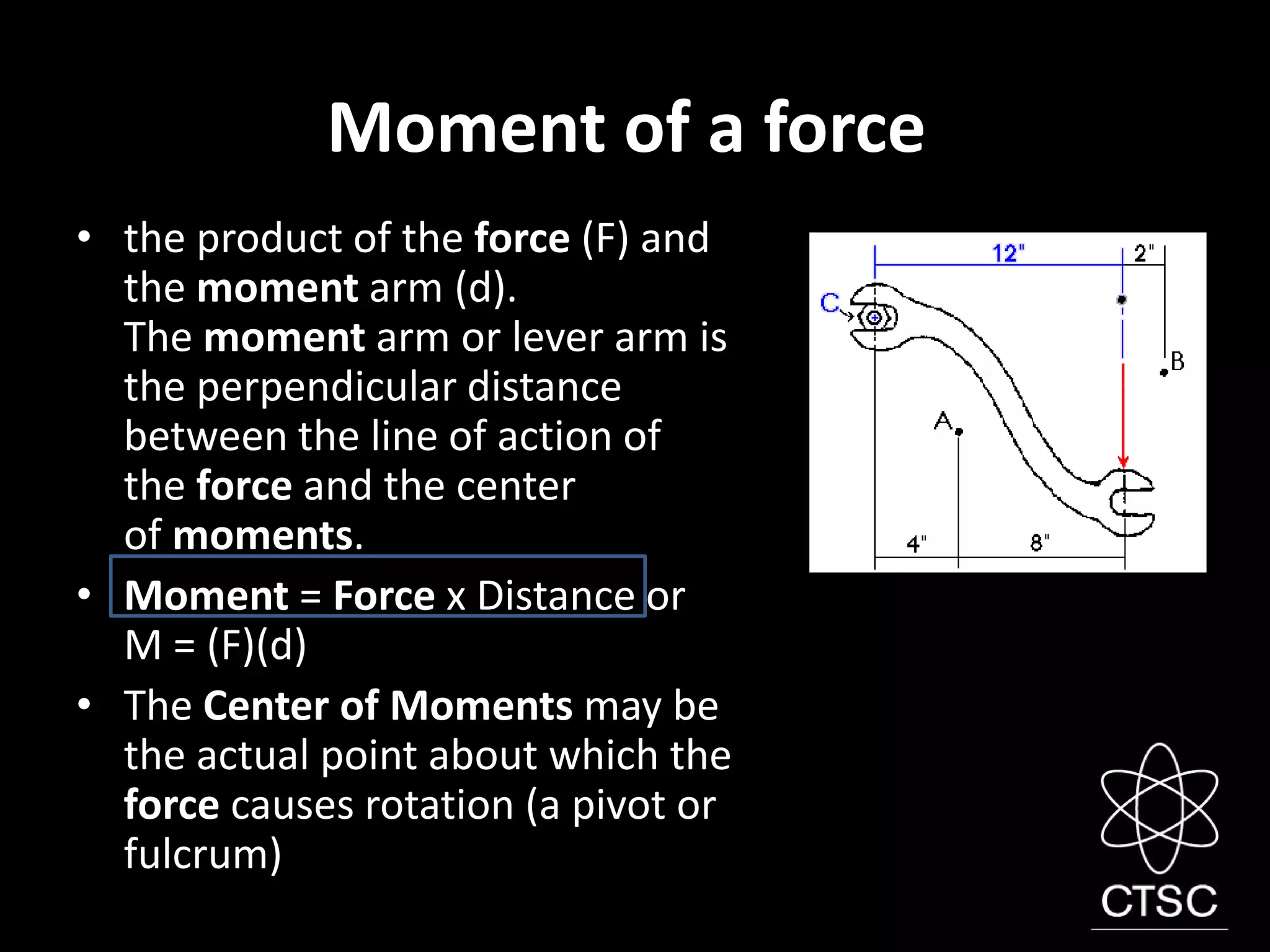
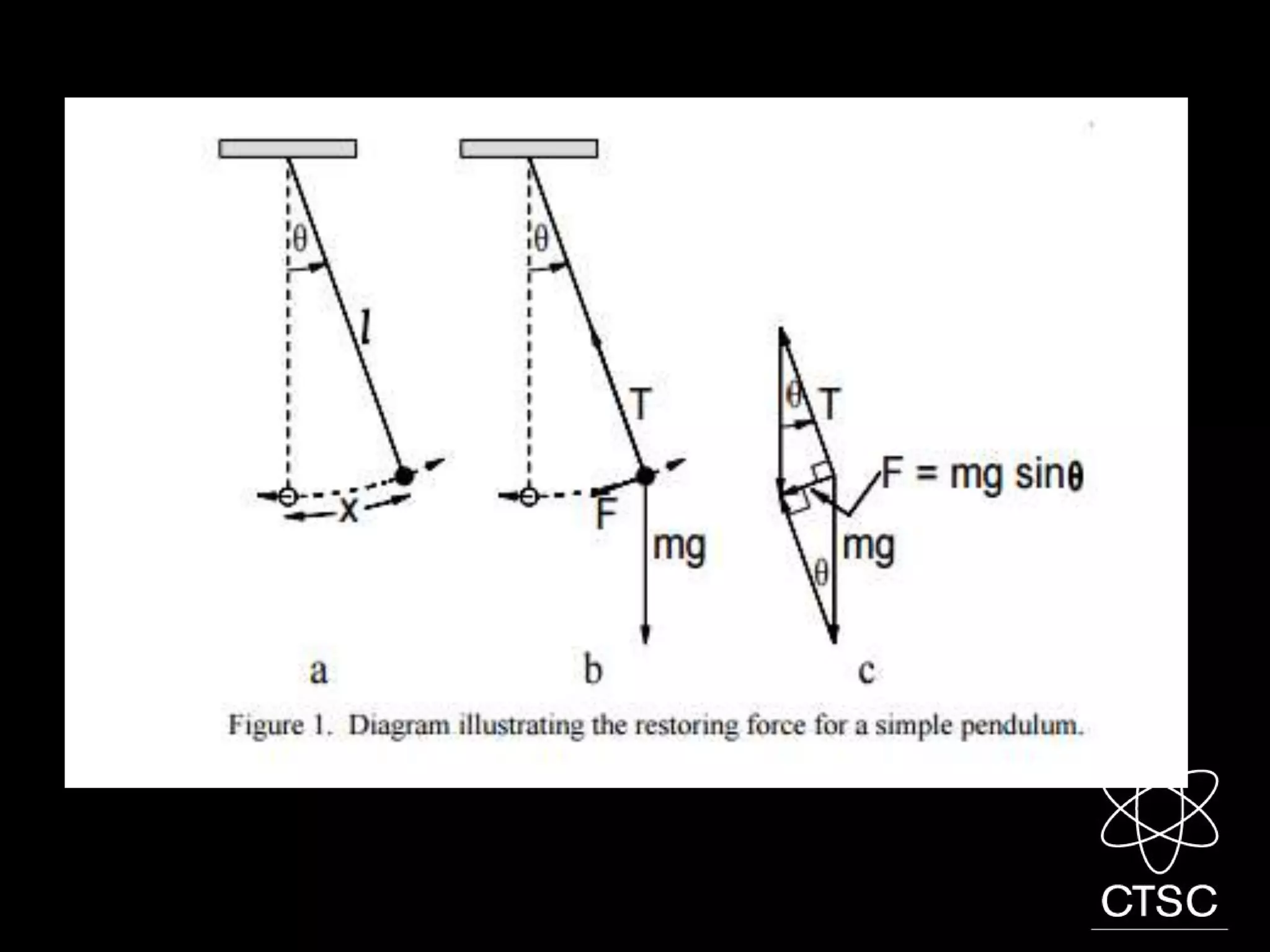
1. A force is a push or pull that can change the motion of an object or cause it to deform. Forces are measured in Newtons and can cause rotation when applied at a distance from a pivot point, known as a moment.
2. Objects in equilibrium experience equal and opposite forces and moments such that the net force and moment are both zero. Levers use moments to multiply applied forces to make lifting loads easier.
