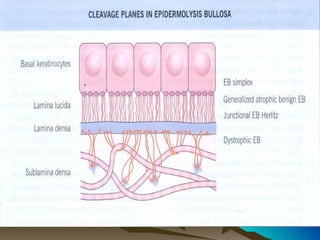
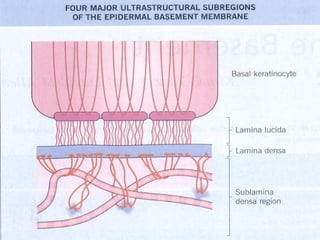
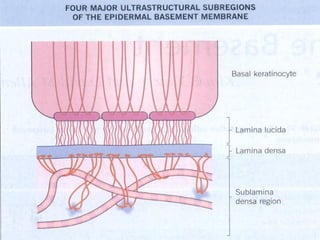
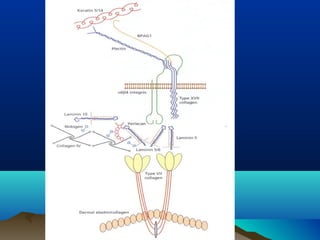
The dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ):
- Is the largest epithelial-mesenchymal junction, attaching the epidermis and papillary dermis.
- Consists of collagenous and non-collagenous molecules that provide a selective permeability barrier and structural foundation securing the epidermis.
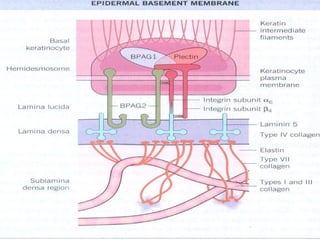
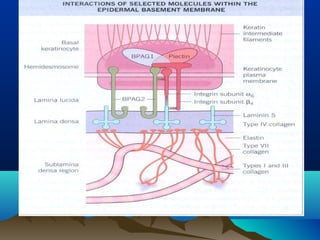
- Its main components are the basal plasma membrane, basement membrane with lamina lucida, densa and fibroreticularis layers, and hemidesmosomes which thickened the keratinocyte plasma membrane.








![• Lamina Lucida
–Anchoring filaments [fine
structure, oriented –
perpenticularly] max
corresponding to HD
–Weakest part of DEJ
• Lamina densa
–Electron dense layer
–Made up of collagen IV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-10-320.jpg)
![• Lamina fibro reticularis
–Anchoring fibrils [ curved structure]
•Can extend to upper part of
dermis/ lamina densa
•Also inserted to anchoring plaque
•Strongest tie for securing
epidermis to dermis
–Elastic micro fibrils [ fibrilin]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-11-320.jpg)

![•Intermediate filament
component
–Keratin 5 and Keratin
14
•Hemidesmosomal
plaque components
–BPAG1 [BP 230]
–Plectin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-14-320.jpg)


![• Lamina densa component
–Type IV collagen
–Nidogen [ entactin]
–Perlecan
• Anchoring fibril
components
–Type VIII collagen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-17-320.jpg)


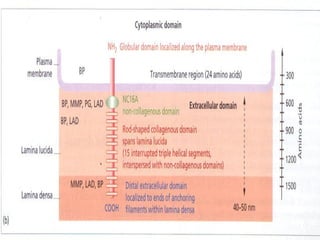
![BPAG2 [ 180Kda
• transmembrane collagen[17]
• Intracellular / extracellular part
• Collagenous / non collagenous
domain
• NC-16A – immunodominant
epitope](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-21-320.jpg)
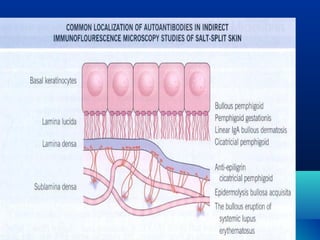
![Autoantibodies
–Bullous pemphigoid
–Cicatricial pemphigoid
–Pemphigoid gestationis
–Linear IgA bullous dermatosis
Mutation –
– Junctional epidermolysis bullosa [
Non- Herlitz type]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-23-320.jpg)
![•Integrin
–Heterodimeric transmembrane
glycoprotein [α , β]
–Promote cell – cell and cell
matrix interaction
–Mutation – junctional EB with
pyloric atresia
–Auto antibody – ocular CP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-24-320.jpg)
![• Laminins
–Hetero trimeric glycoprotein [αβγ]
–Structural component of extra
cellular matrix stabilized by
interchain disulphide bonds
–Laminin 1 - α1β1γ1
–Laminin 5 - α 3 β3 γ2
–Auto antibody – anti epiligrin CP
–Mutation - Junctional EB herlitz
type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-26-320.jpg)

![•Collagen IV
–Main constituent of lamina densa
–2 polypeptide [α1 and α2]
–Large C terminal globular domain
–Aminoterminal at the other end
–Bind covalently at amino terminal to
form tetramers or spiders
–Point of overlap is referred to as 7s
domain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-28-320.jpg)
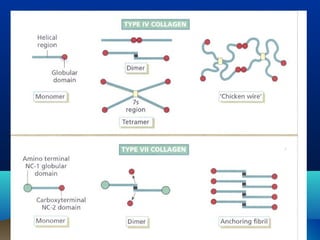
![•Nidogen
–150 Kda glycoprotein
–Stabilizer of basement membrane,
binding to Type IV collagen, perlecan
and laminin
• Perlecan [ Heparan sulphate
proteoglycan]
–Stabilizer of basement membrane
–Help for turn over and synthesis of
basement membrane](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-30-320.jpg)
![Target common to autoimmune andTarget common to autoimmune and
inherited blistering diseasesinherited blistering diseases
Protein
target
Auto immune
disease
Genetic disease
1 Plectin EB asso. Muscle
dystrophy
2 BPAG1 BP EB [Non-Herlitz]
3 BPAG2 BP, PG, CP, LABD
4 Laminin – 5 Antiepiligrin CP Junctional EB [ Herlitz]
5 α6 β4 integrin Ocular CP Junctional EB with
pyloric atresia
6 Type VII
collagen
EB acquisita
Bullous SLE
Dystrophic EB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dejblue-171111091837/85/Dermo-epidermal-junction-32-320.jpg)