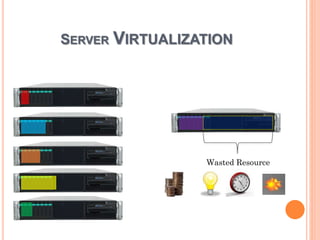
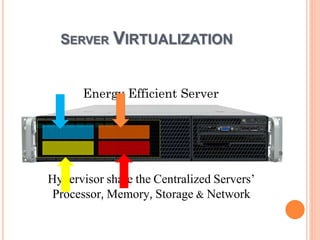
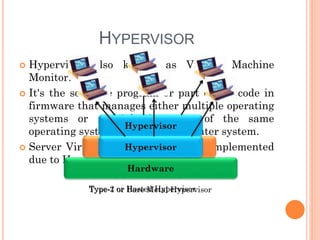
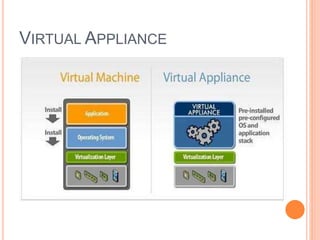
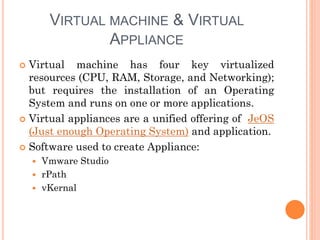
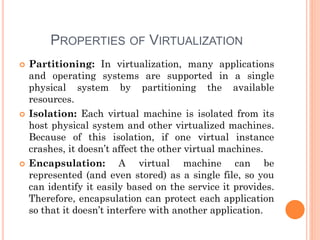
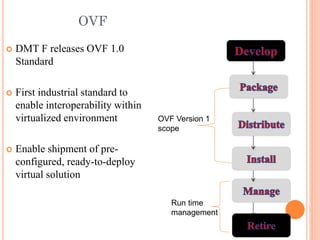
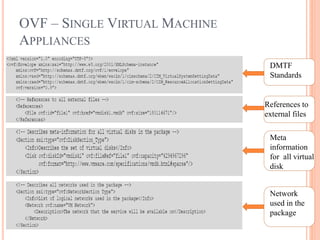
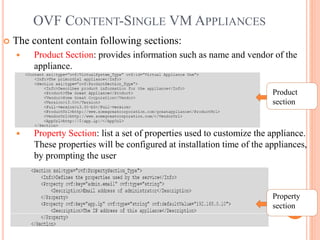
This document discusses virtualization and its role as the backbone of cloud computing. It defines virtualization as the creation of virtual versions of hardware platforms, operating systems, storage devices and network resources. The document outlines different types of virtualization including hardware/server virtualization, storage virtualization, network virtualization, and desktop virtualization. It describes how server virtualization works using hypervisors to divide physical servers into multiple virtual machines. The benefits of virtualization discussed include resource sharing, load balancing, easier backup and recovery, and scalability.