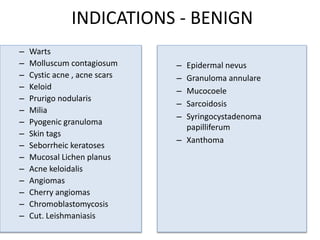
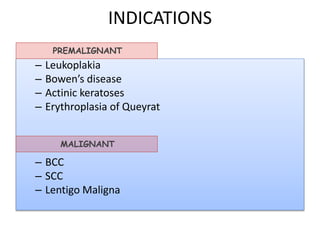
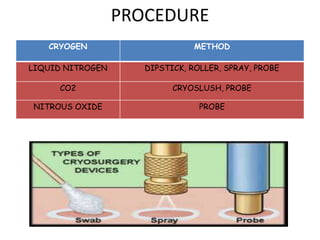
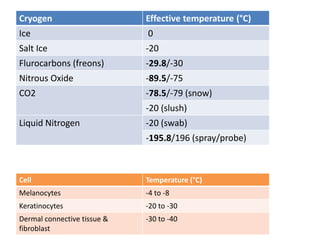
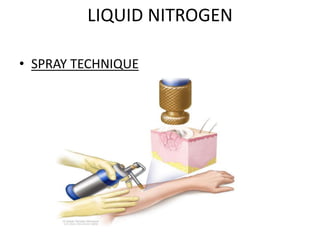
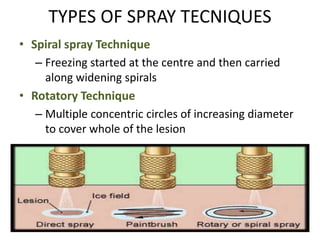
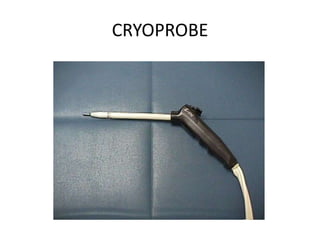
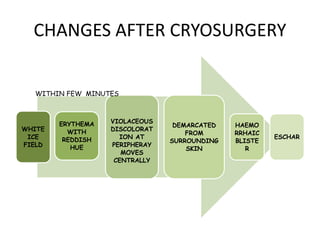
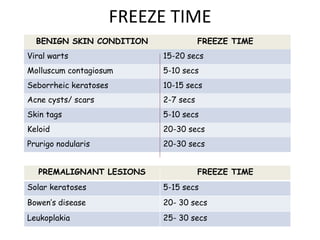
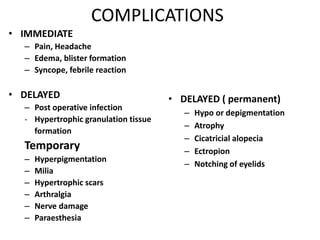
The document outlines various cryotherapy techniques for treating skin conditions, including benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions. It details indications, contraindications, methods of application such as liquid nitrogen, cryoprobes, and complications associated with treatment. It also discusses post-procedure care and the advantages and disadvantages of cryotherapy as a treatment modality.