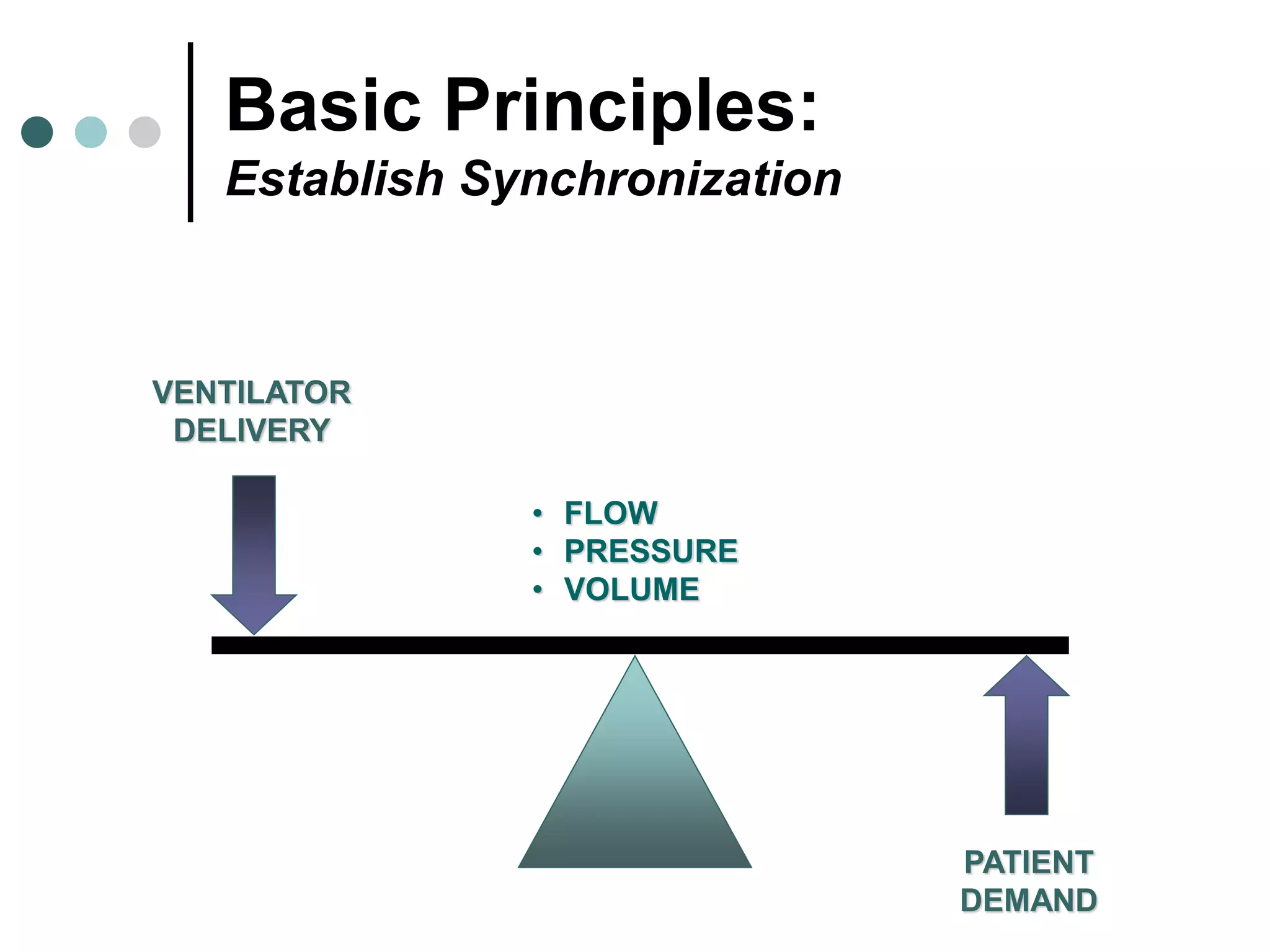
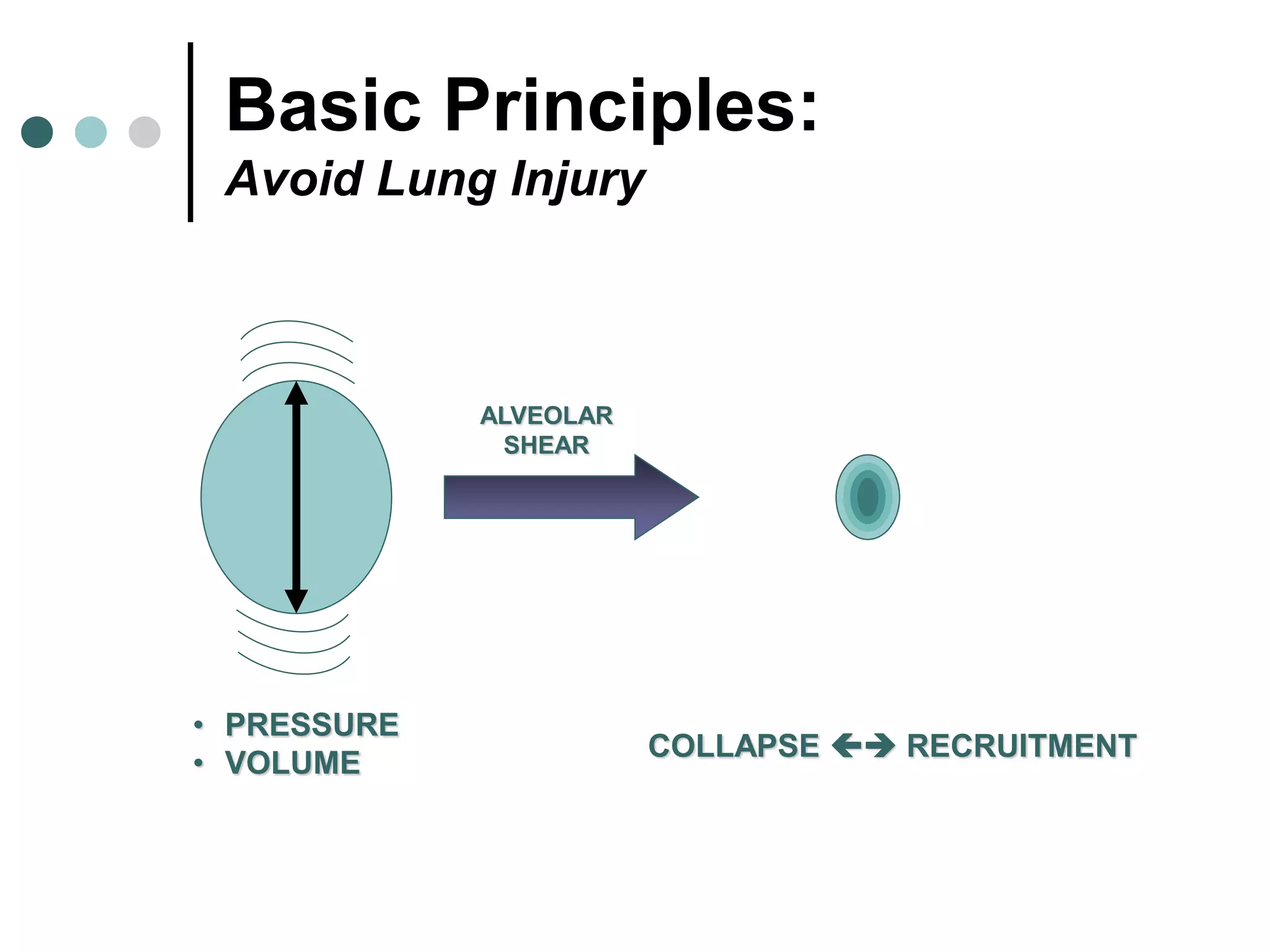
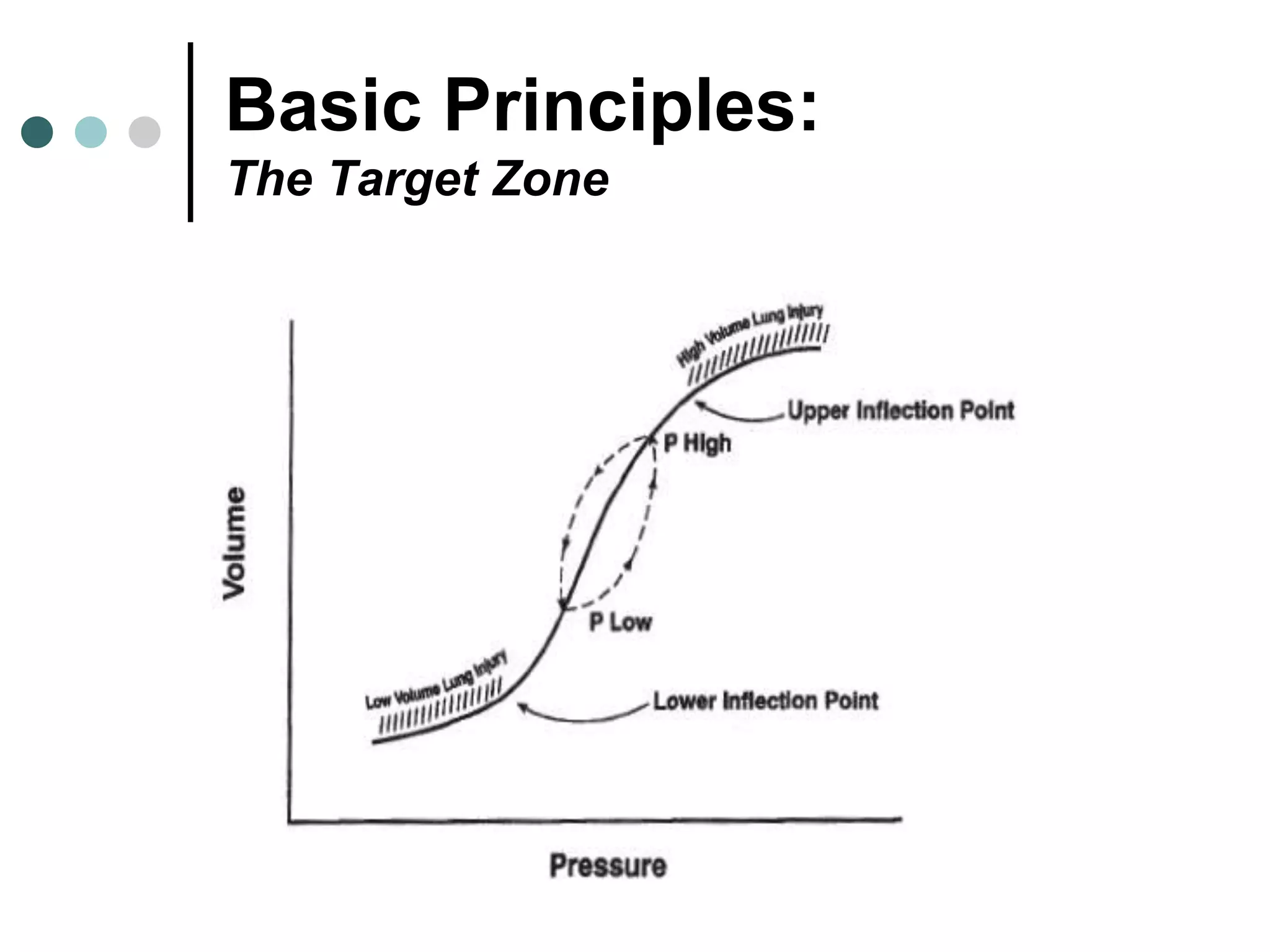
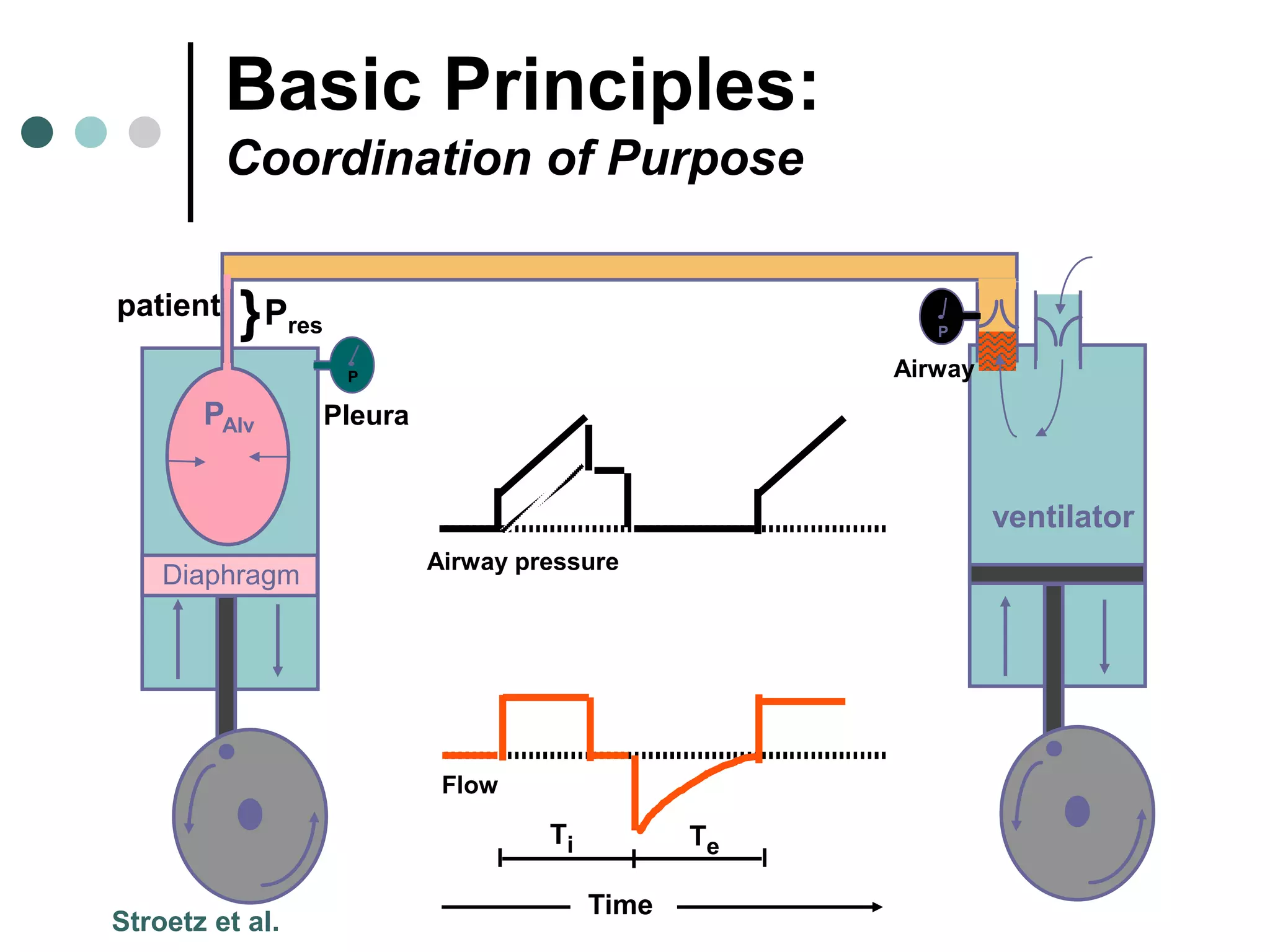
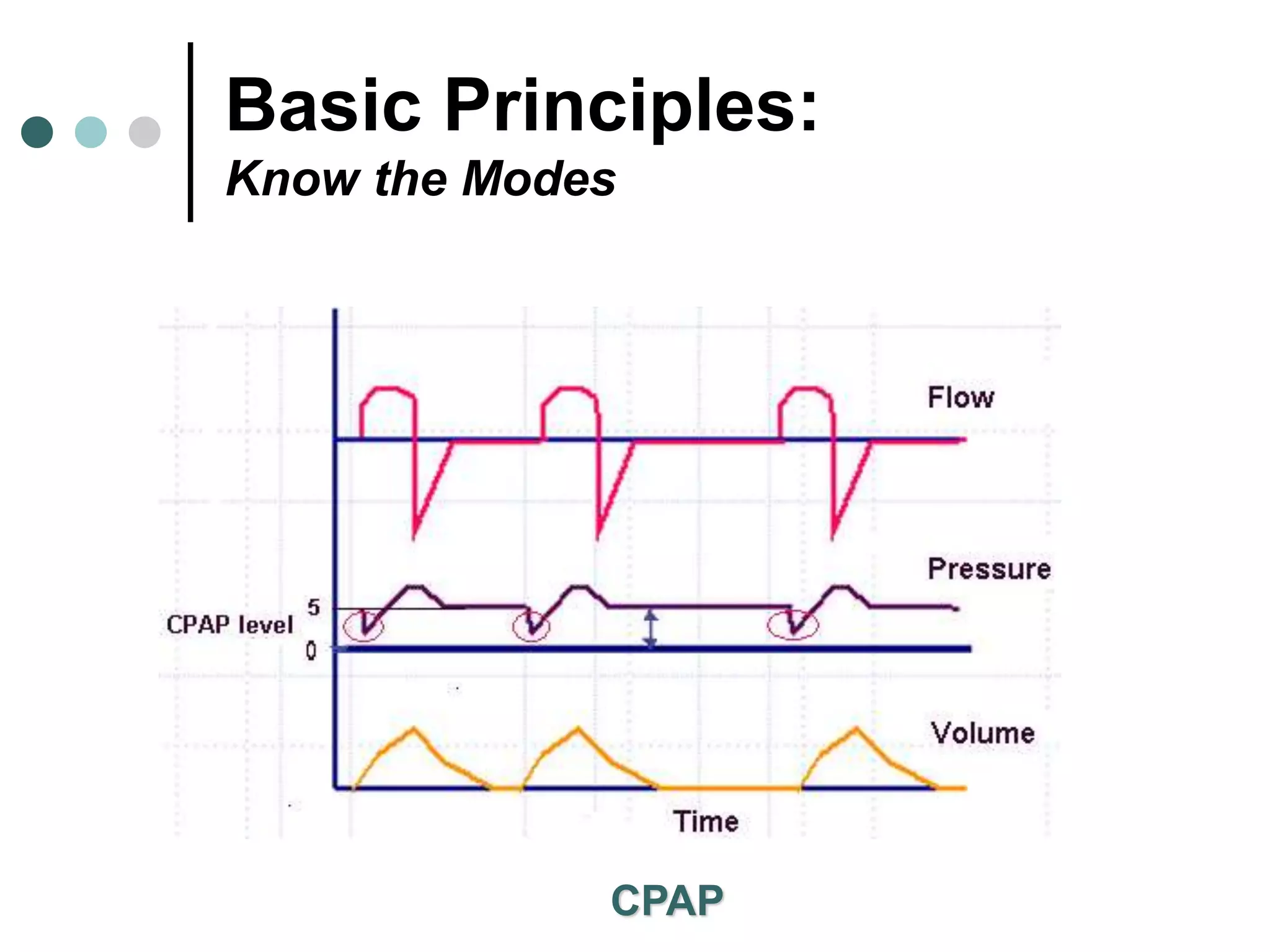
