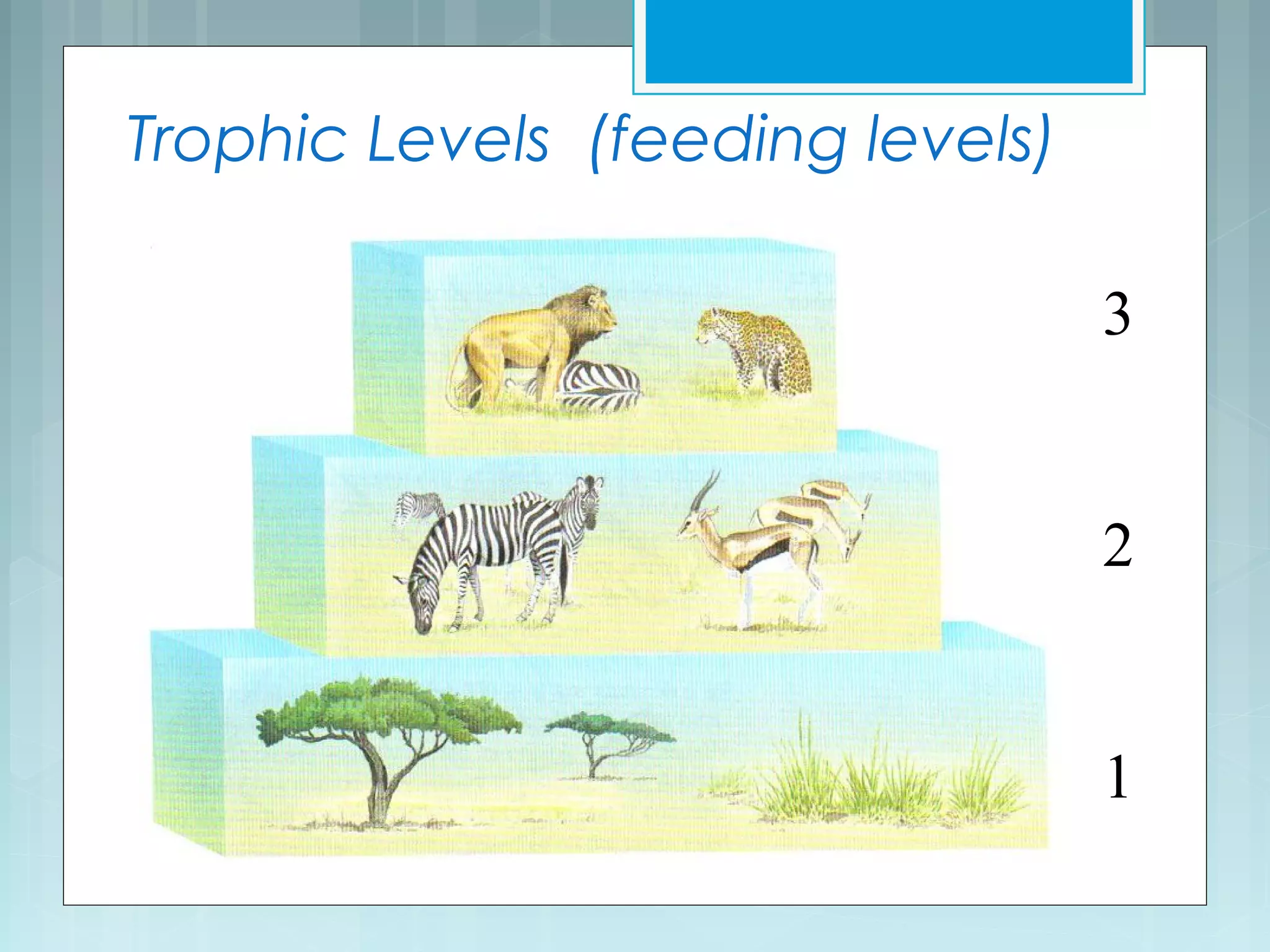
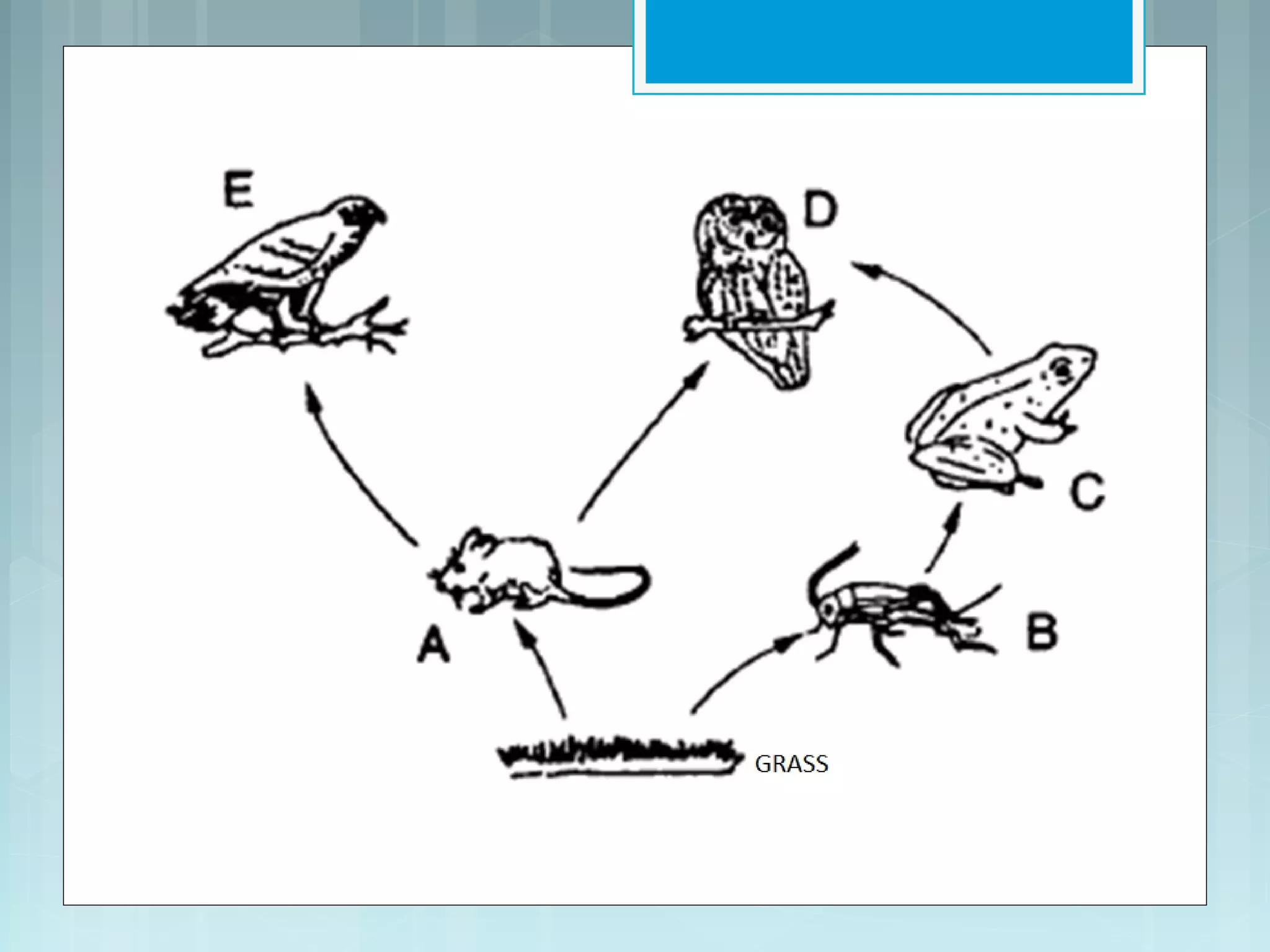
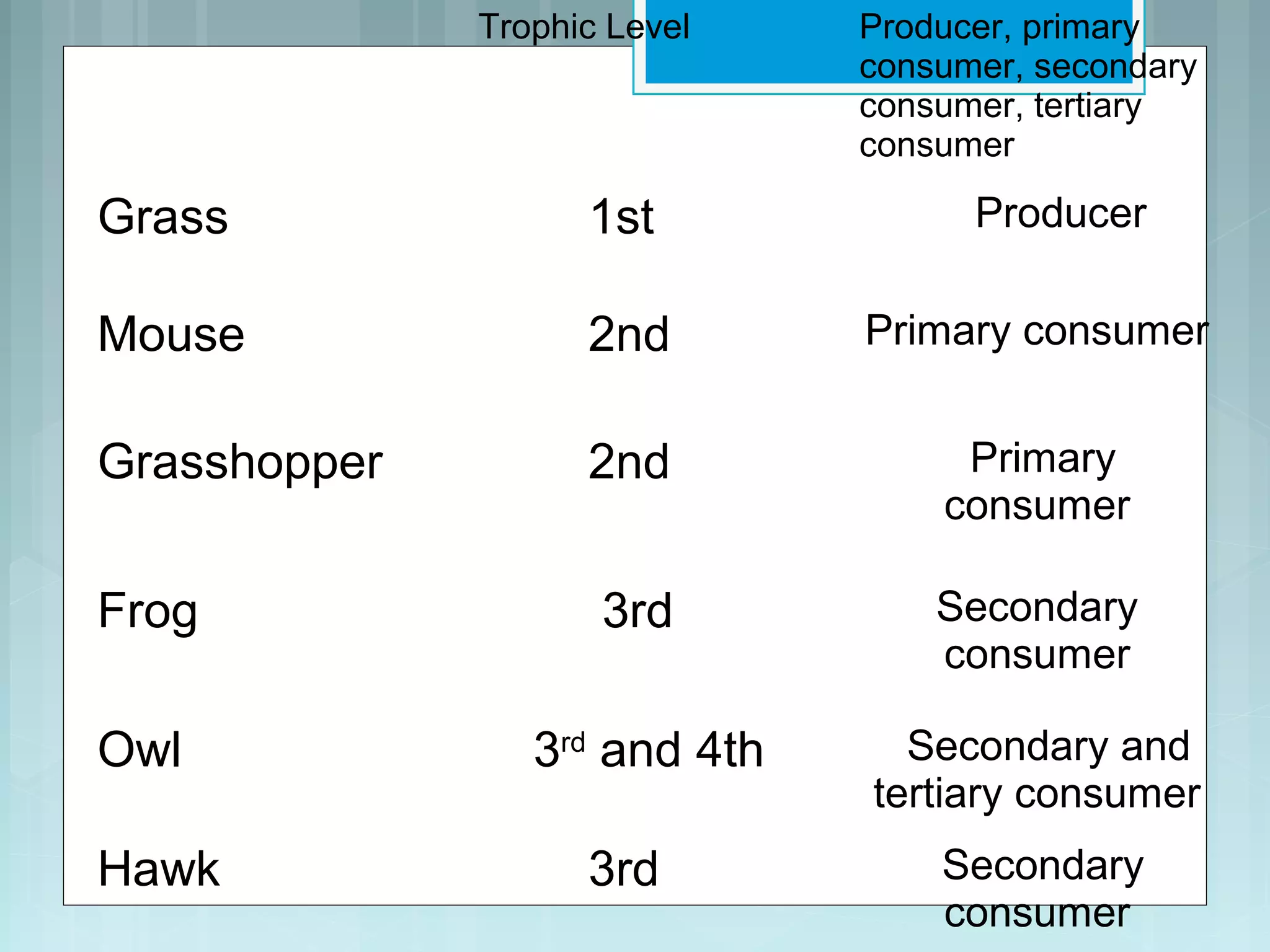
