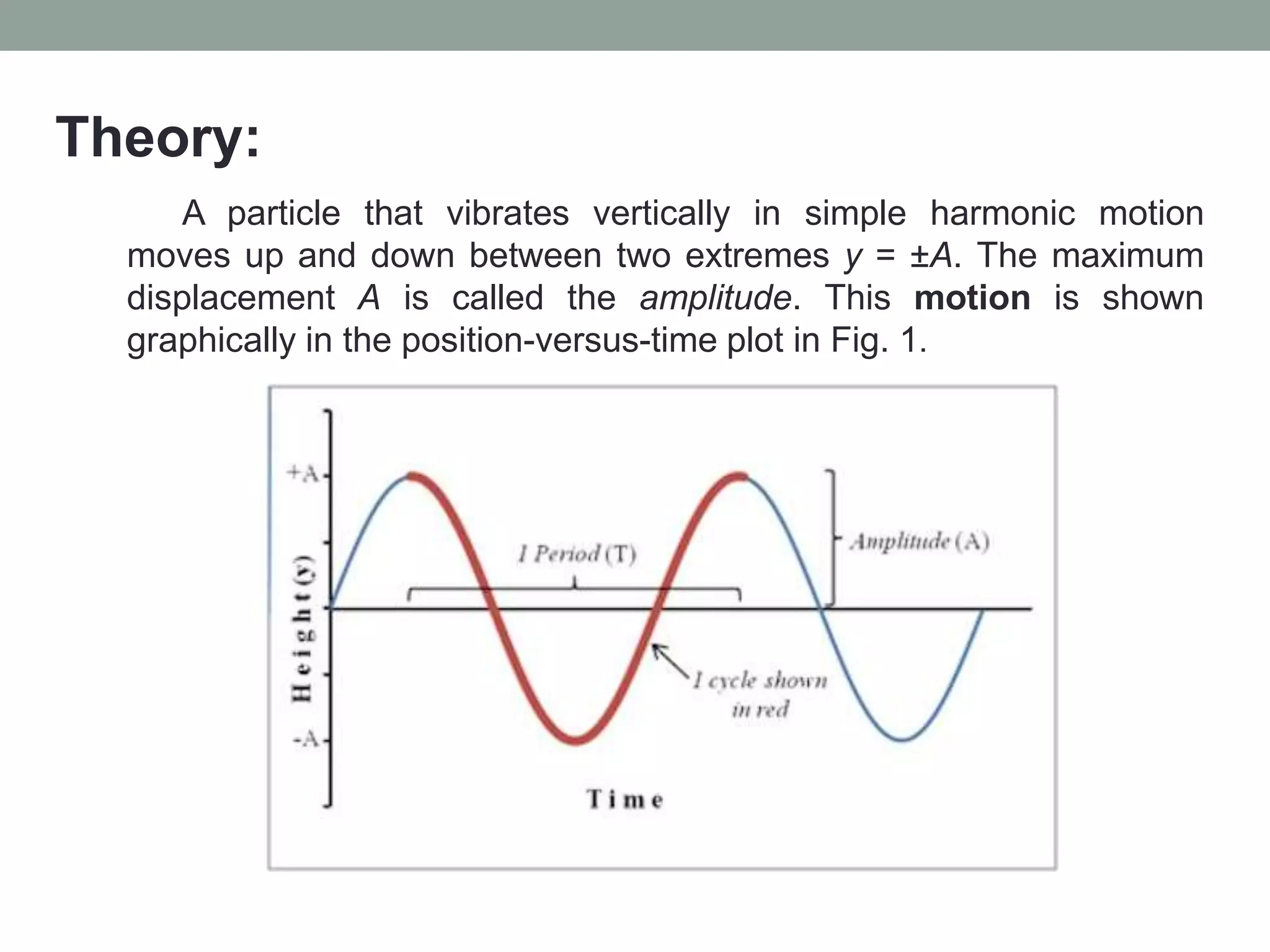
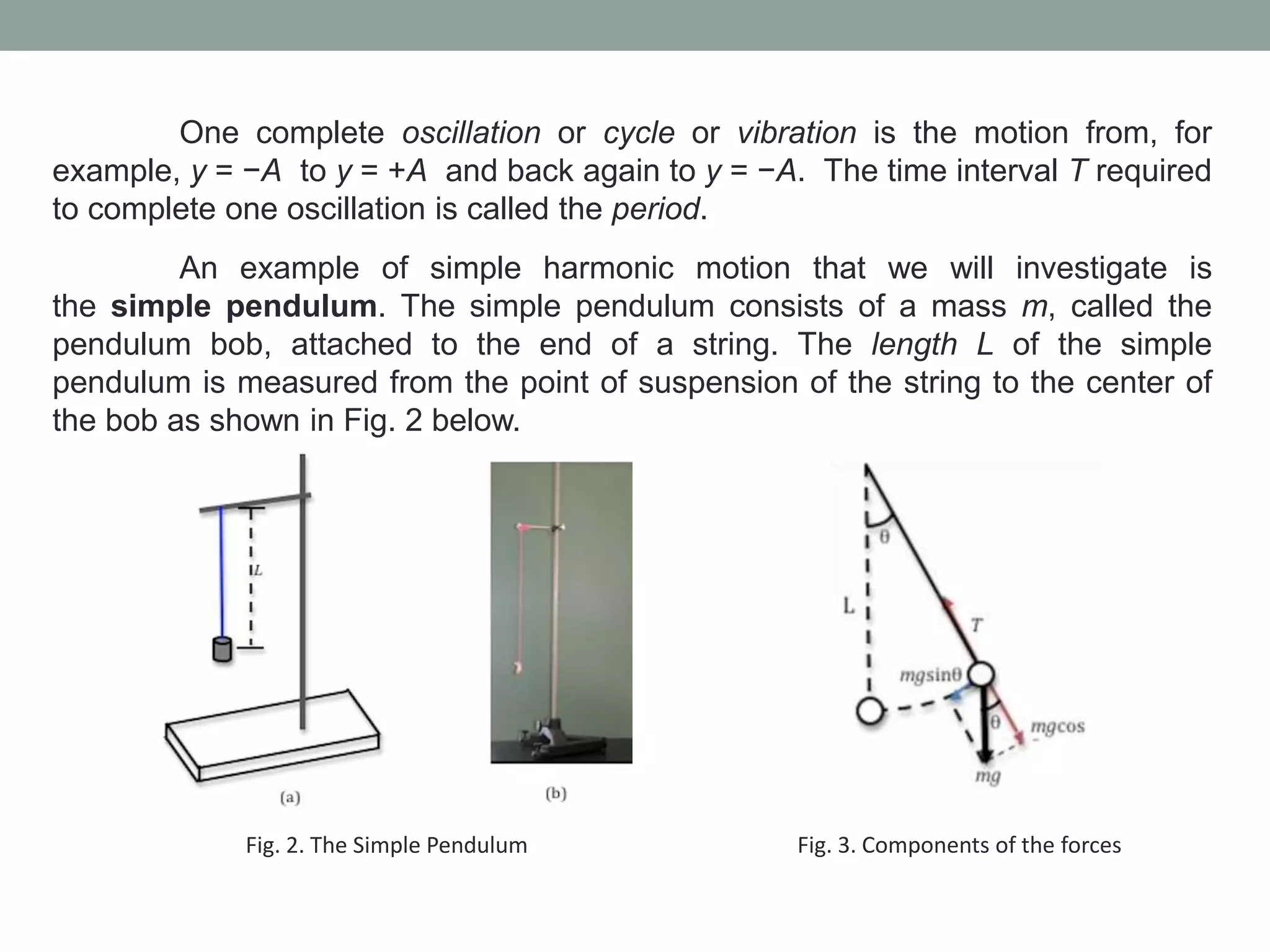
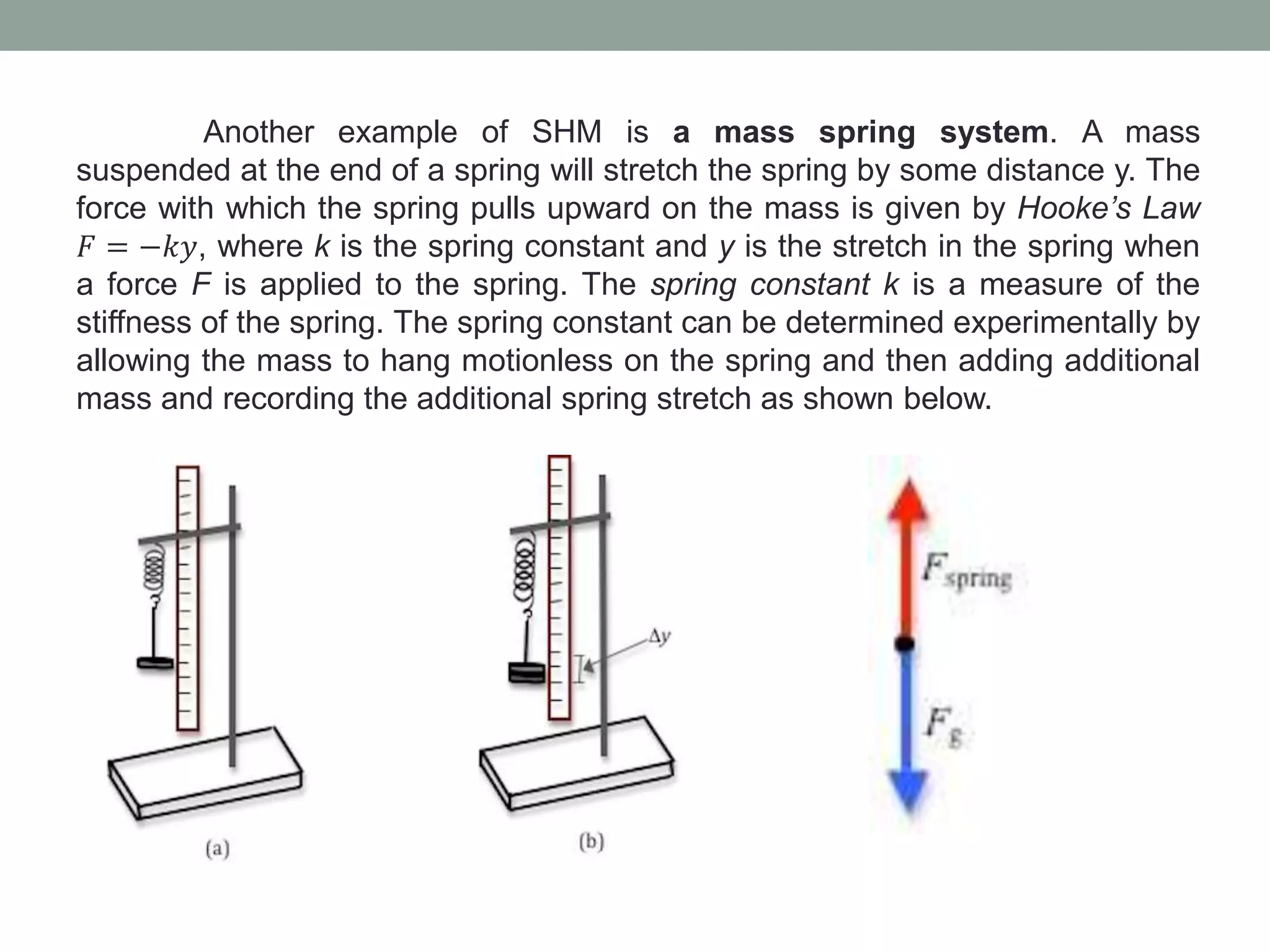