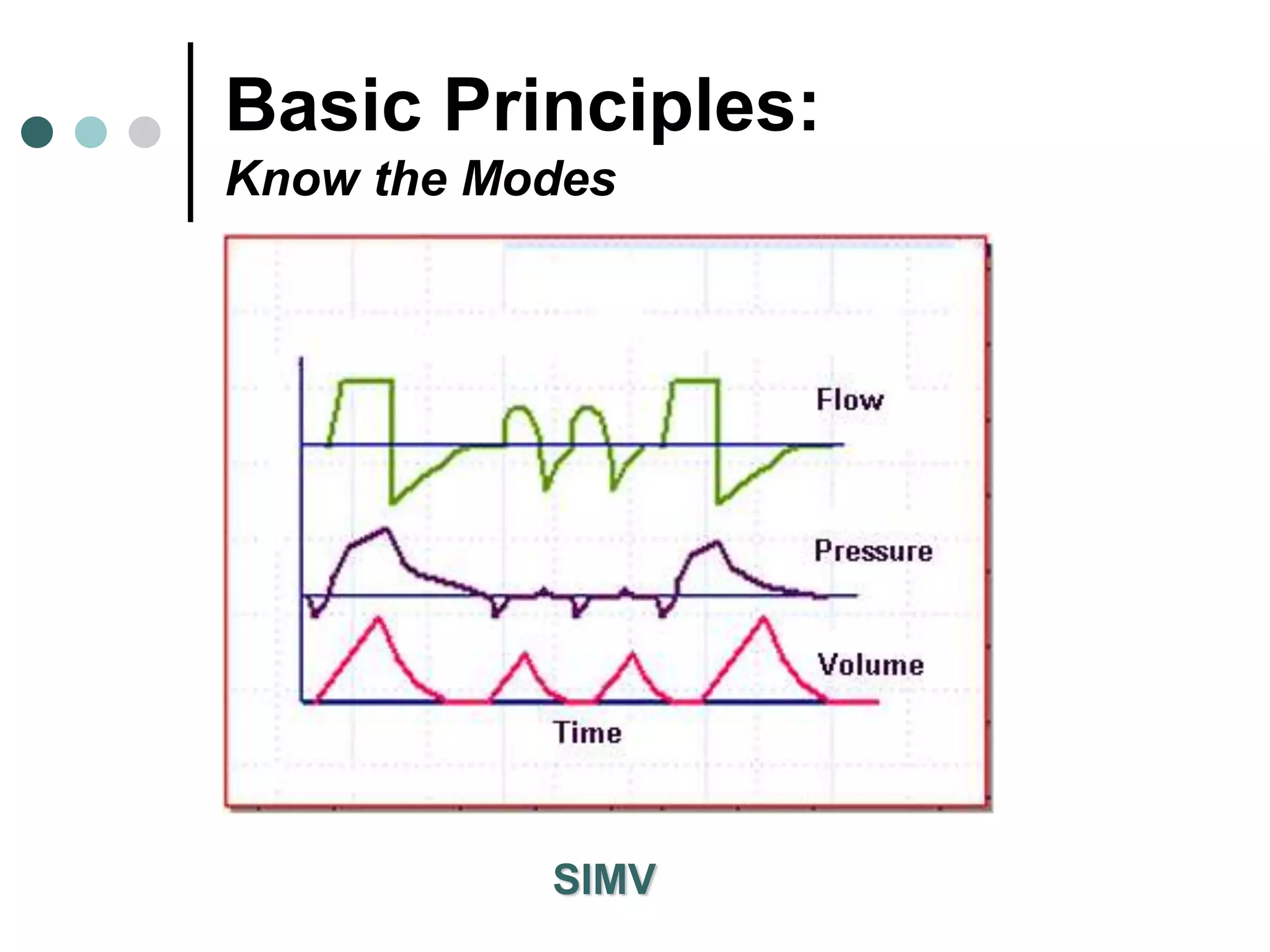
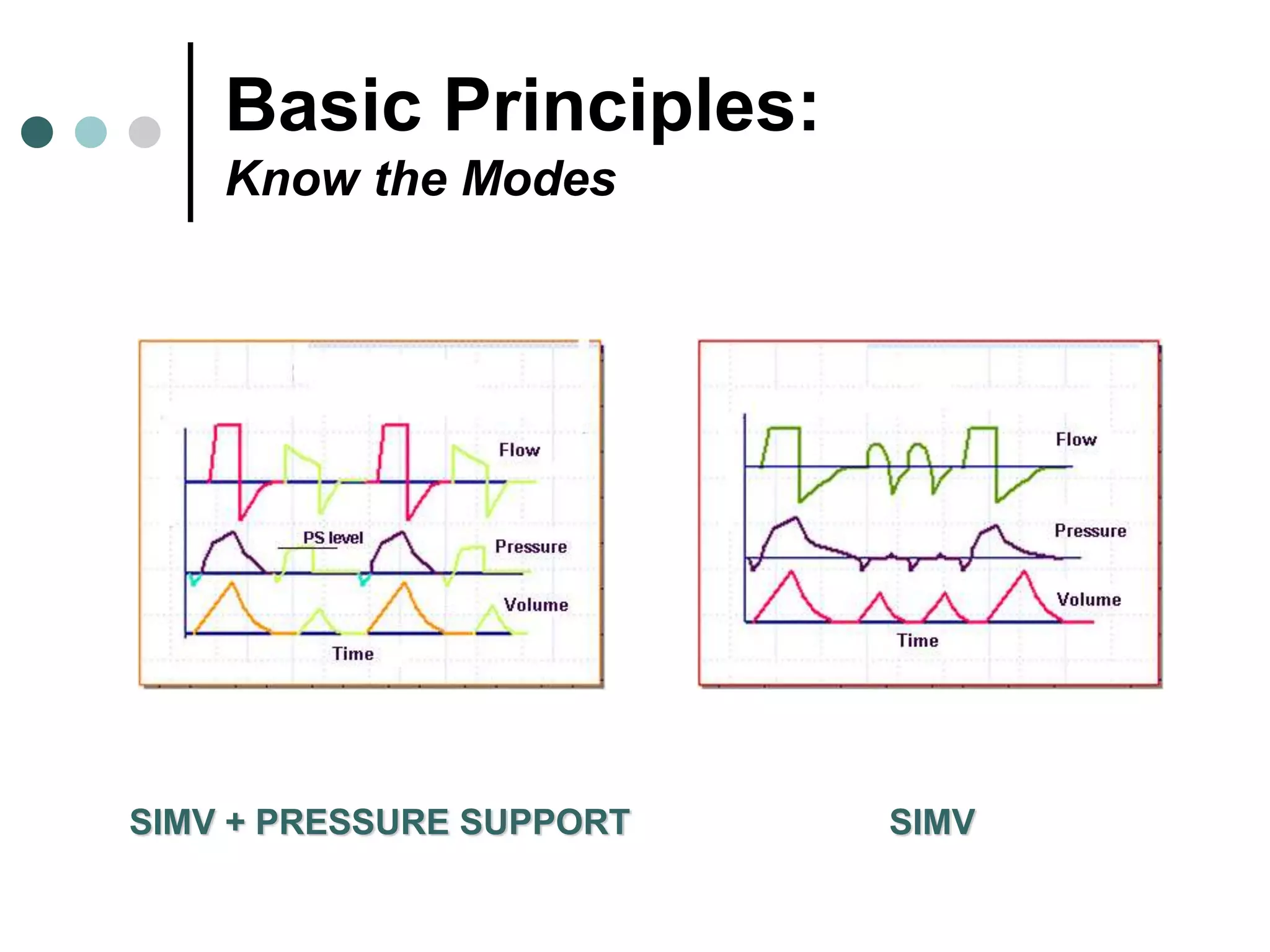
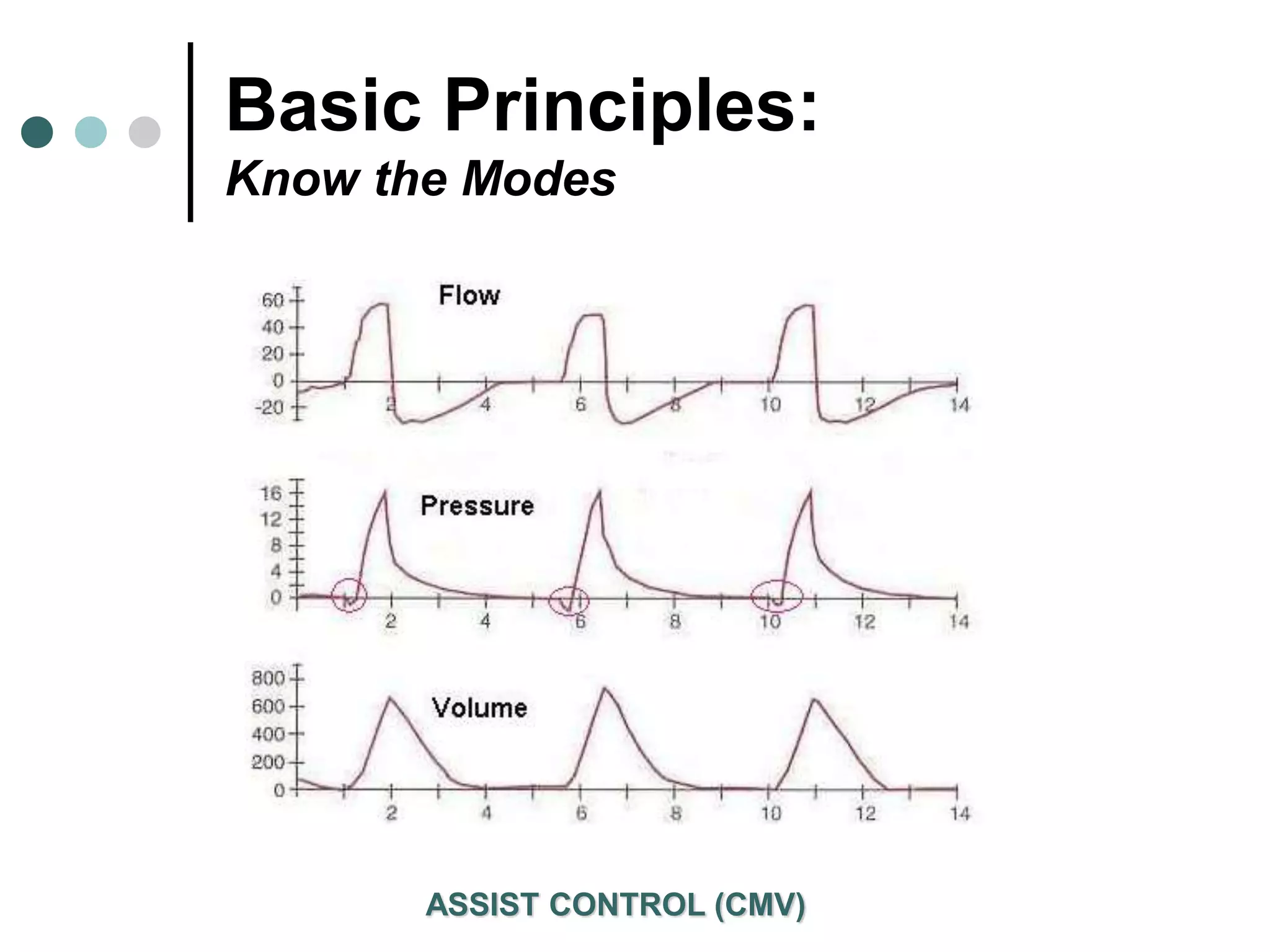
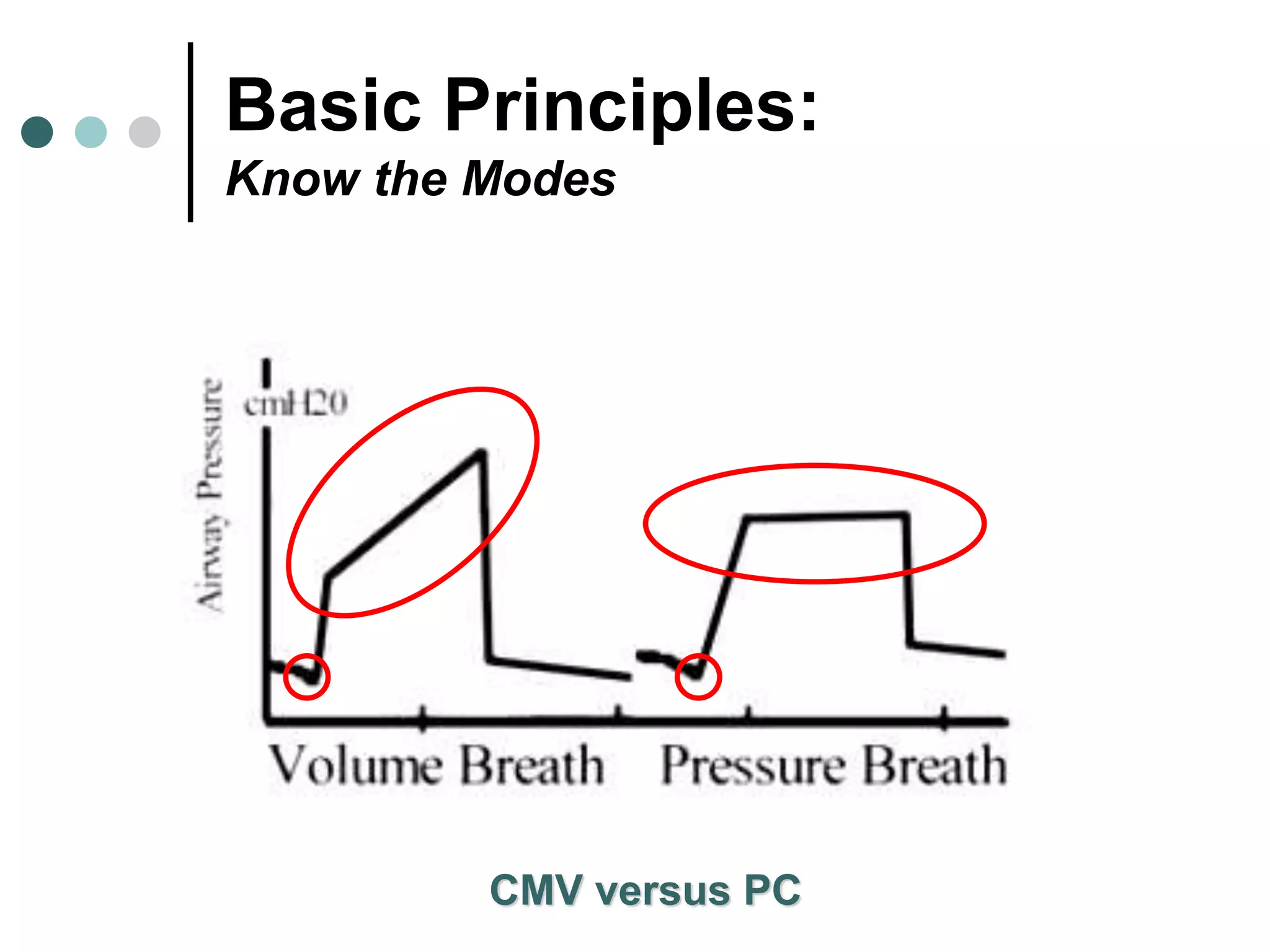
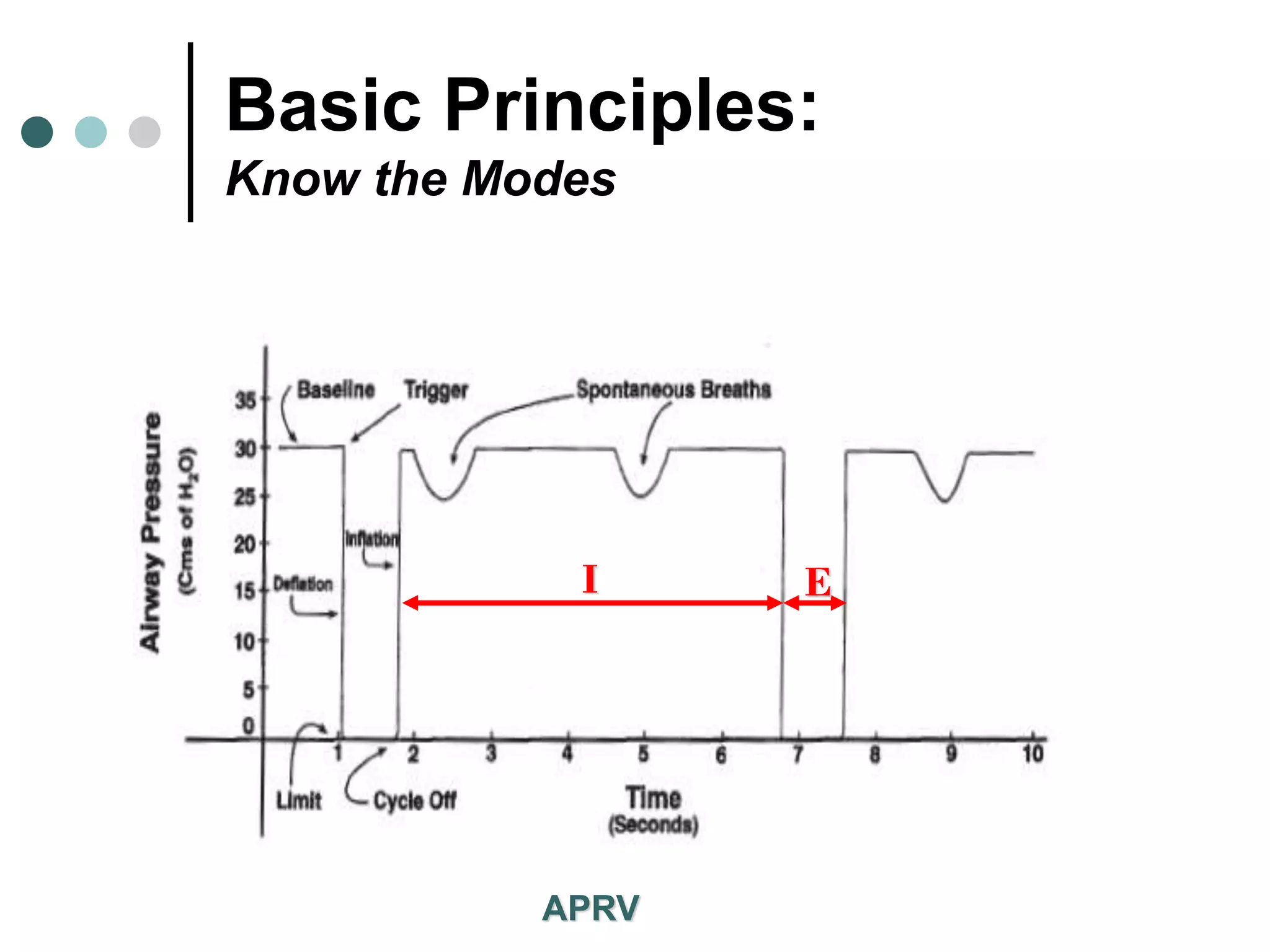
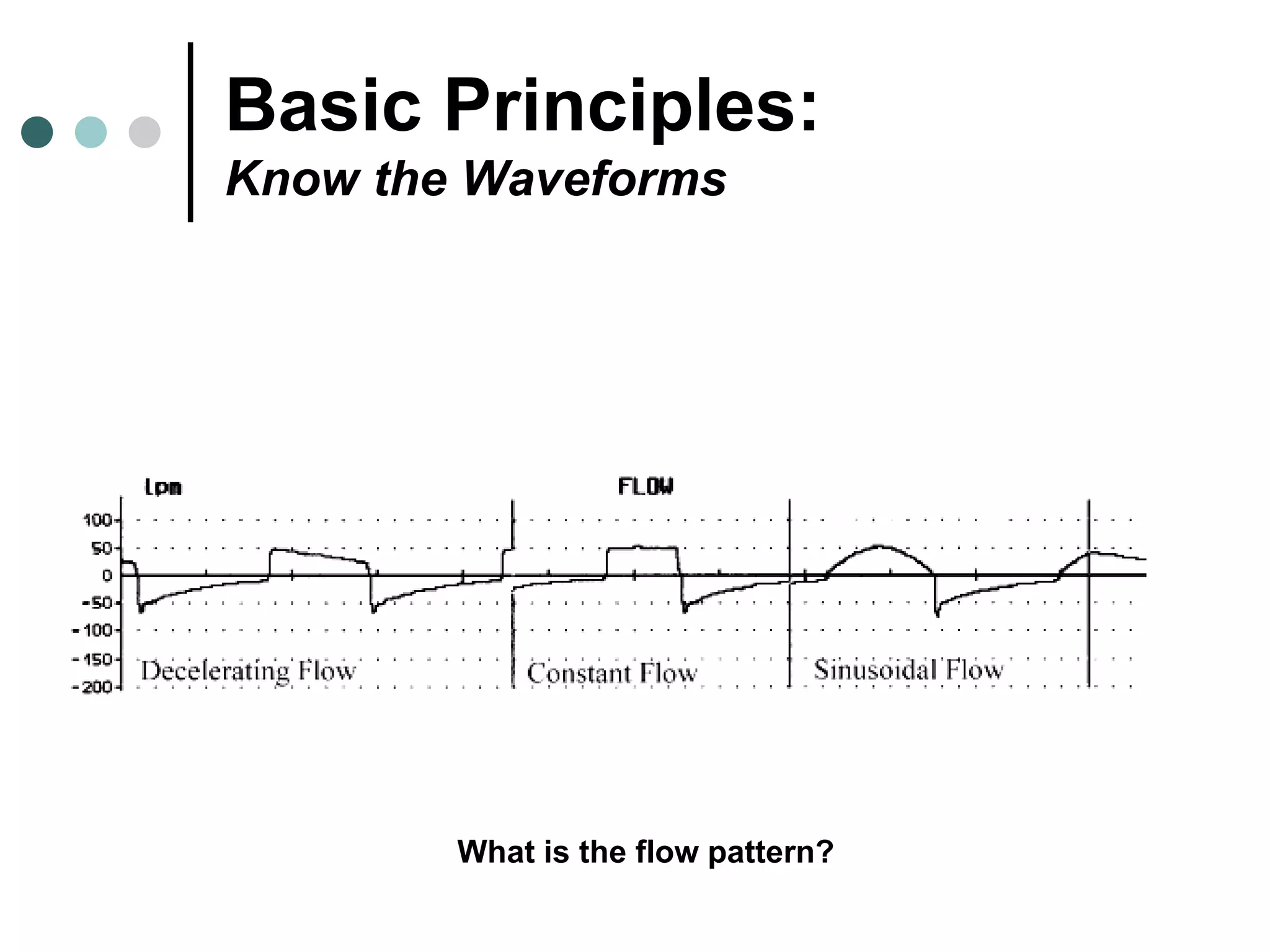
