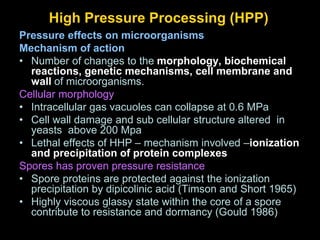
High Pressure Processing (HPP) involves subjecting foods to high pressures between 300-800 MPa for short periods of time to pasteurize foods without affecting their sensory qualities or significantly reducing their shelf life. HPP inactivates microorganisms and enzymes through changes to cellular structures and biochemical reactions. Properly applied HPP can reduce pathogens like Listeria and Salmonella by over 6 log while maintaining food quality and functional properties.