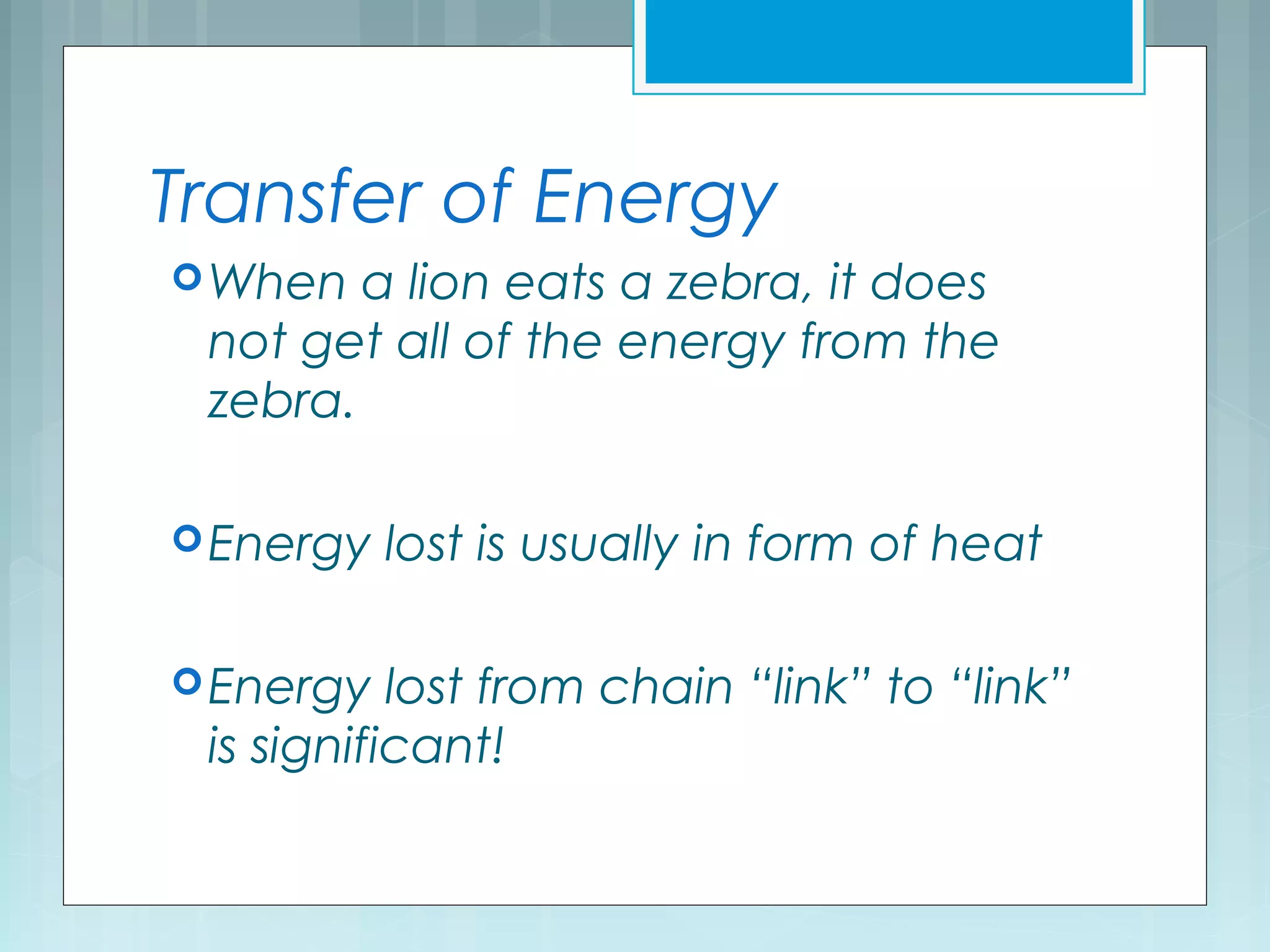
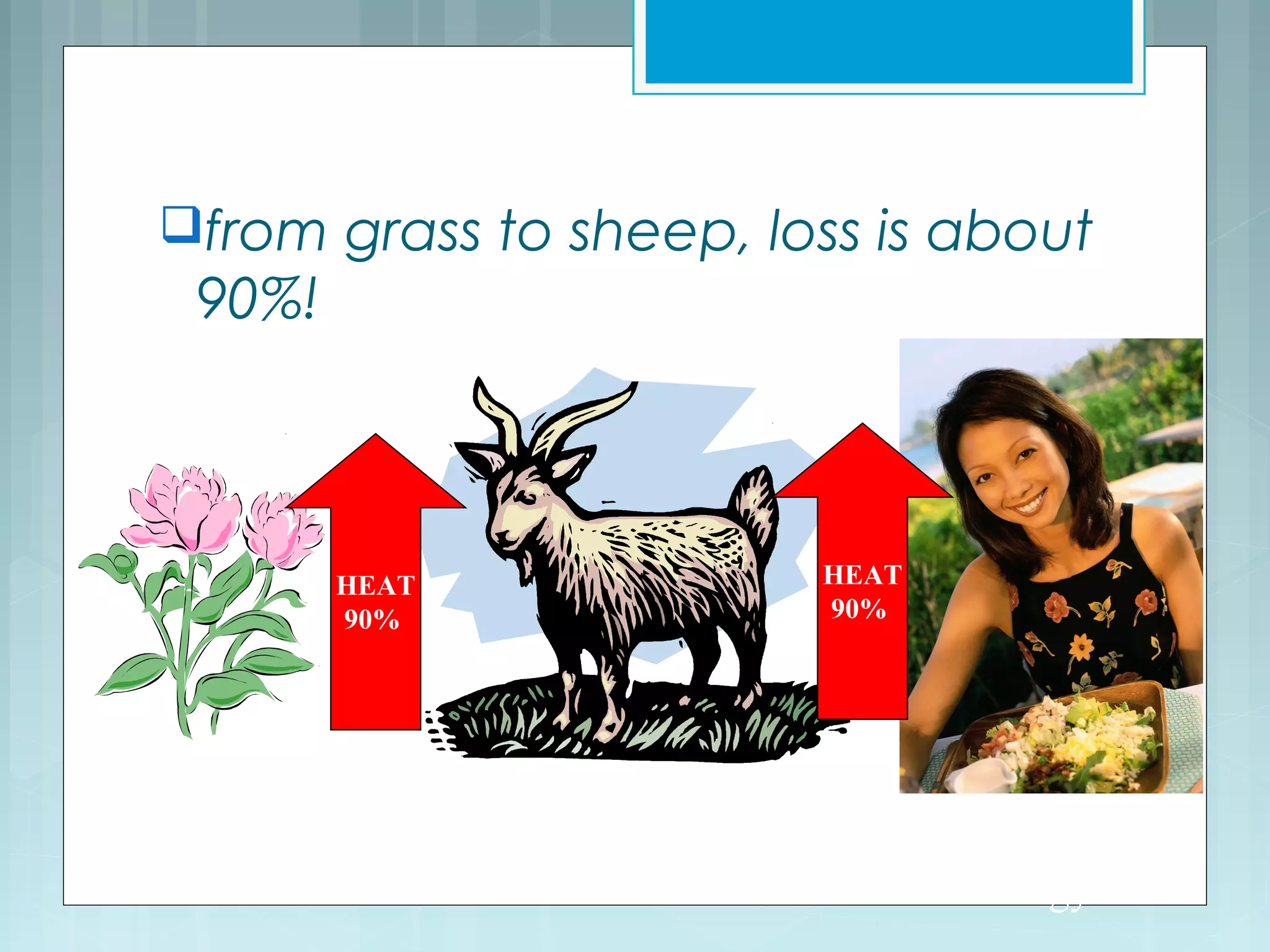
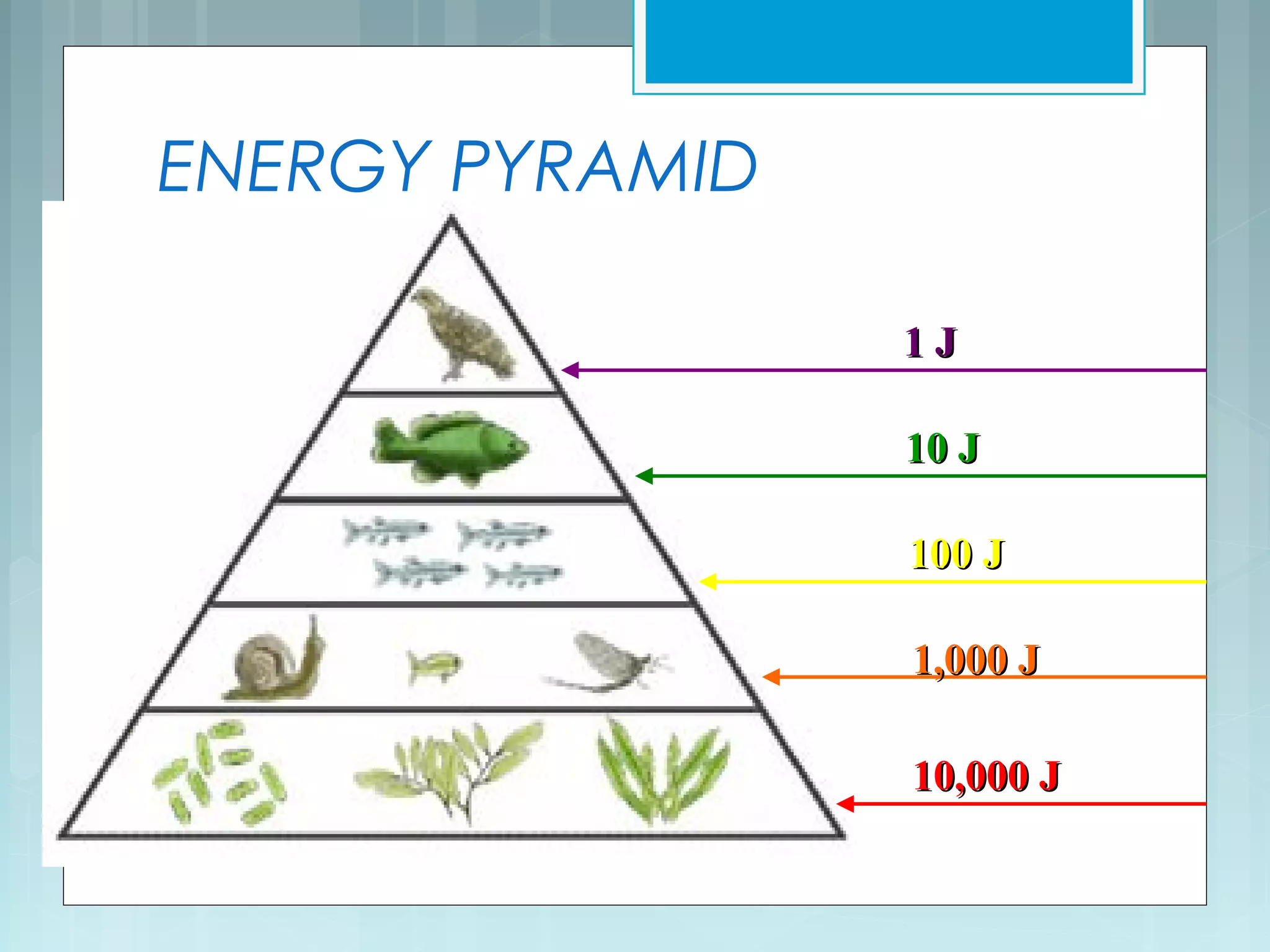