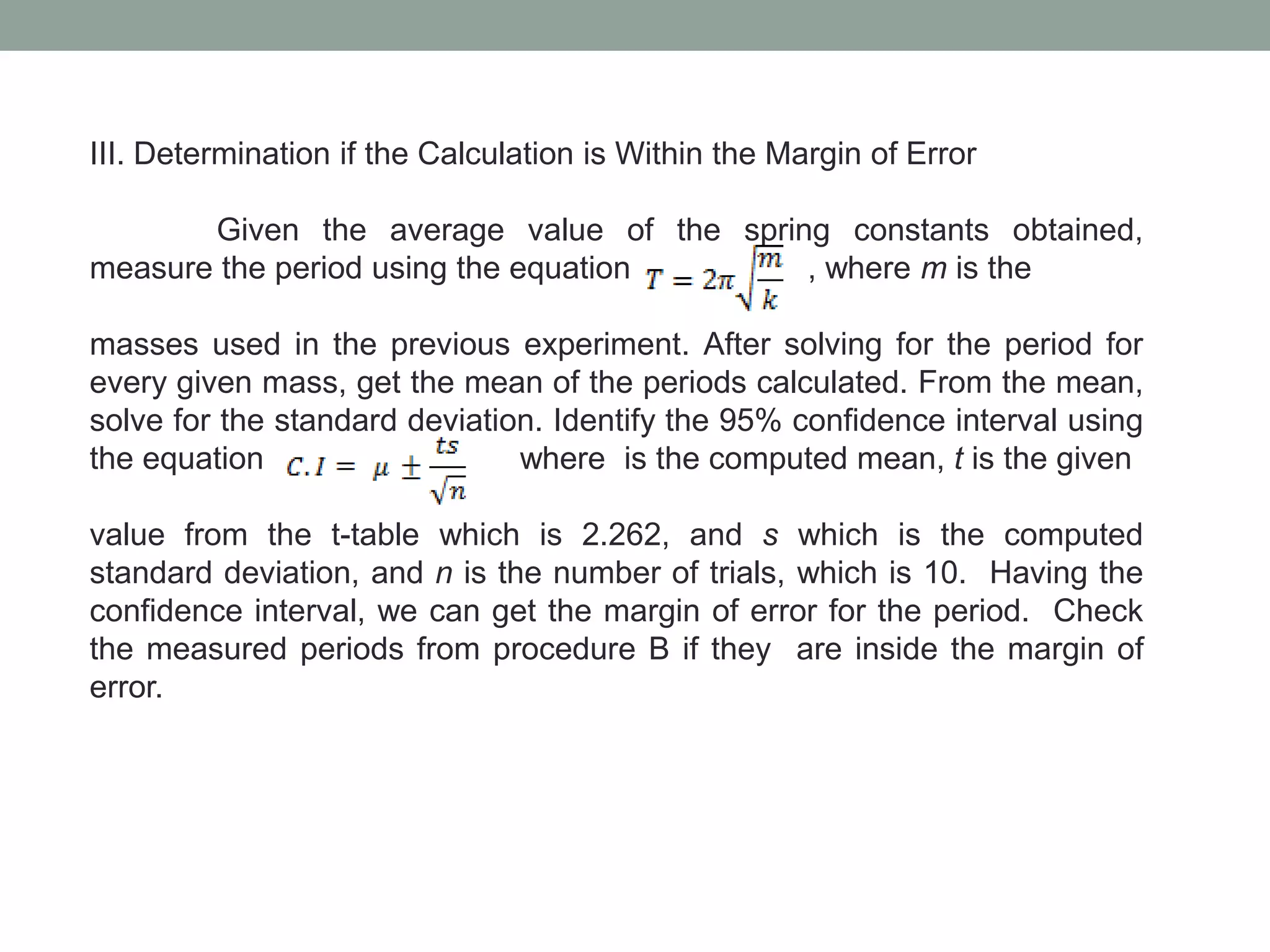
1) The experiment aims to validate equations for the period of a simple pendulum and a mass-spring system undergoing simple harmonic motion.
2) A simple pendulum and mass-spring system are used to determine the acceleration due to gravity and spring constant.
3) Variables like length, mass, angle of displacement are changed to study their effect on the period of oscillation based on theoretical equations.