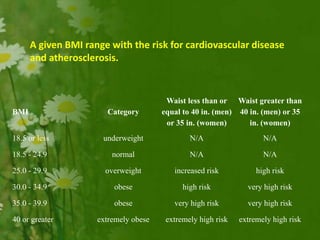
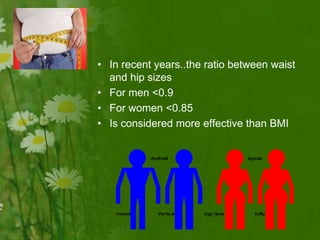
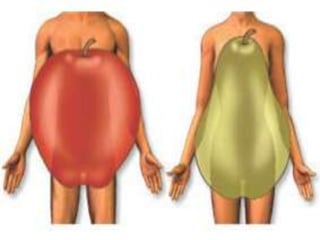
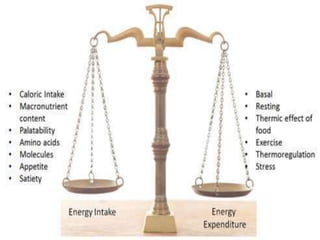
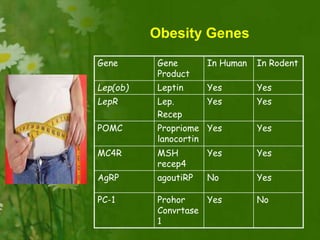
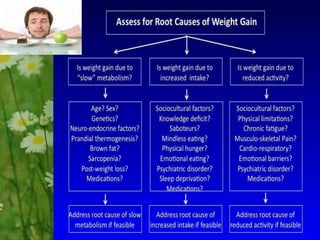
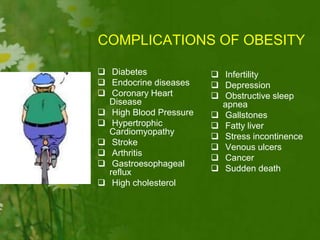
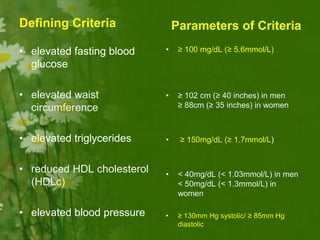
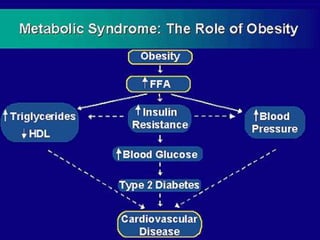
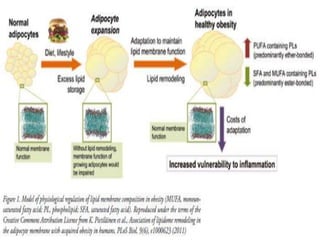
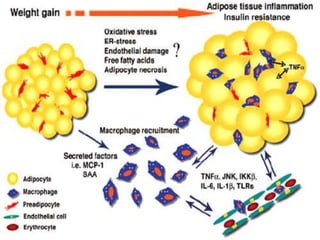
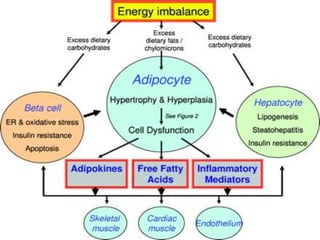
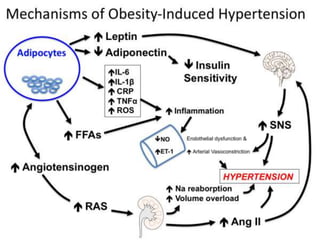
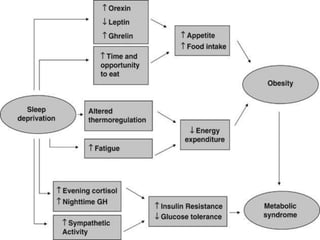
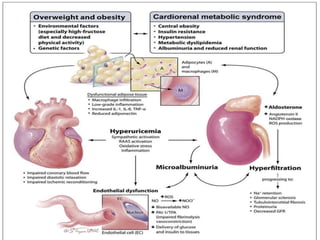
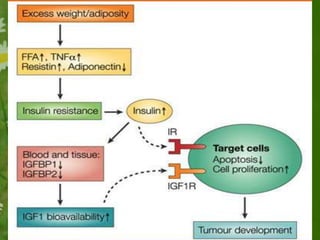
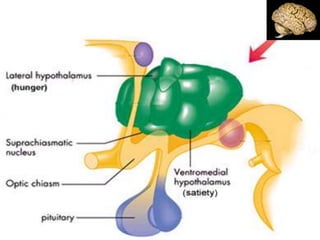
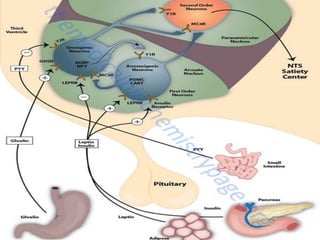
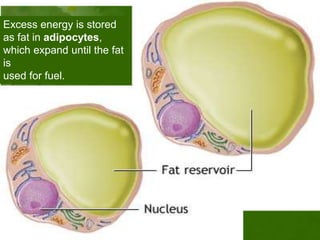
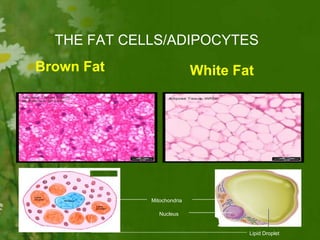
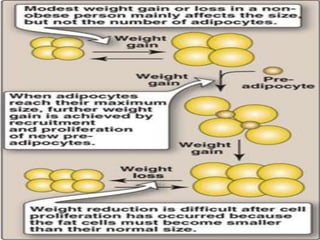
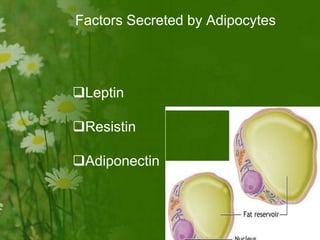
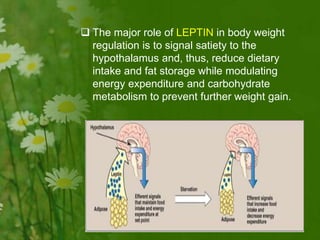
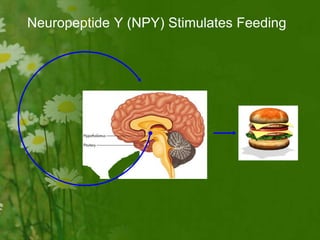