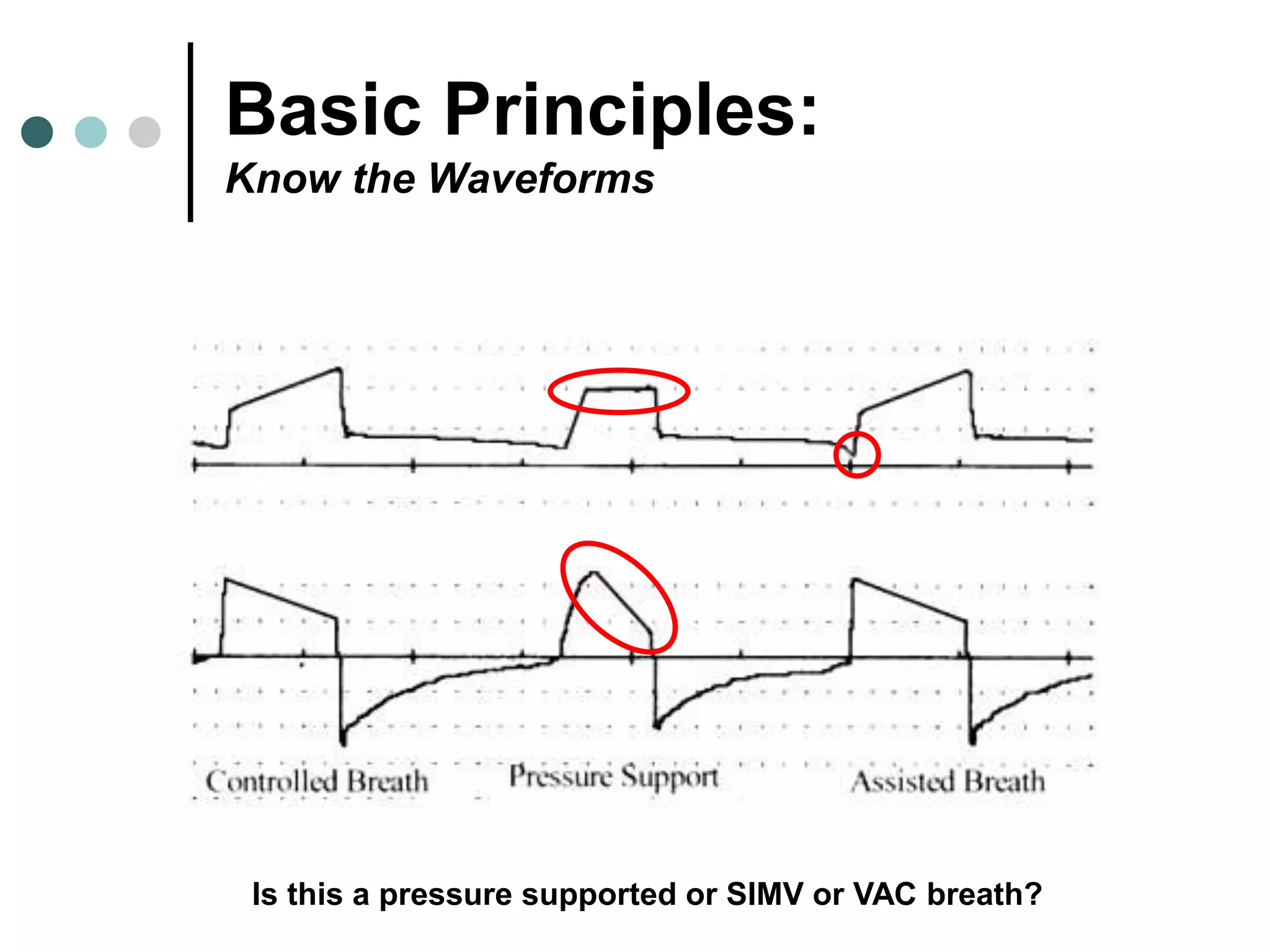
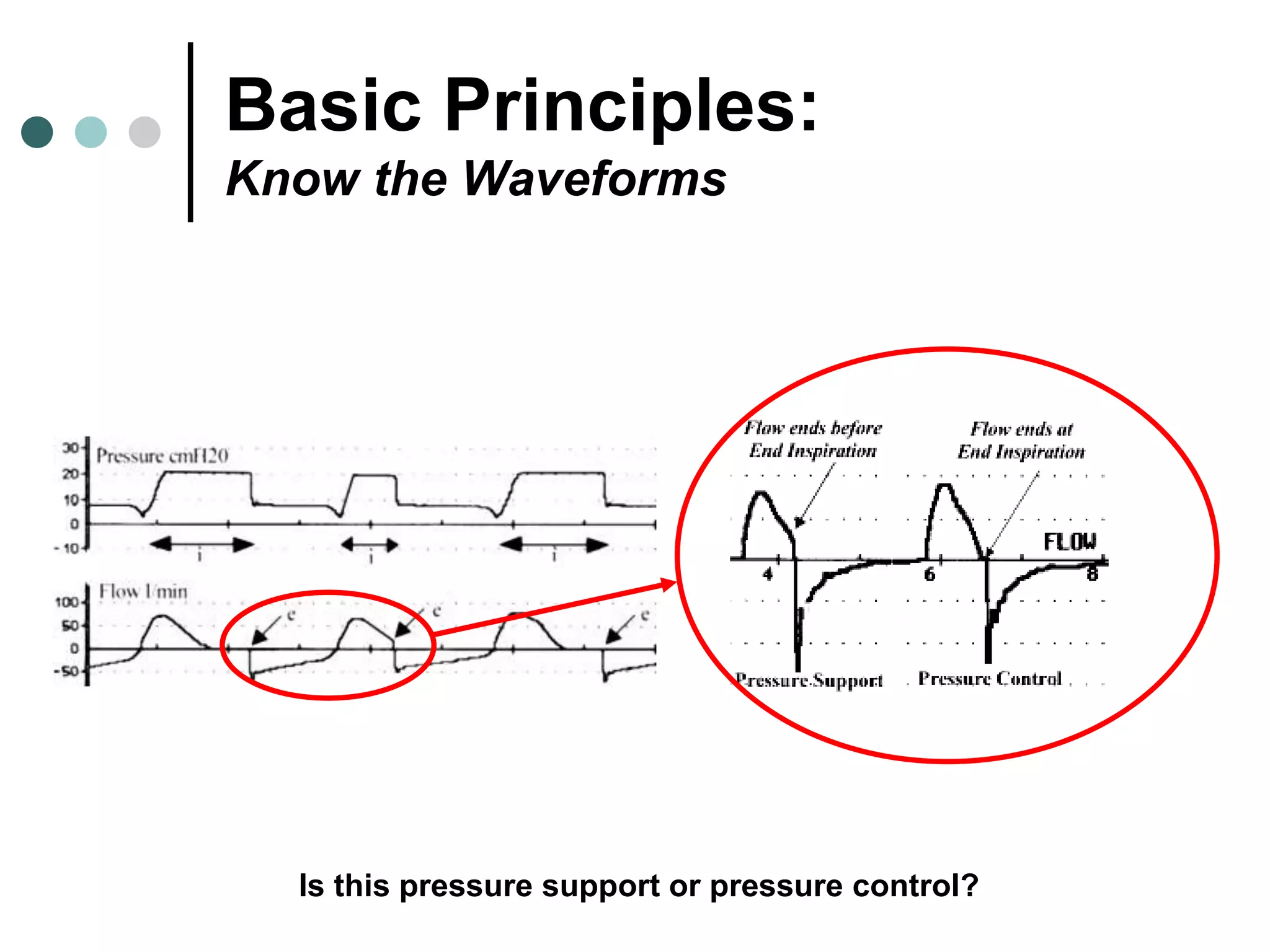
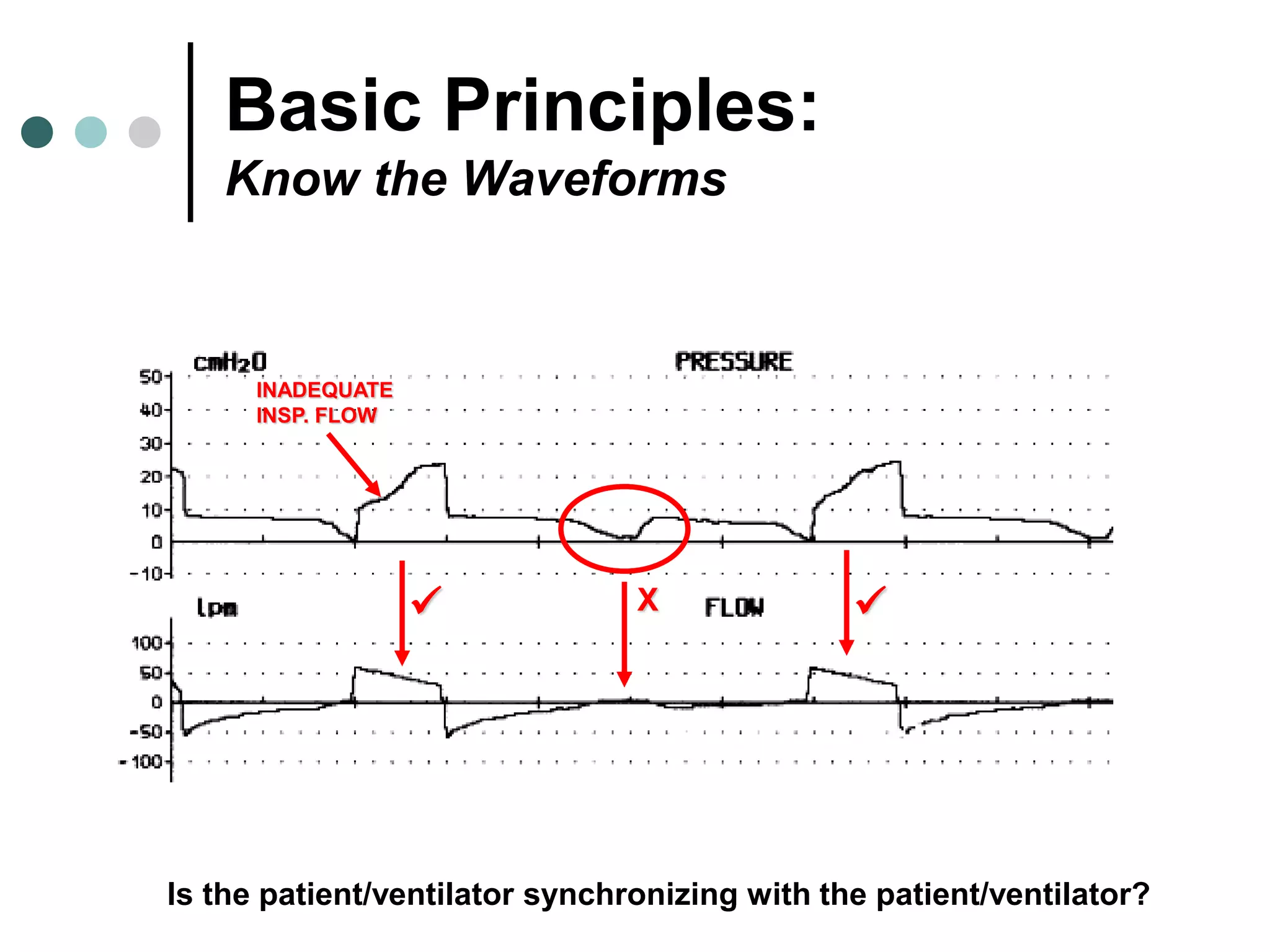
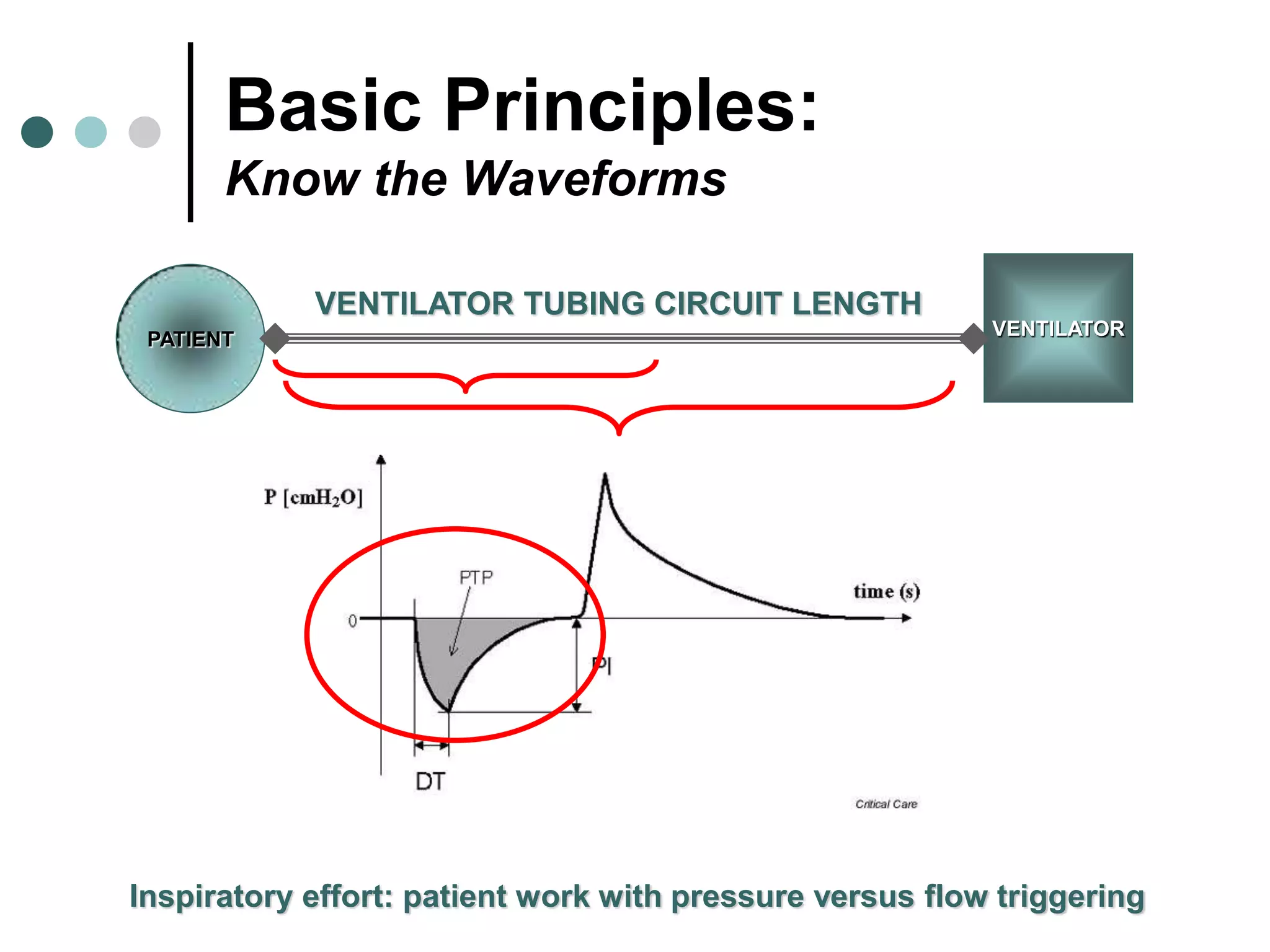
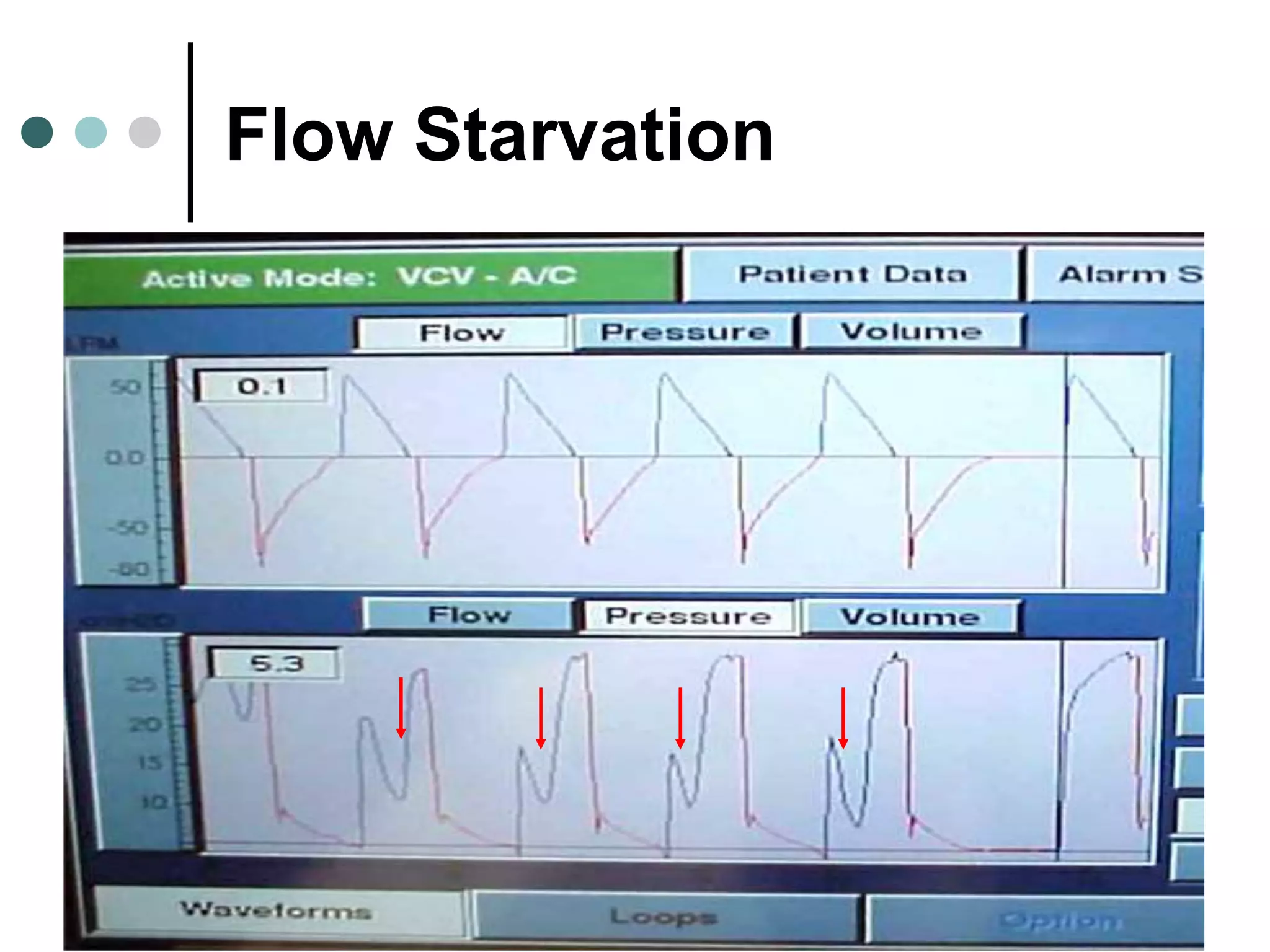
