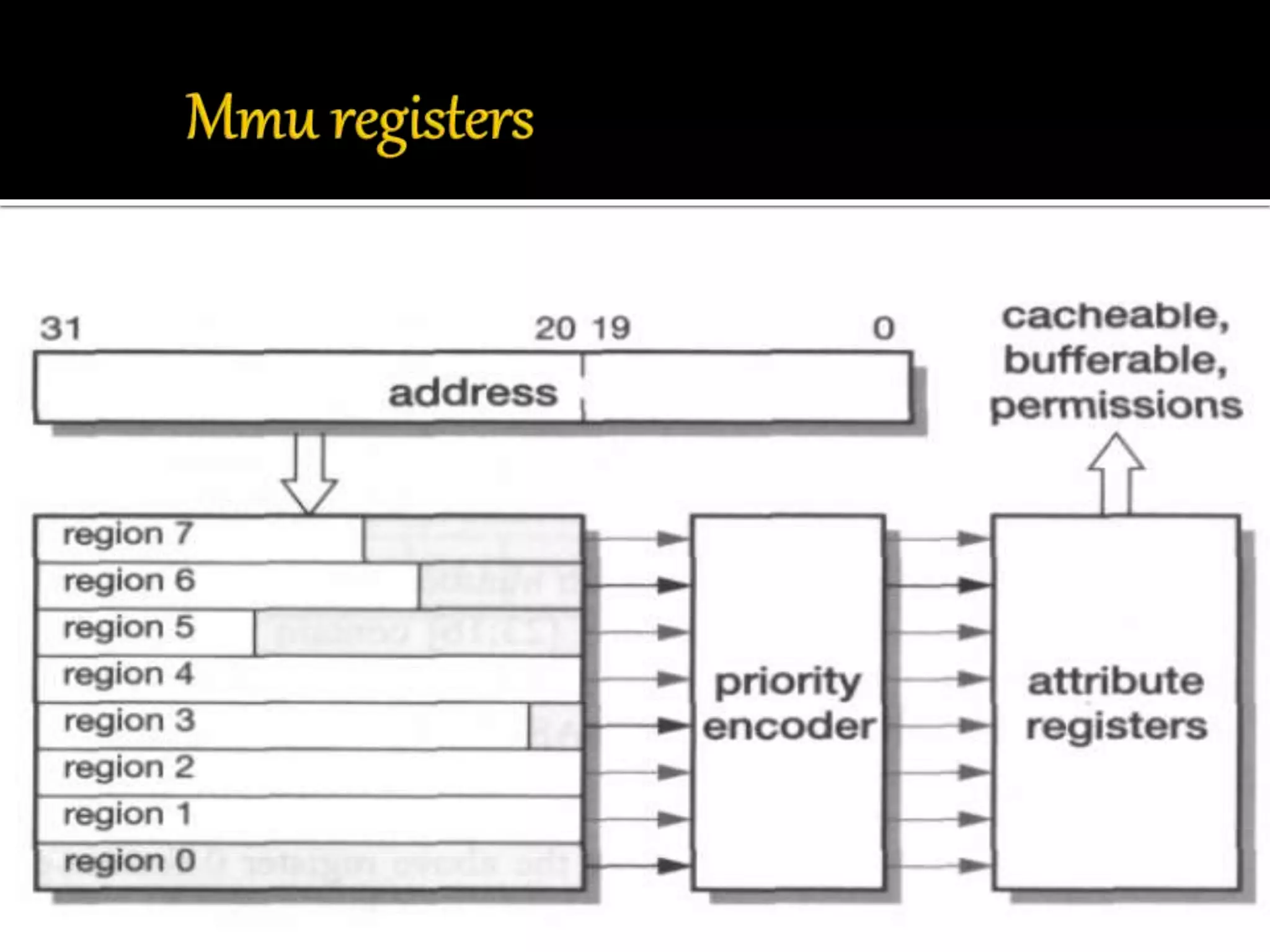
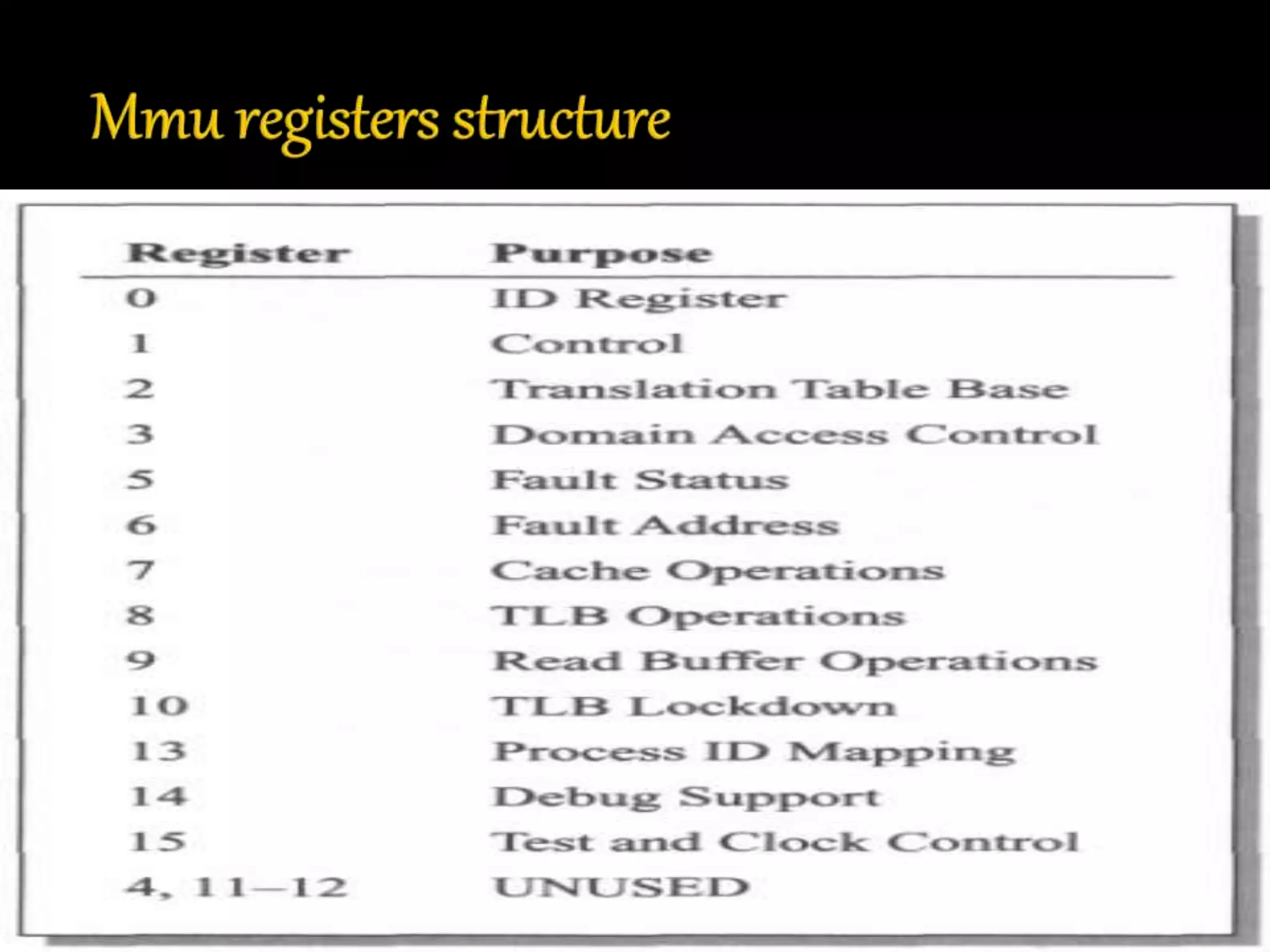
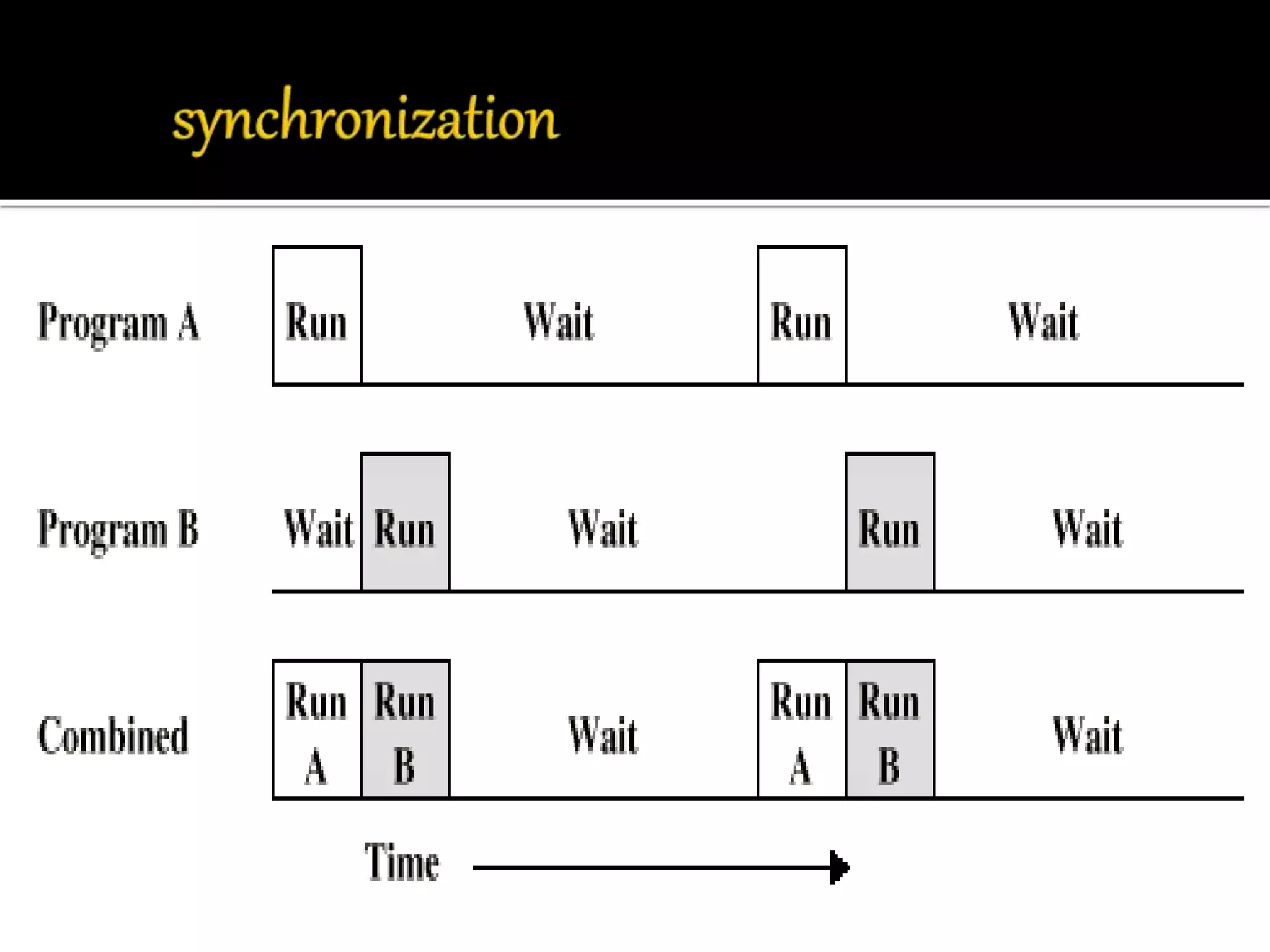
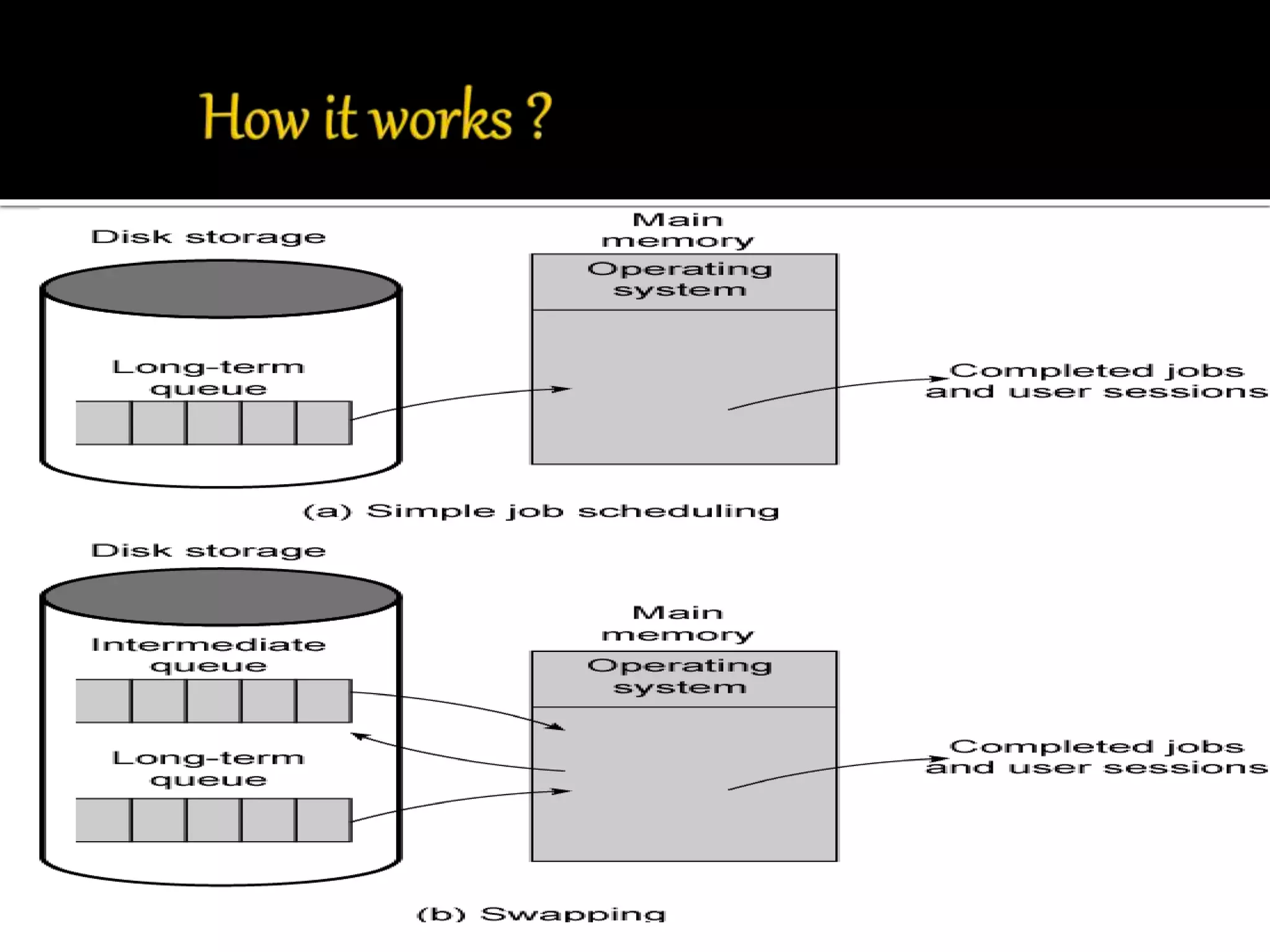
This document discusses the ARM processor and operating systems. It begins with an introduction and brief history of ARM. ARM is a 32-bit RISC processor that is small in size, has high performance, and low power consumption. The document then discusses ARM architecture, memory management units, synchronization, swapping, context switching, and input/output functions. It also covers the ARM partnership model and powered products. Operating systems help run programs concurrently without data loss through functions like memory management, privileged mode operation, and resource allocation.









![address register
multiply
data out register
instruction
decode
&
control
incrementer
register
bank
barrel
shif ter
A[31:0]
data in register
ALU
control
P
C
PC
A
L
U
b
u
s
A
b
u
s
B
b
u
s
register](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sanjayesdpptarmarchitecturesupportforopesystem-141101011826-conversion-gate01/75/EMBEDDED-SYSTEM-DESIGN-ARM-architecture-support-for-operating-system-by-sanjay-d-dhandare-14-2048.jpg)