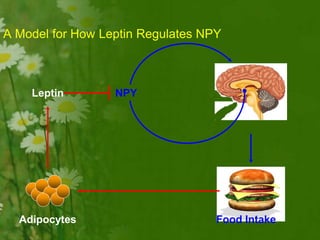
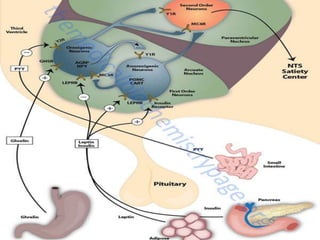
This document discusses metabolic consequences of obesity and the metabolic syndrome. It defines appetite, hormones that regulate hunger and satiety, and how excess calories are stored as fat. Factors secreted by fat cells like leptin, resistin, and adiponectin are described. Obesity is defined as BMI over 30 kg/m2 and methods for assessing obesity are provided. Genetic and environmental factors that can lead to obesity are listed, along with complications of obesity such as diabetes and heart disease. The metabolic syndrome is characterized as a clustering of risk factors including abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.








![BMI = (weight [kg]) / (height
[m])2.
Body mass index (BMI)
or Quetelet index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metabolicconsequencesofobesity-150902164547-lva1-app6892/85/Metabolic-consequences-of-obesity-19-320.jpg)