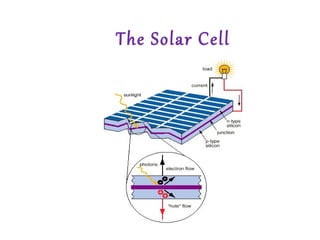
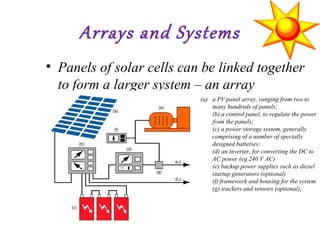
Solar cells convert sunlight directly into electricity through a process where photons knock electrons loose from semiconductor materials like silicon. The electrons then flow as a current that can be drawn off the top and bottom contacts of the solar cell to be used as power. Solar cells provide renewable and sustainable power for applications from small electronics to large solar panel arrays. They are particularly useful for powering remote devices without access to electricity grids. The most efficient solar cells are made from single crystalline silicon, with efficiencies up to 25%, while thin film technologies continue advancing toward flexible solar cells and improved efficiency.