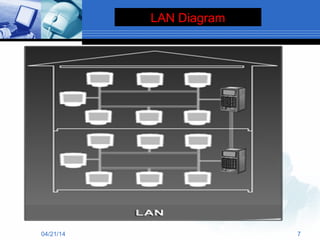
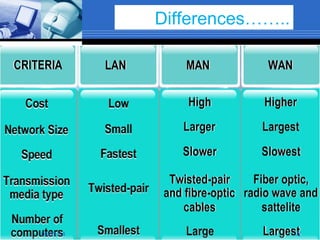
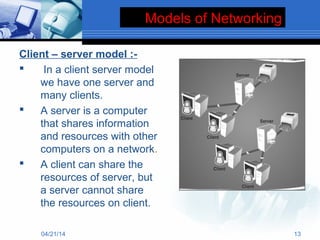
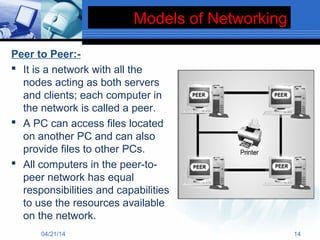
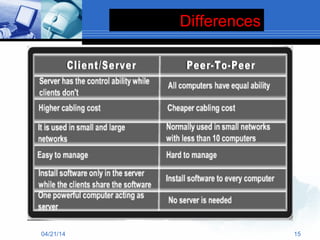
The document presents information about computer networks. It defines a computer network as consisting of two or more linked computers that share resources and allow communication. The document discusses different types of networks like LAN, MAN, and WAN; networking devices like routers and hubs; models like client-server and peer-to-peer; and applications of networks like resource and information sharing and communication. It provides diagrams to illustrate LAN, MAN, and WAN configurations.