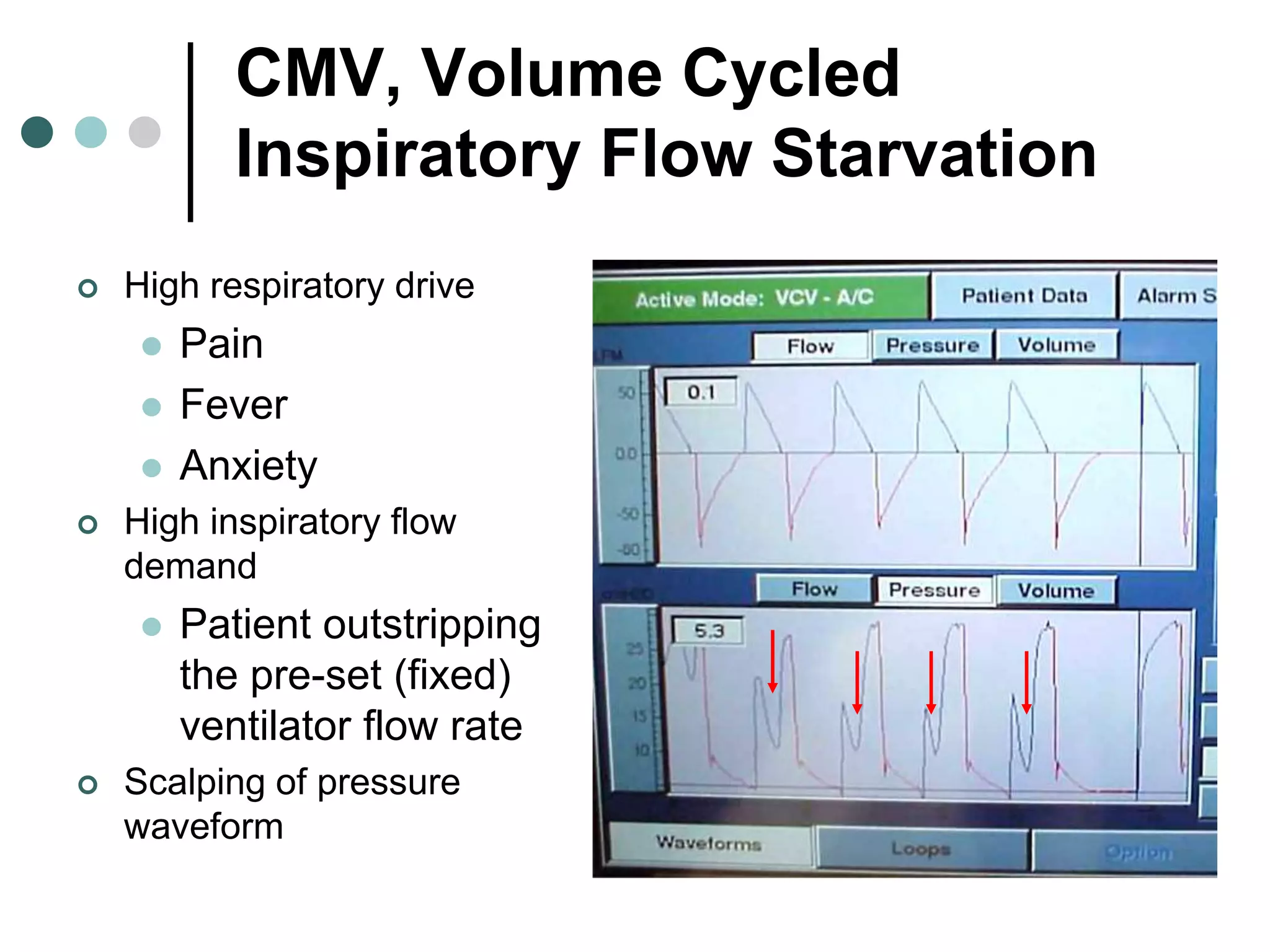
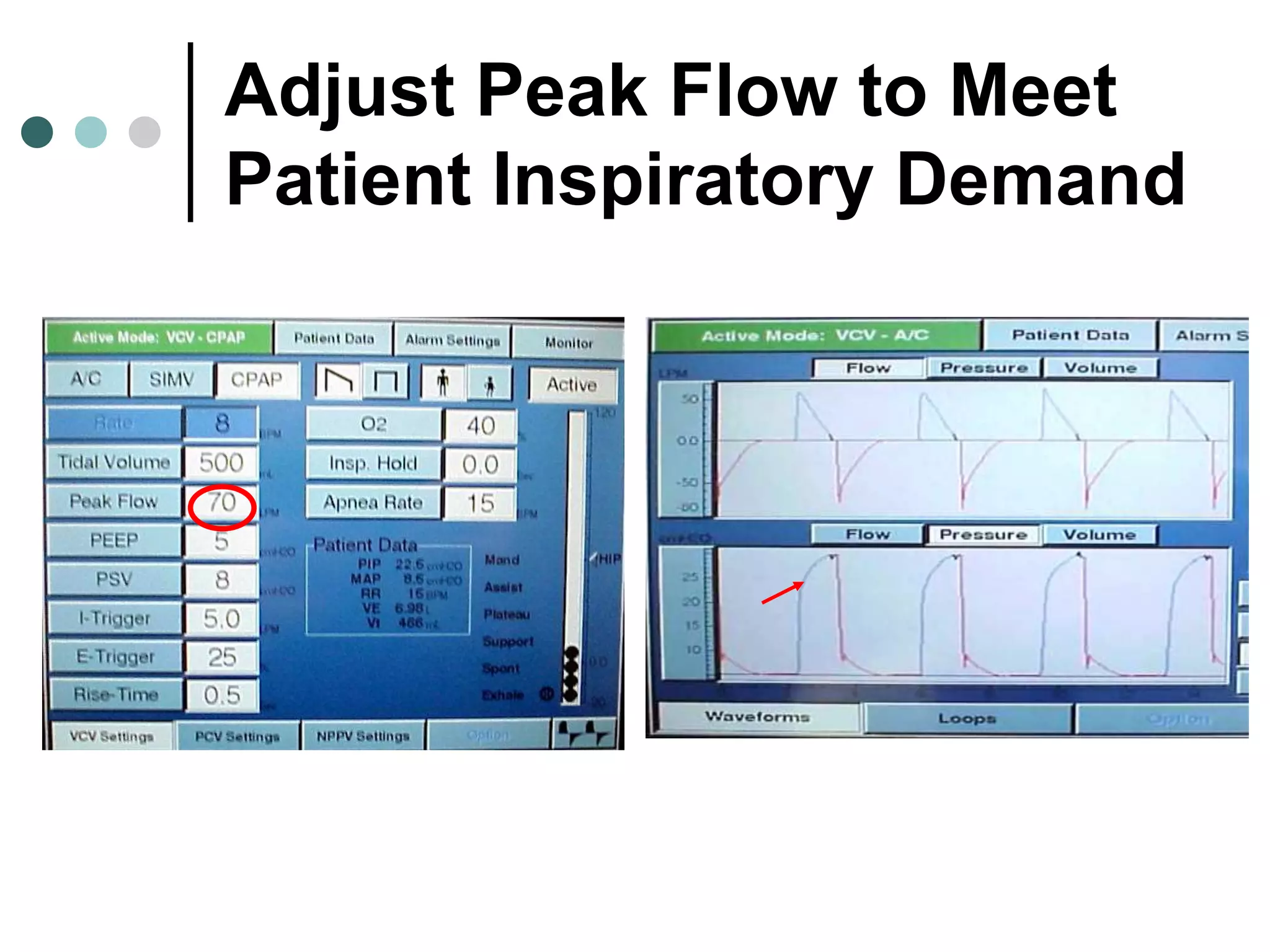
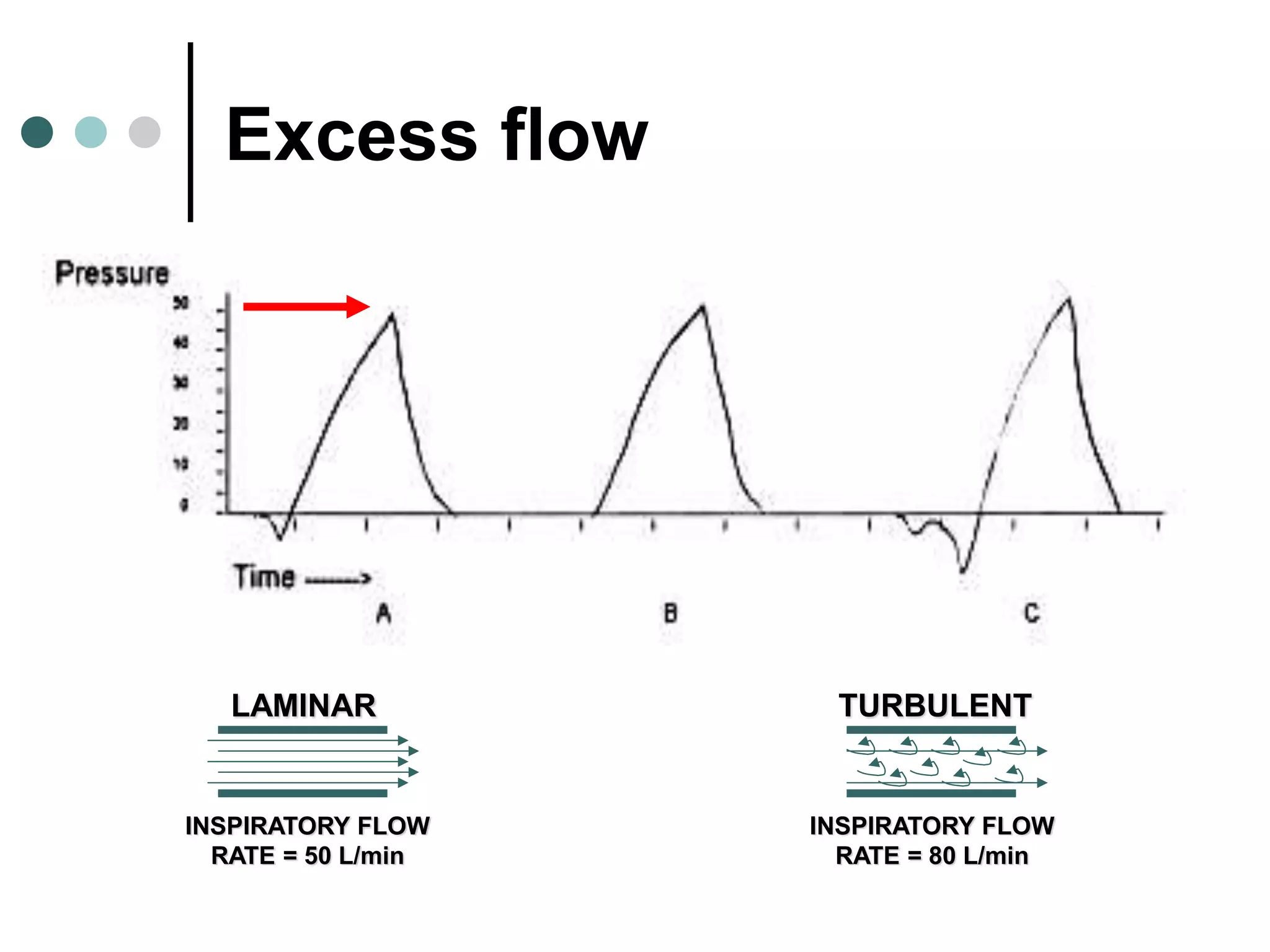
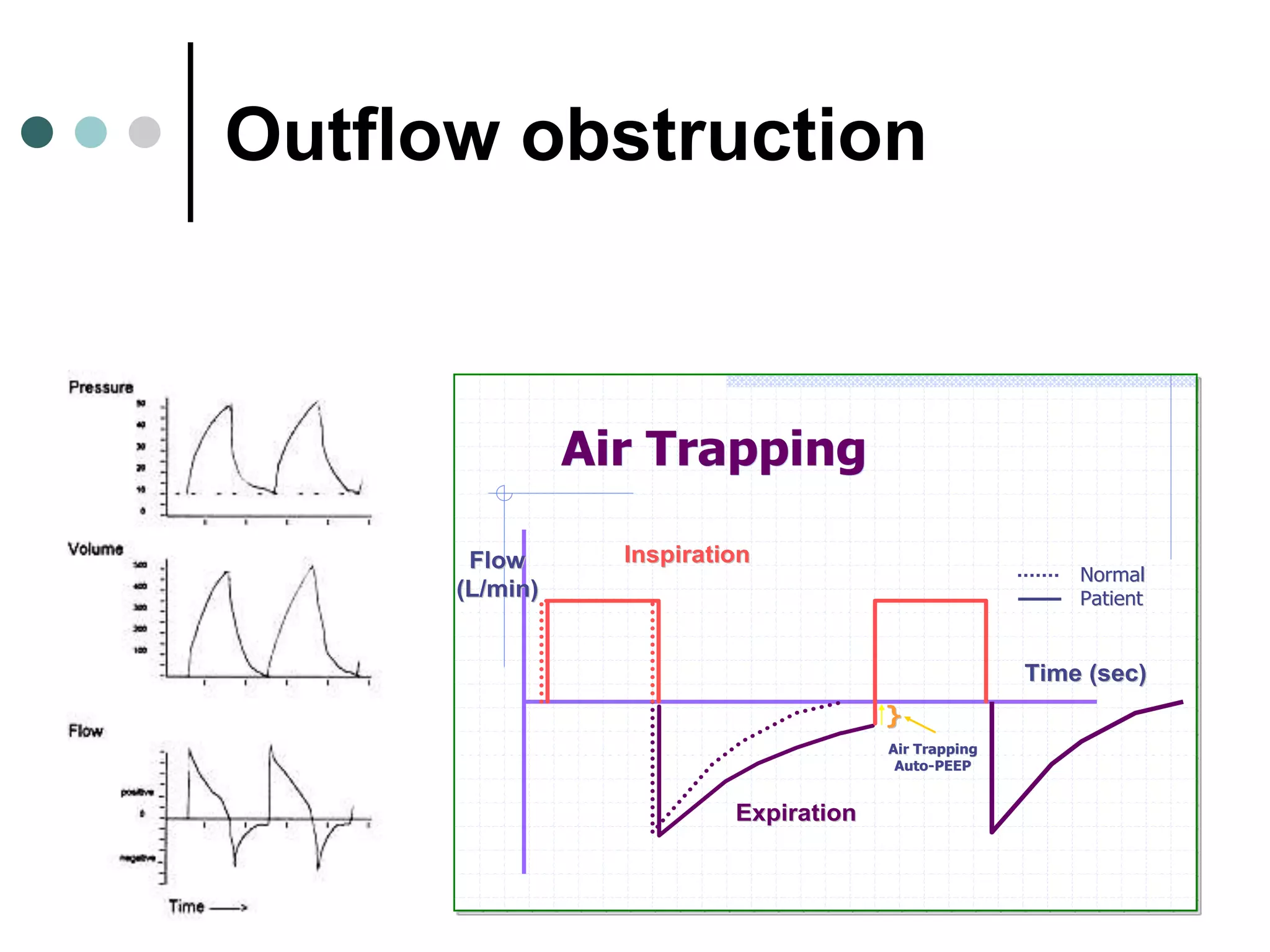
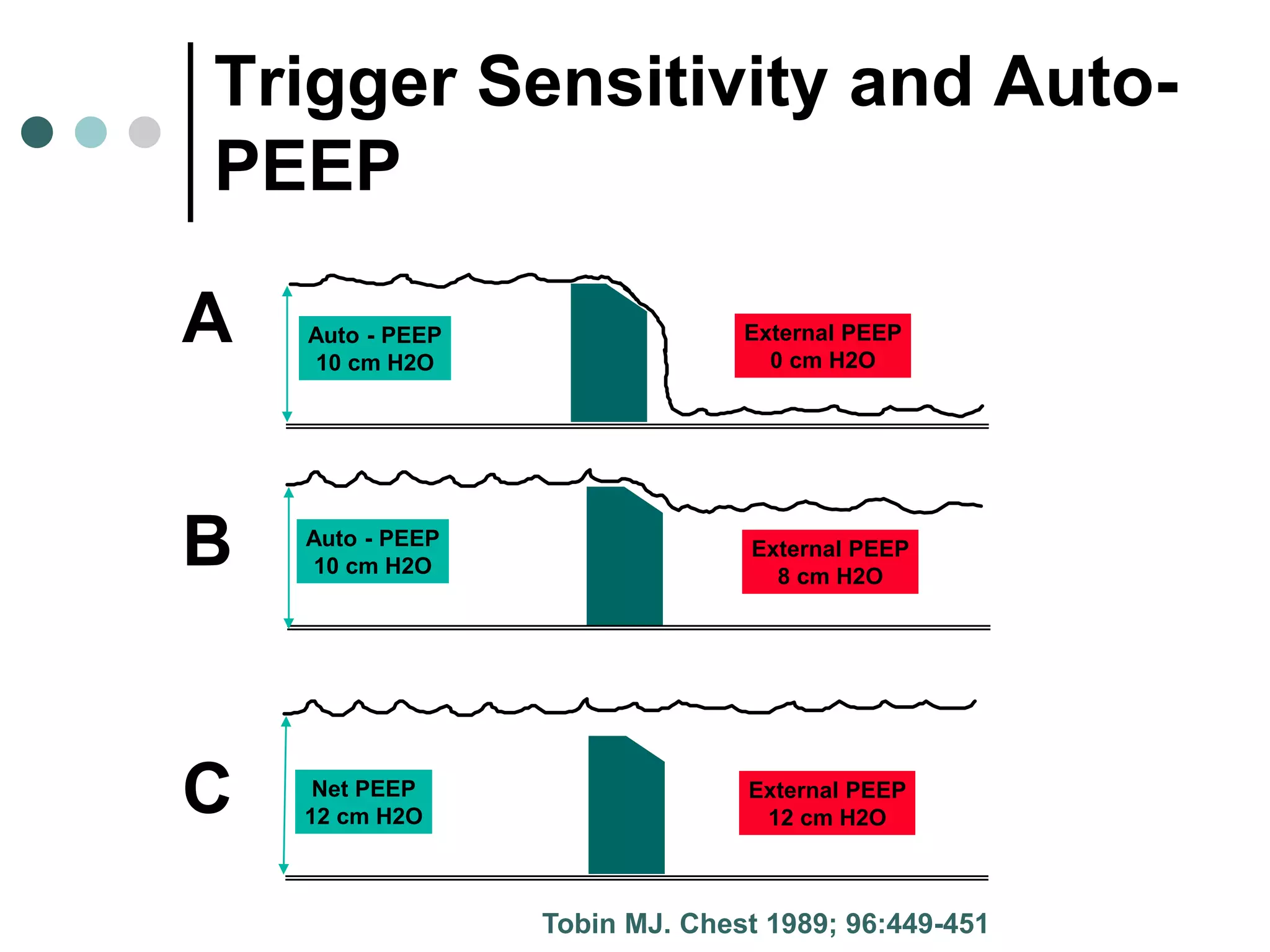
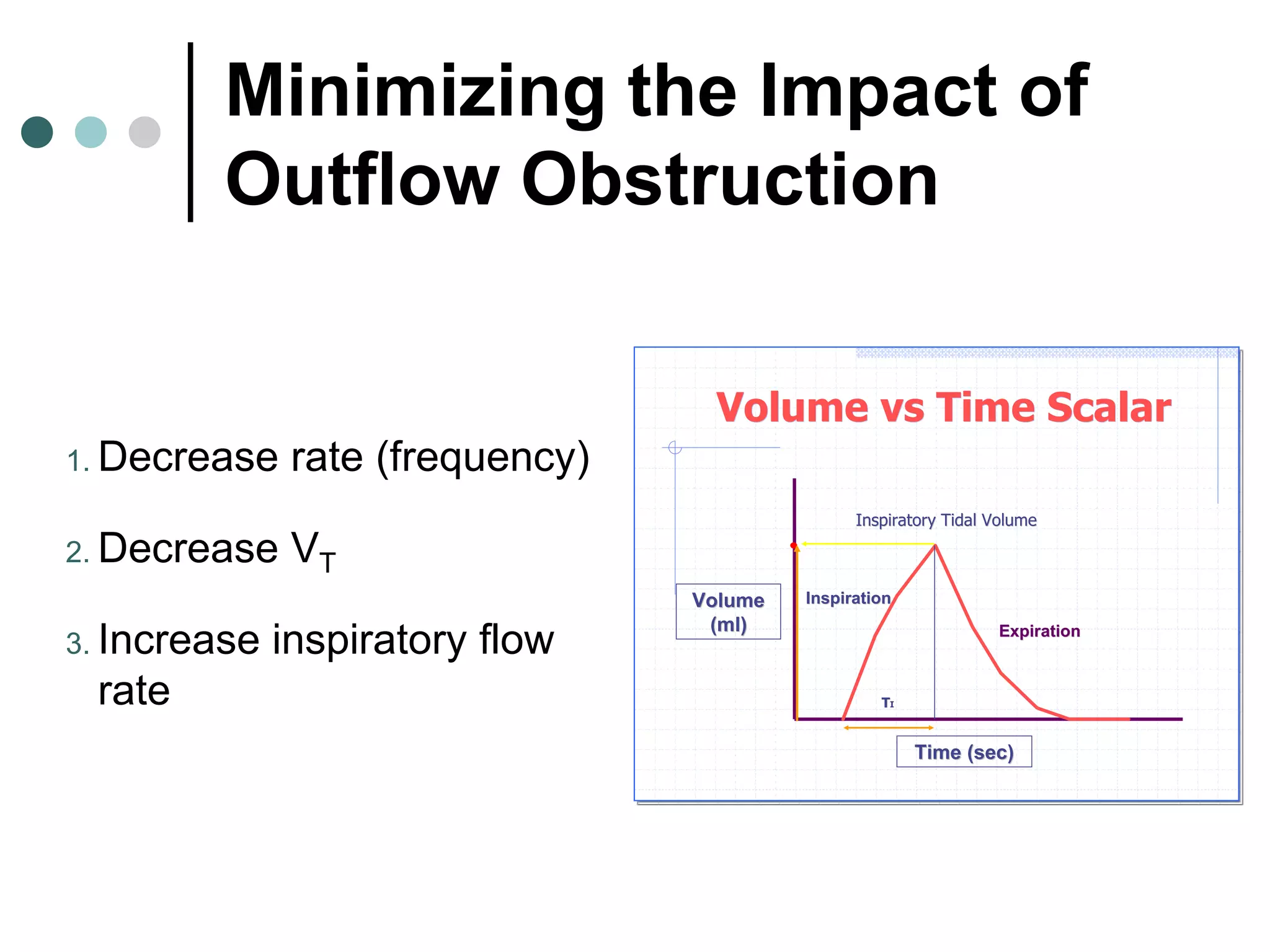