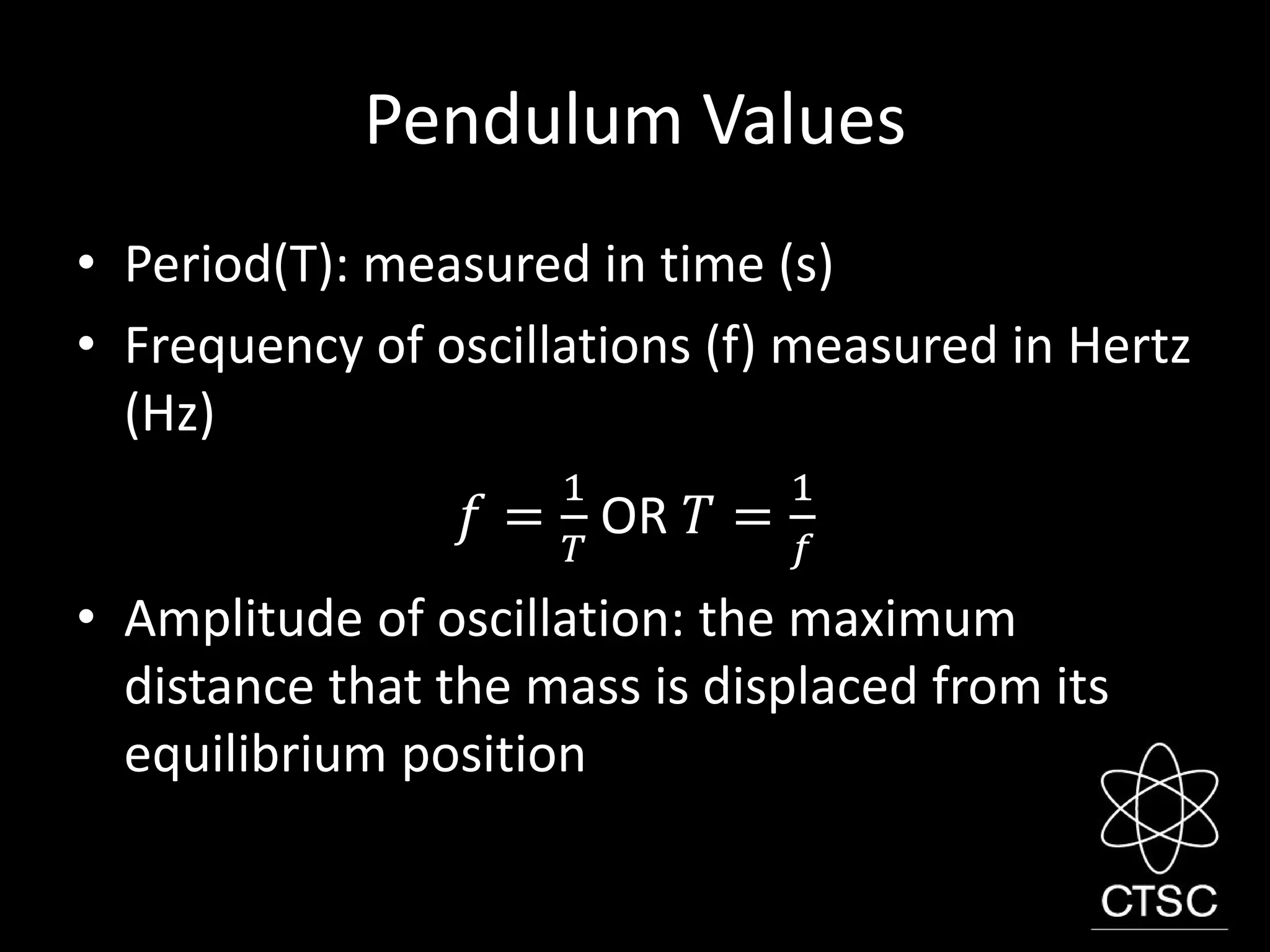
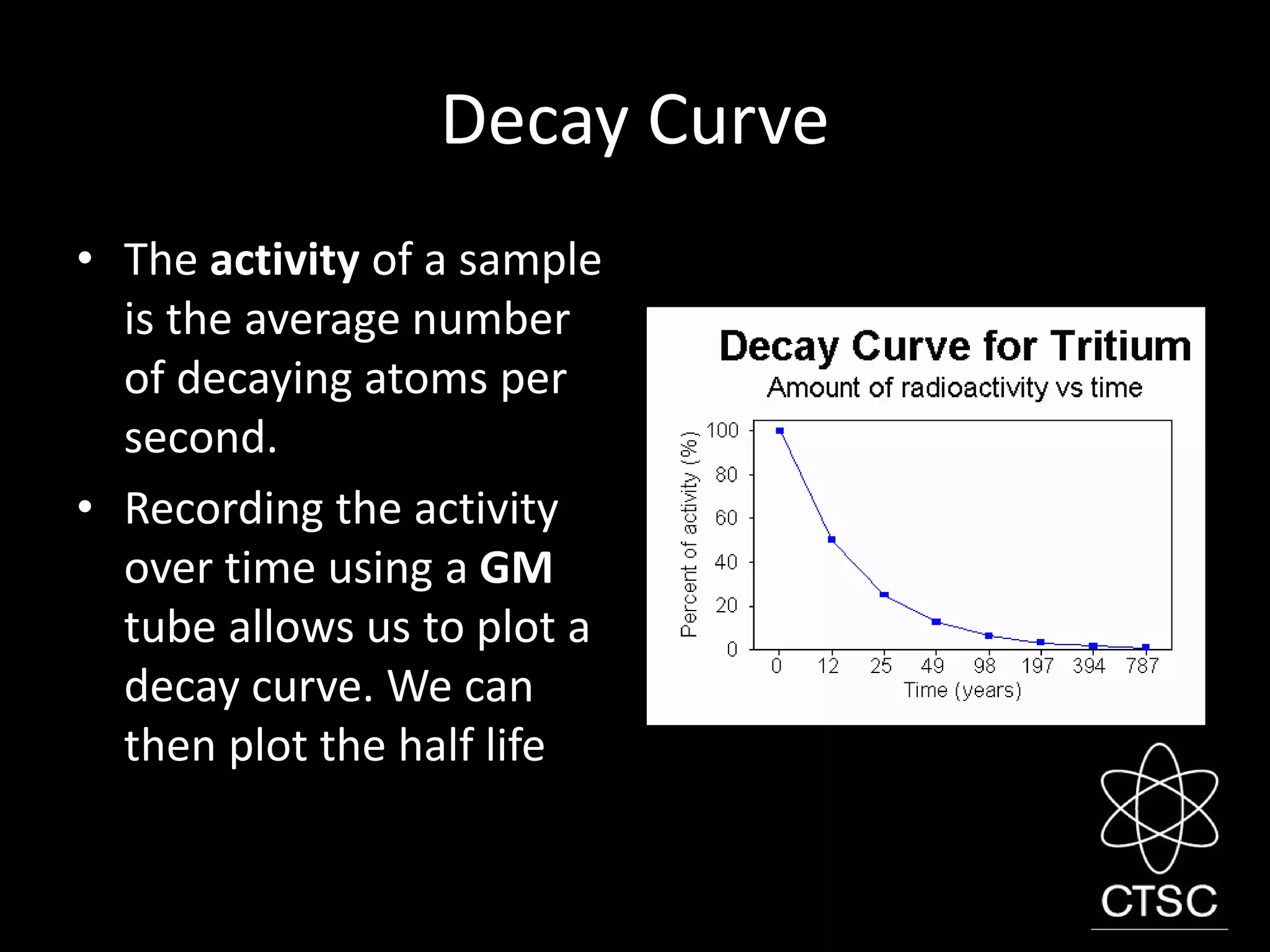
3. Radioactivity is the spontaneous decay of unstable atomic nuclei. It involves the emission of alpha, beta, or gamma radiation. Radioactive decay occurs at a constant rate described by an isotope's half-life and can be used for applications like radiotherapy or dating artifacts.