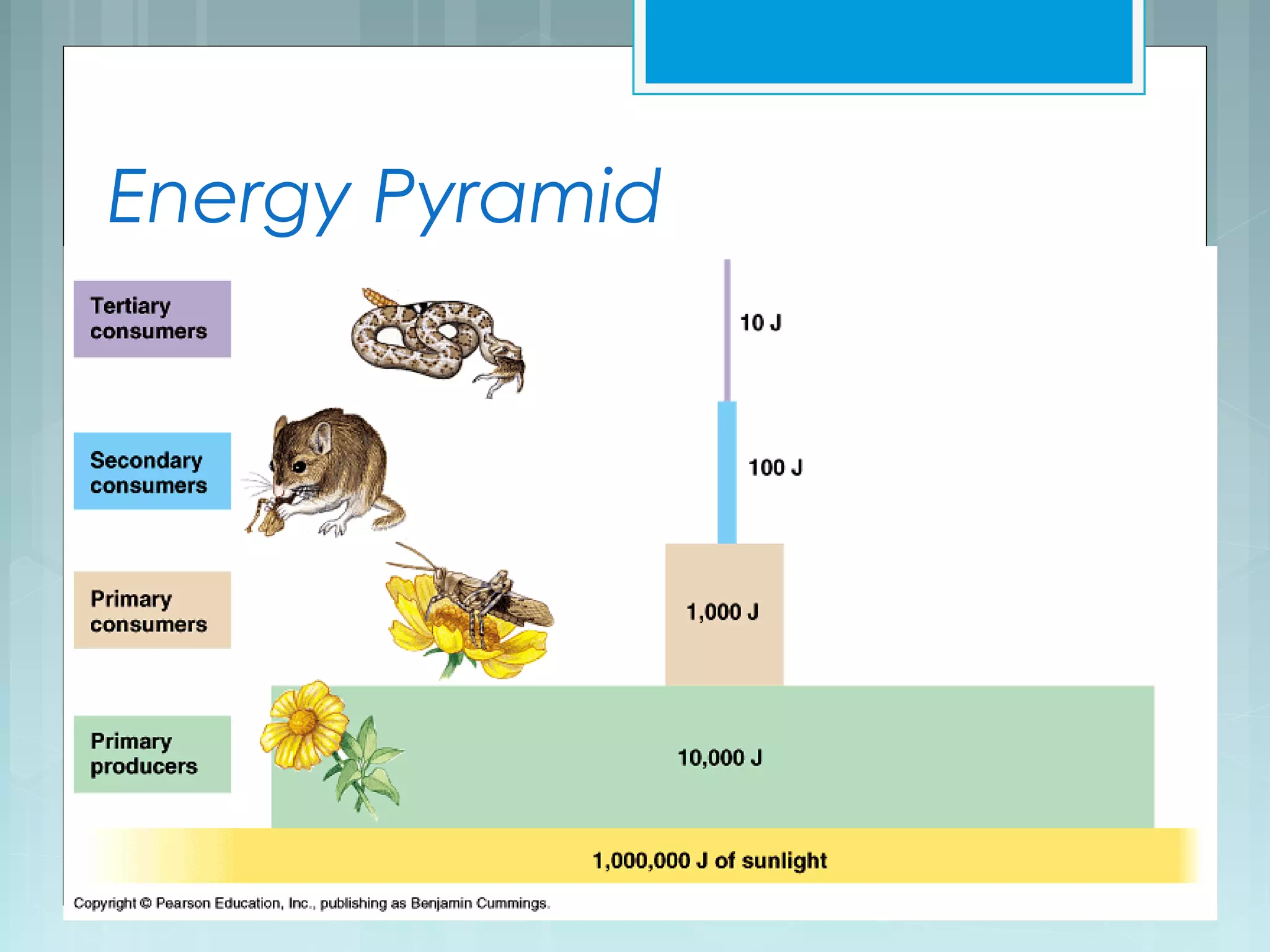
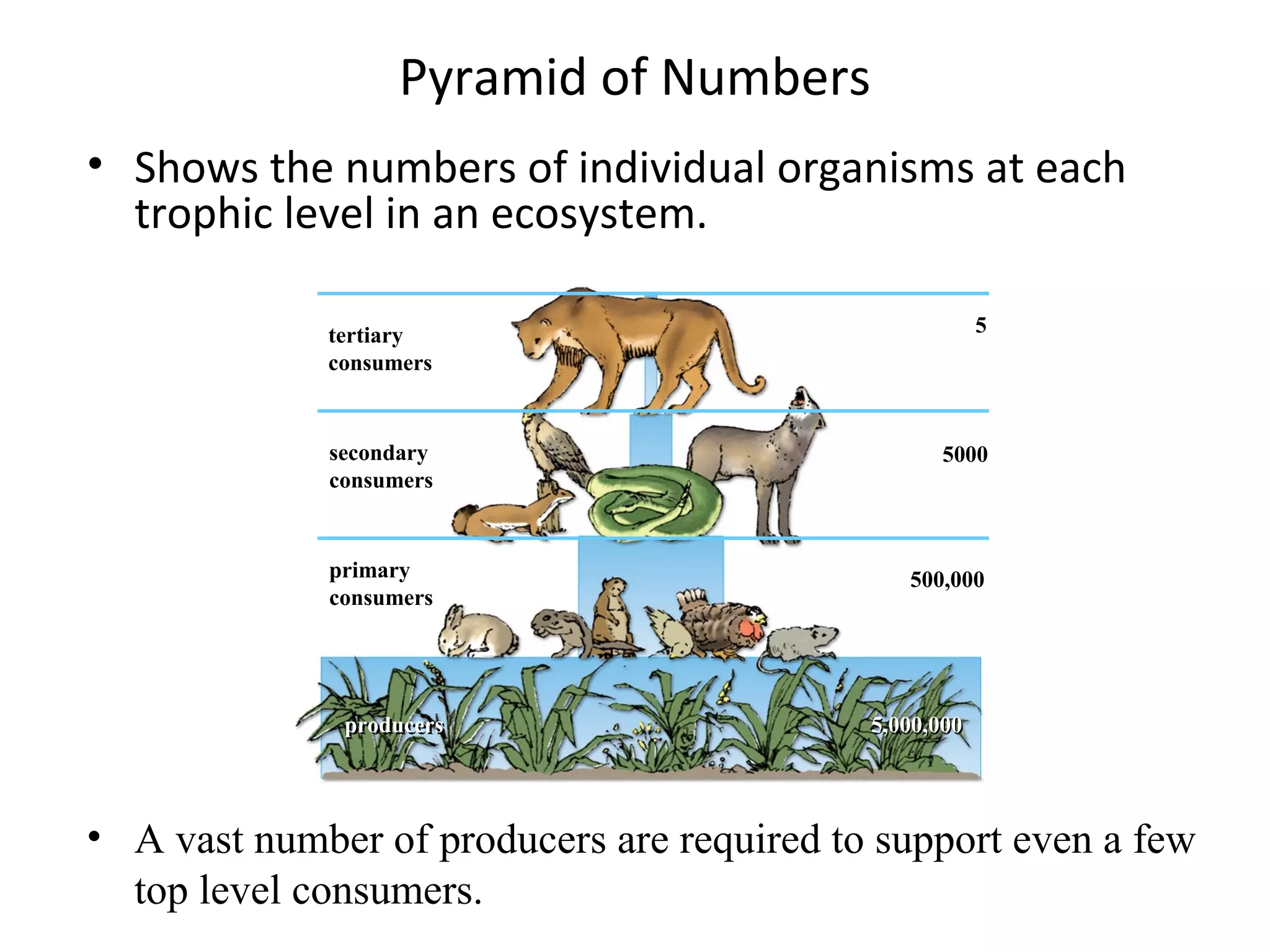
This document discusses trophic levels and energy transfer through food chains and webs. It defines key terms like trophic levels, apex predators, and detritivores. Food chains show the transfer of energy from producers at the first trophic level through primary, secondary, tertiary and sometimes quaternary consumers. Most organisms participate in complex food webs rather than simple food chains. Energy is lost at each trophic level, with typically only 10% being transferred, demonstrated through ecological pyramids which show the decrease in biomass and numbers of organisms at higher trophic levels due to this energy loss.