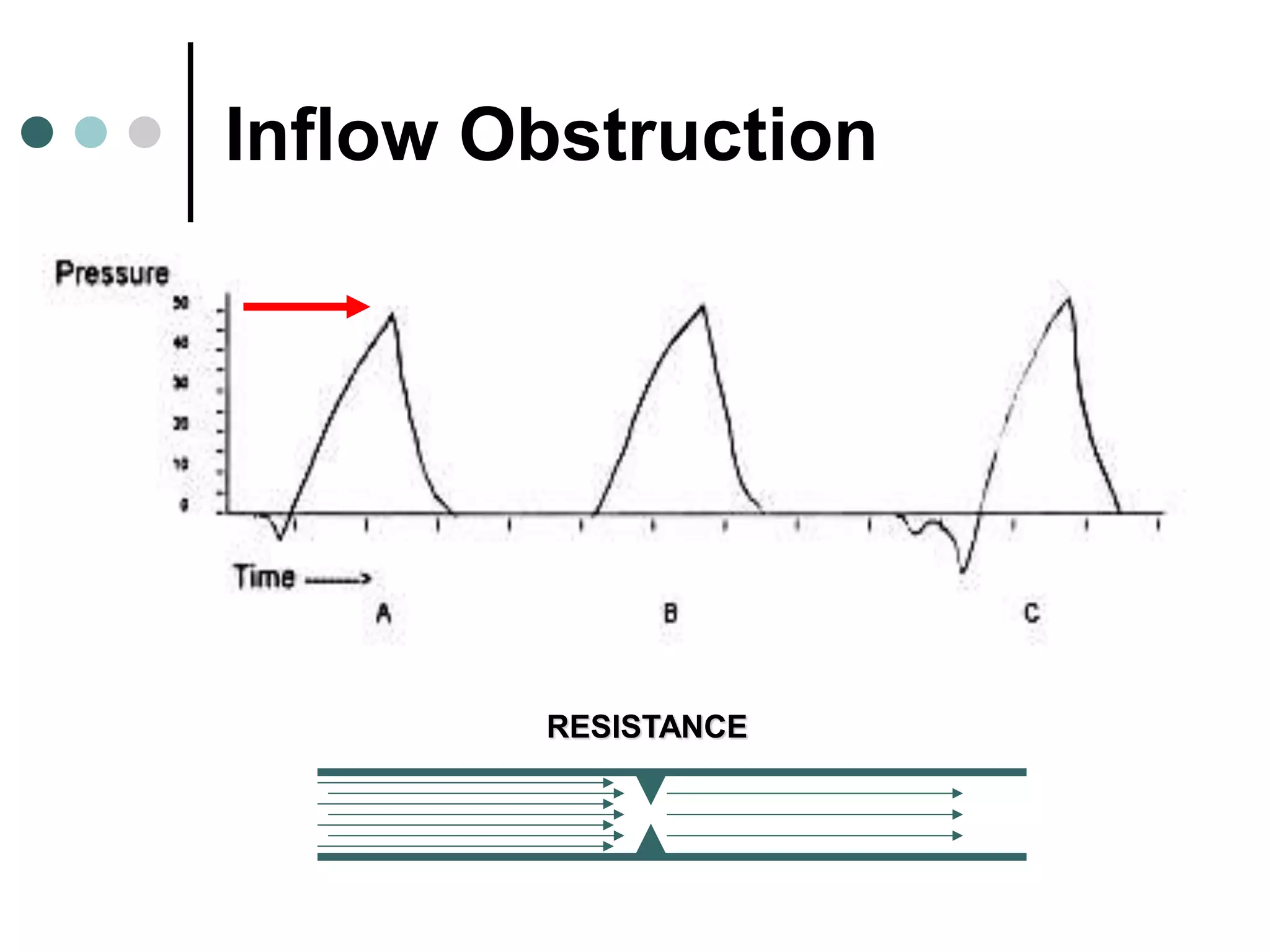
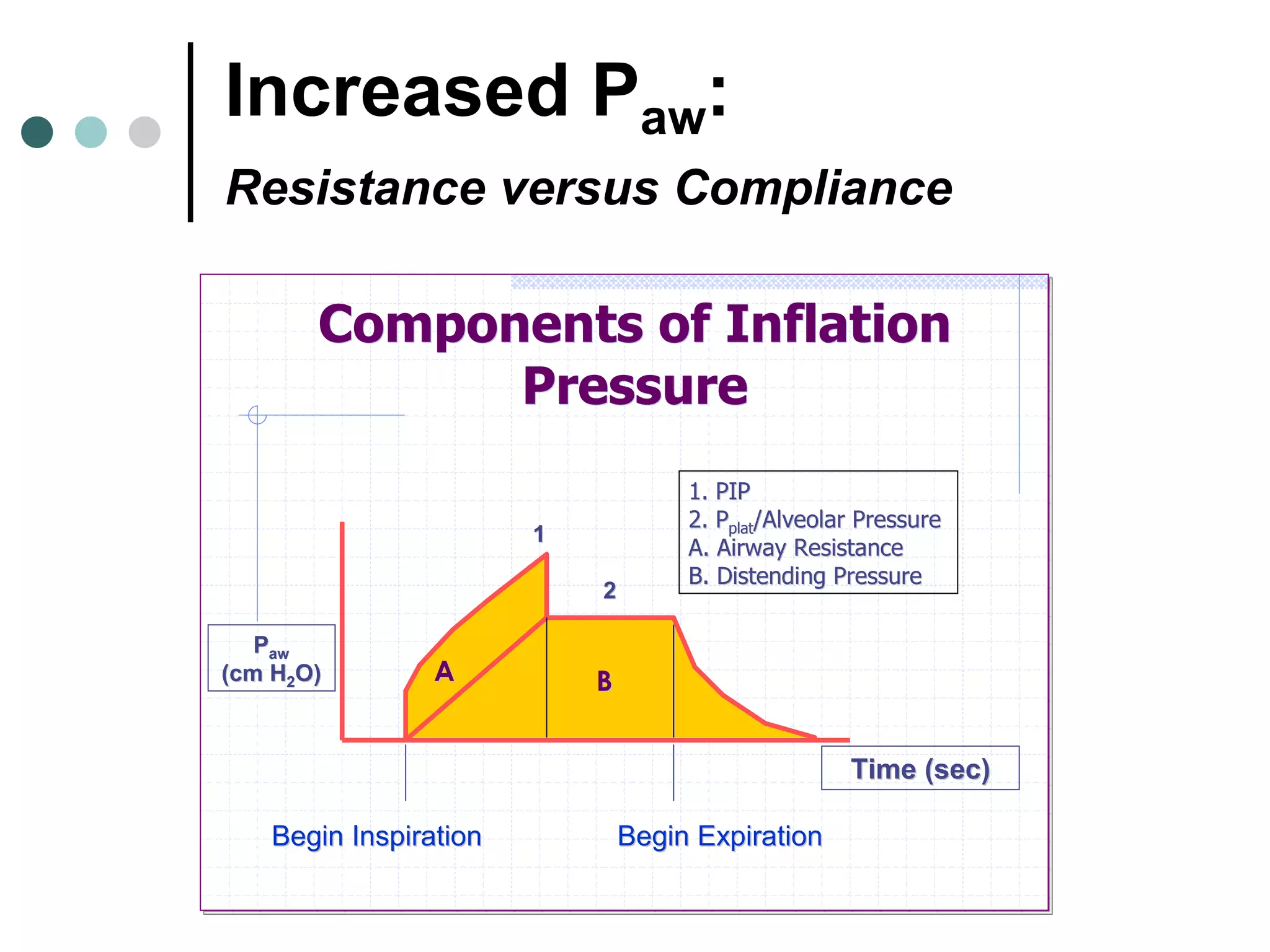
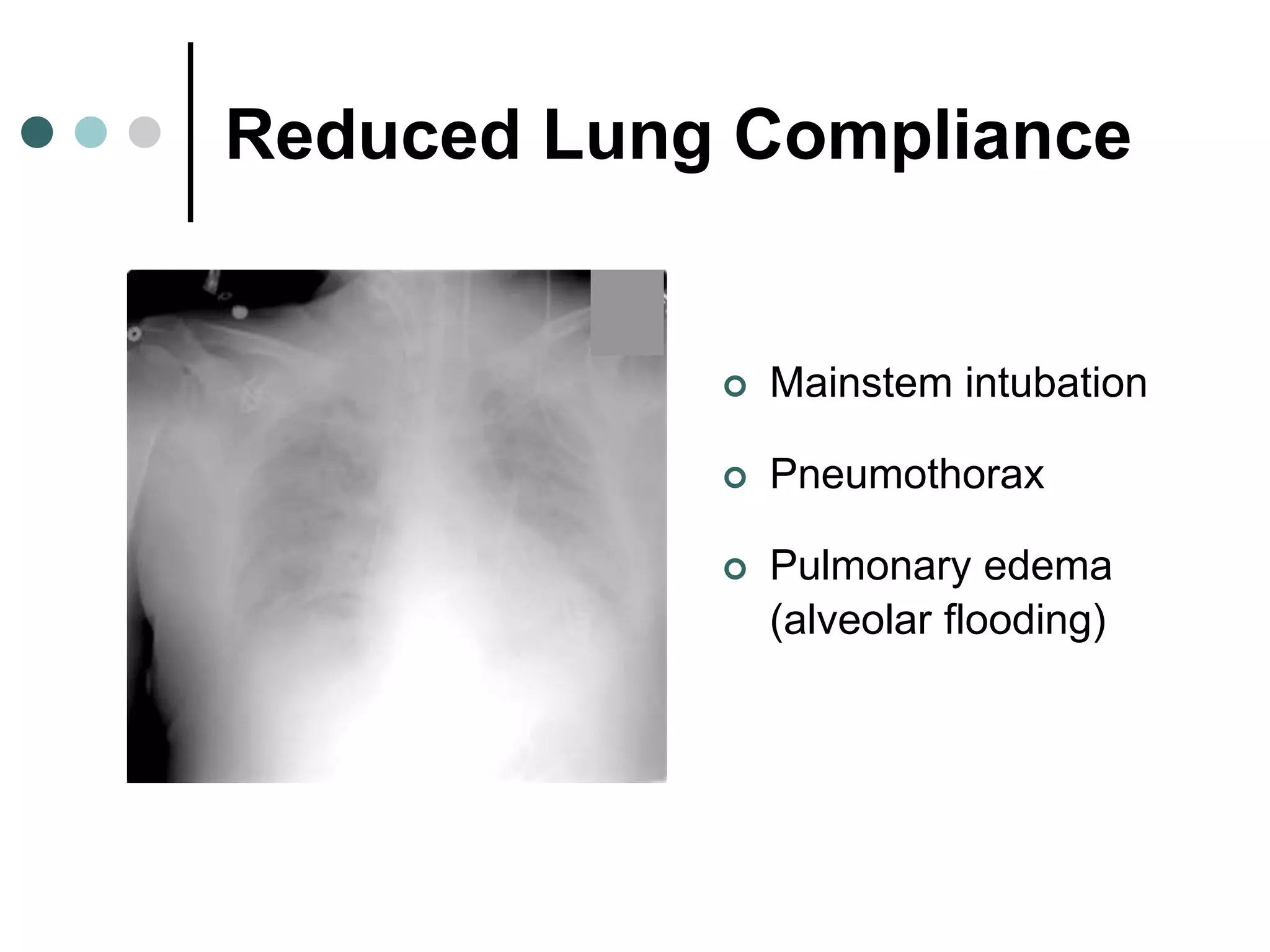
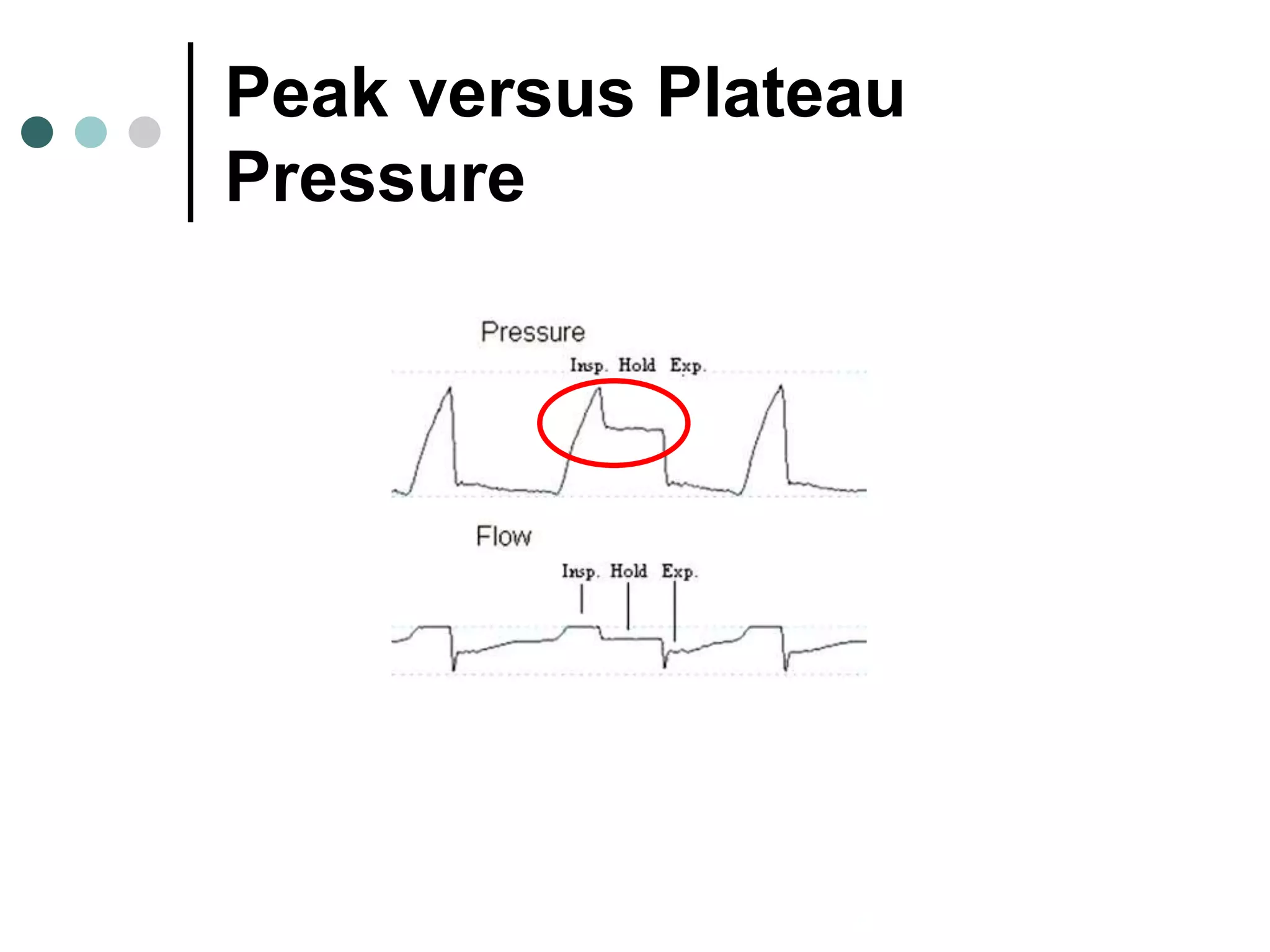
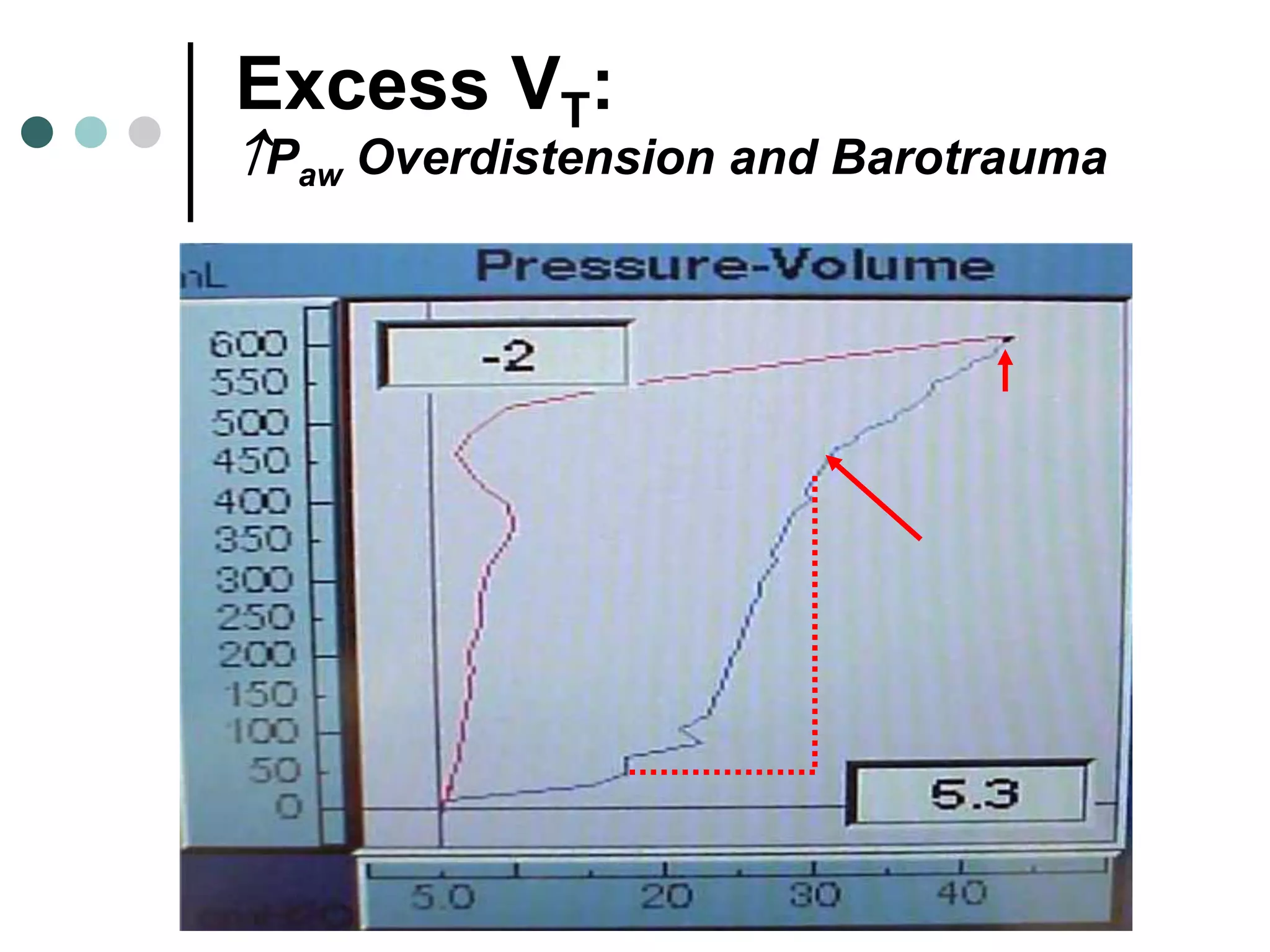
