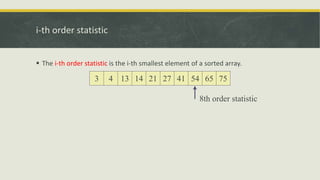
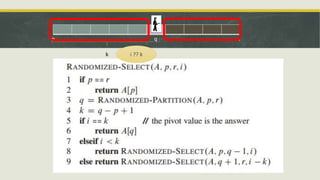
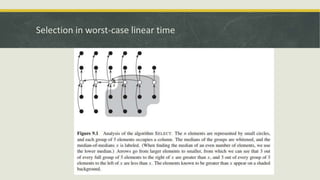
This document discusses order statistics and medians. It defines the i-th order statistic as the i-th smallest element of a sorted array. The median is defined as the halfway point of a data set. For an odd number of elements, the median is the (n+1)/2 order statistic, and for an even number it is defined as the average of the n/2 and n/2+1 order statistics. Methods for finding the minimum and maximum in expected linear time using pairs are presented. Selection algorithms for finding the k-th order statistic in expected and worst-case linear time using techniques like median of medians are also summarized.