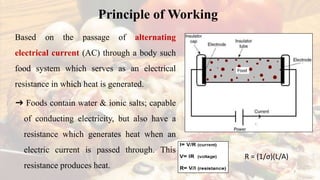
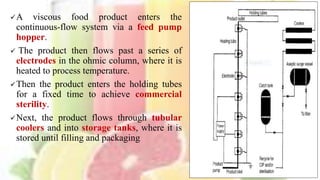
Ohmic heating is a method where alternating electric current passes through food, generating heat due to the food's electrical resistance, resulting in rapid and uniform heating. Initially used in the early 20th century for pasteurizing milk, its commercial applications have grown, particularly for high-value ready meals and sensitive liquid foods. The technology offers advantages such as reduced product damage, efficiency, and minimal nutrient loss, but faces challenges like complex conductivity relationships and regulatory approval for multi-phase food products.