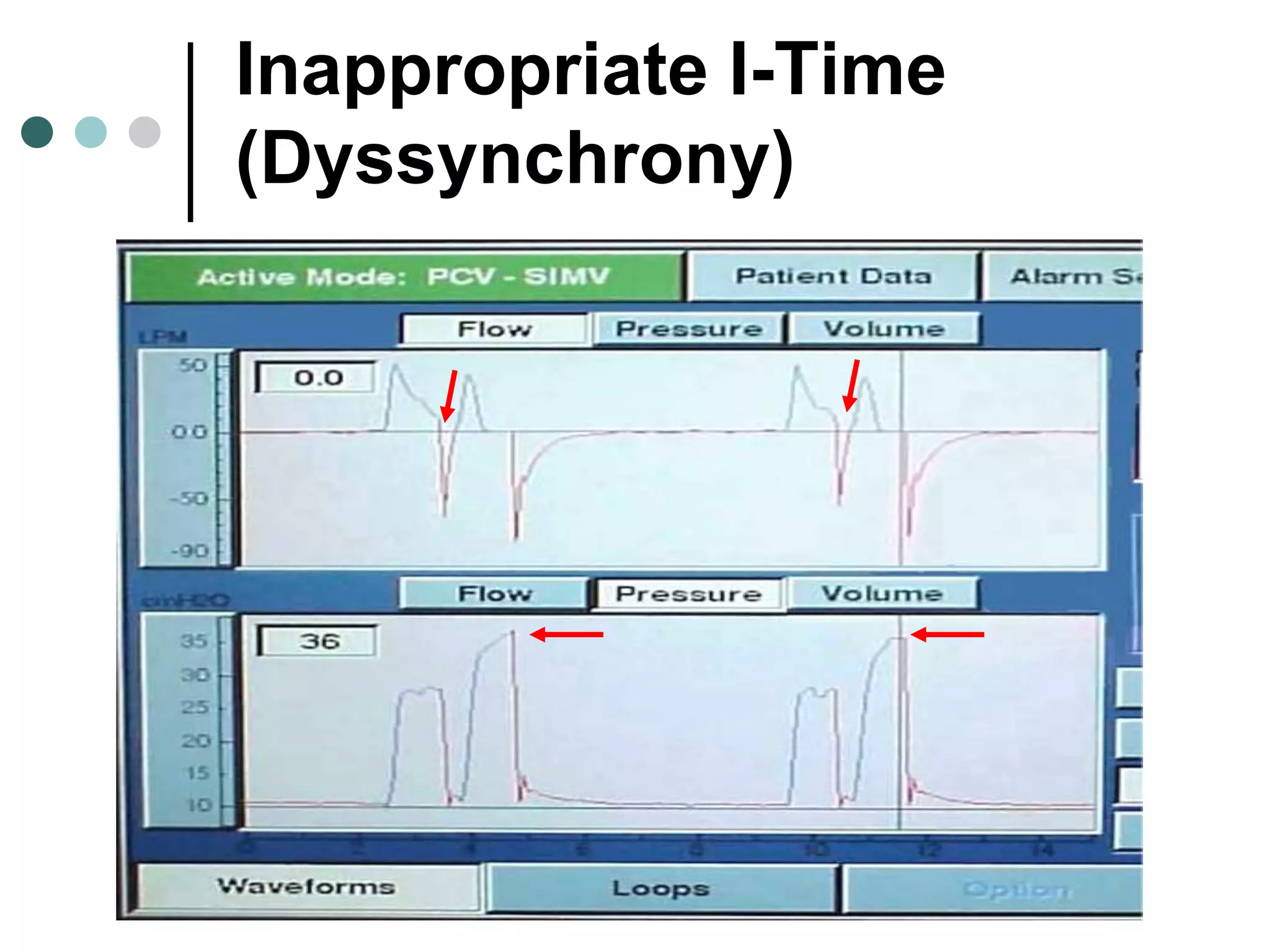
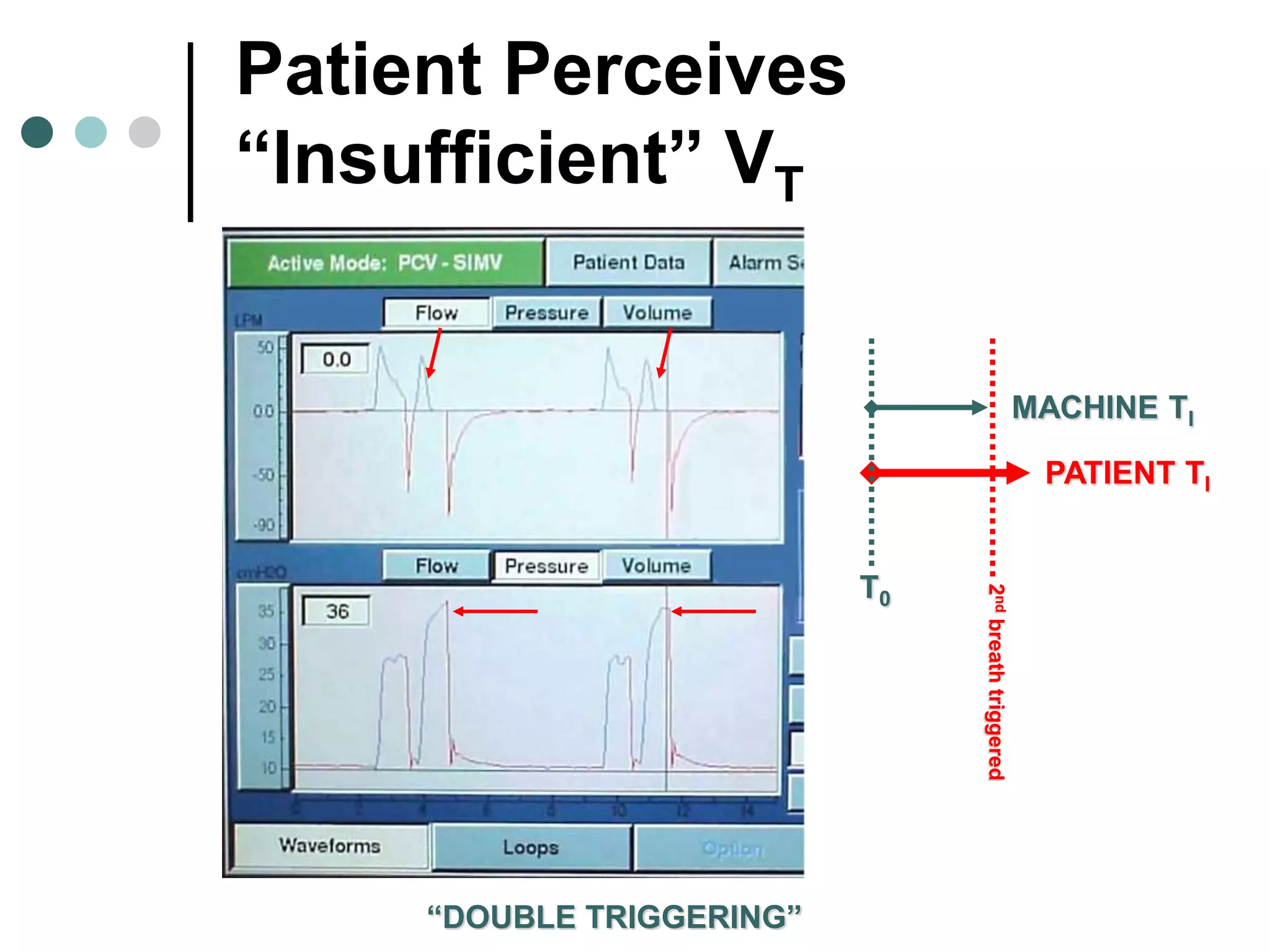
This document provides an overview of basic mechanical ventilation principles and techniques. It discusses establishing harm-free goals, synchronization between patient demand and ventilator delivery, avoiding lung injury through proper pressure and volume settings, identifying the target lung zone, modes of ventilation including CPAP, SIMV, APRV, and disorders related to flow such as starvation, excess flow, outflow obstruction, and inflow obstruction. Key conclusions are to understand ventilator waveforms, synchronize the ventilator to the patient, analyze problems, and use sedation judiciously.