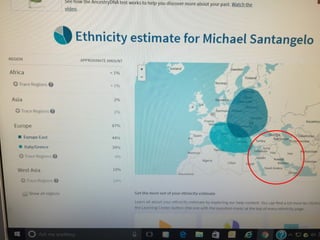
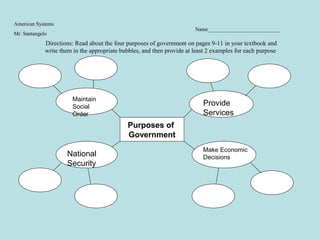
This document discusses the key features and purposes of government. The four essential features of the state are population, territory, sovereignty, and government. State and country generally have the same meaning and refer to a political community with definite boundaries and an independent government. There are around 200 countries in the world today, though the exact number is difficult to determine. The main purposes of government are to maintain social order, provide national security, make economic decisions, and provide essential public services. Examples of each purpose are given such as courts, police, and laws for social order and the military and alliances for national security.