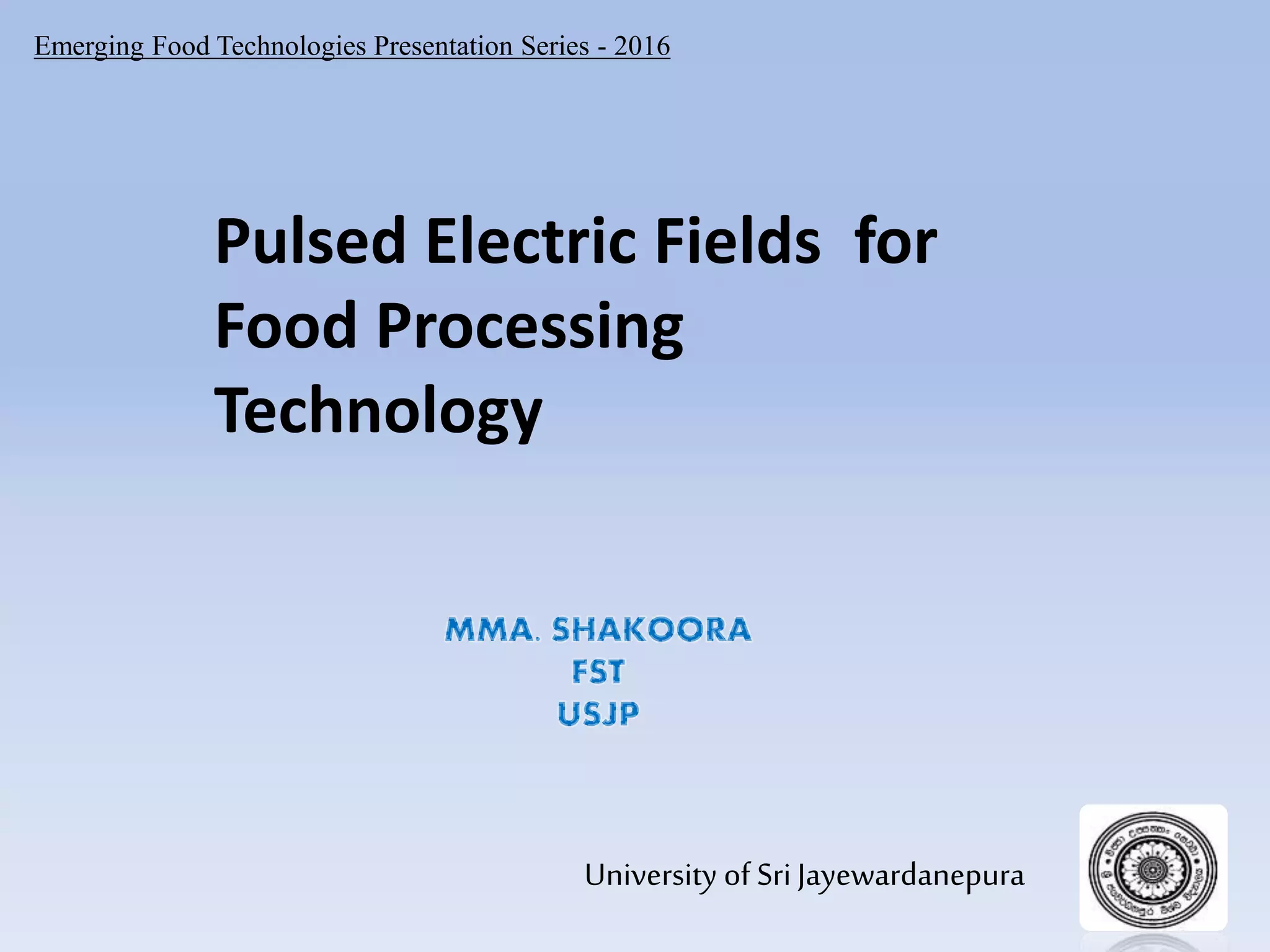
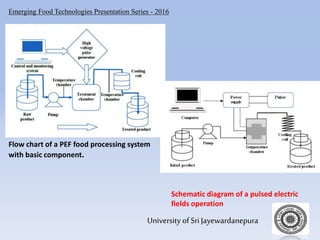
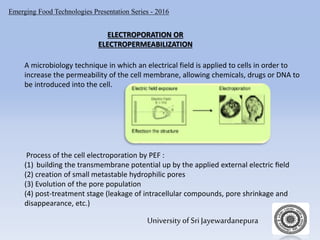
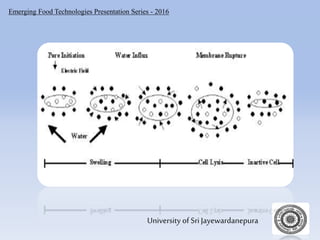
The document presents an overview of pulsed electric fields (PEF) as a non-thermal food preservation technology that enhances food quality and extends shelf life by inactivating microbial contaminants. It outlines the system components, principles, and factors influencing PEF treatment, detailing its advantages over traditional methods, such as better retention of sensory attributes and reduced thermal damage. Challenges include limited application to certain food products and the need for improved measurement and scaling for commercial use.