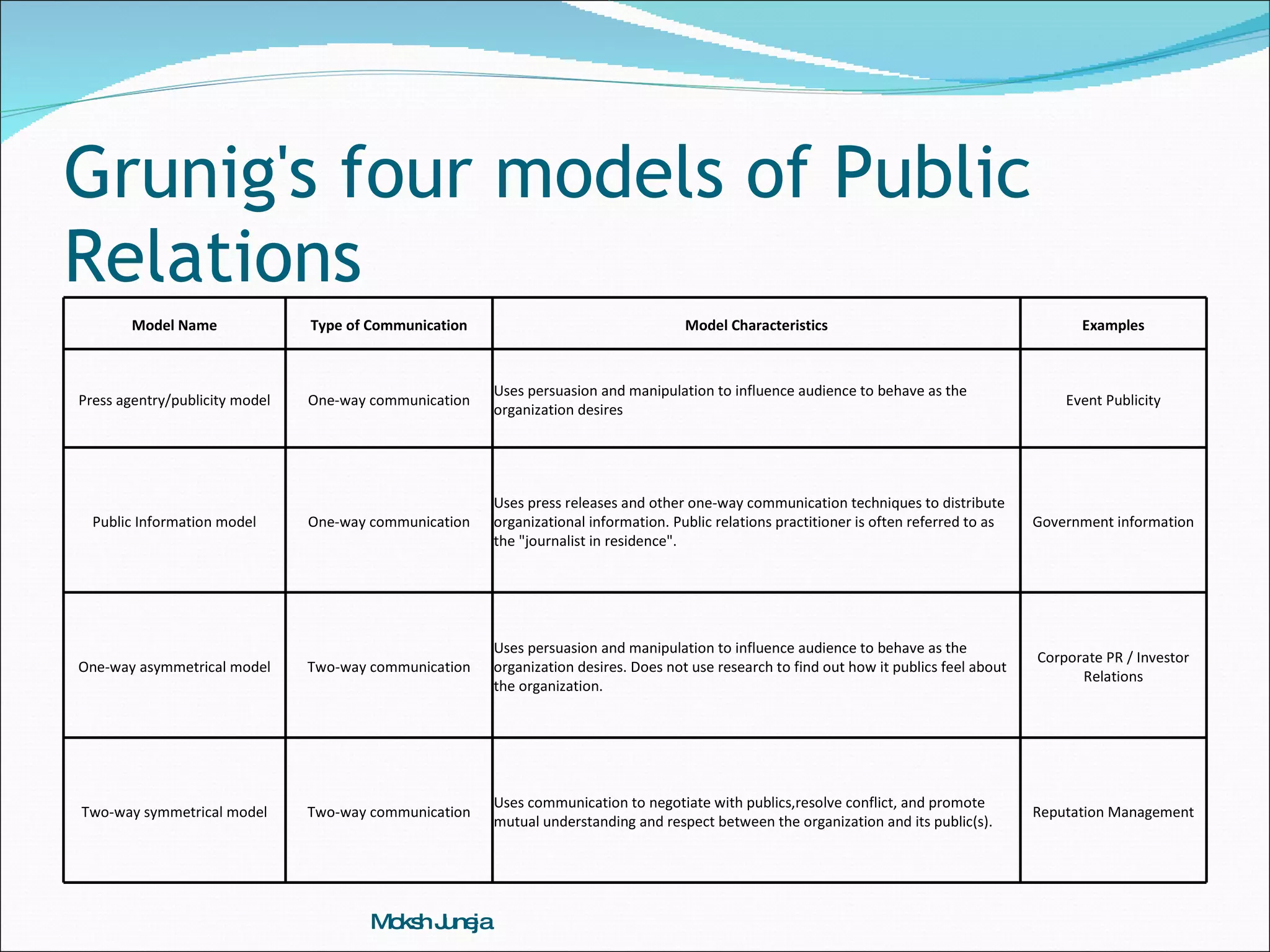
The document provides an overview of corporate communications and public relations. It defines communication and discusses models of communication, including linear, interactive, and transactional models. It also defines corporate communications and discusses the corporate communications mix, aspects of corporate communication, and tools and scope of corporate communication. Models of public relations are presented, including press agentry, public information, one-way asymmetric, and two-way symmetric models. The roles and areas addressed by corporate communications professionals are outlined.









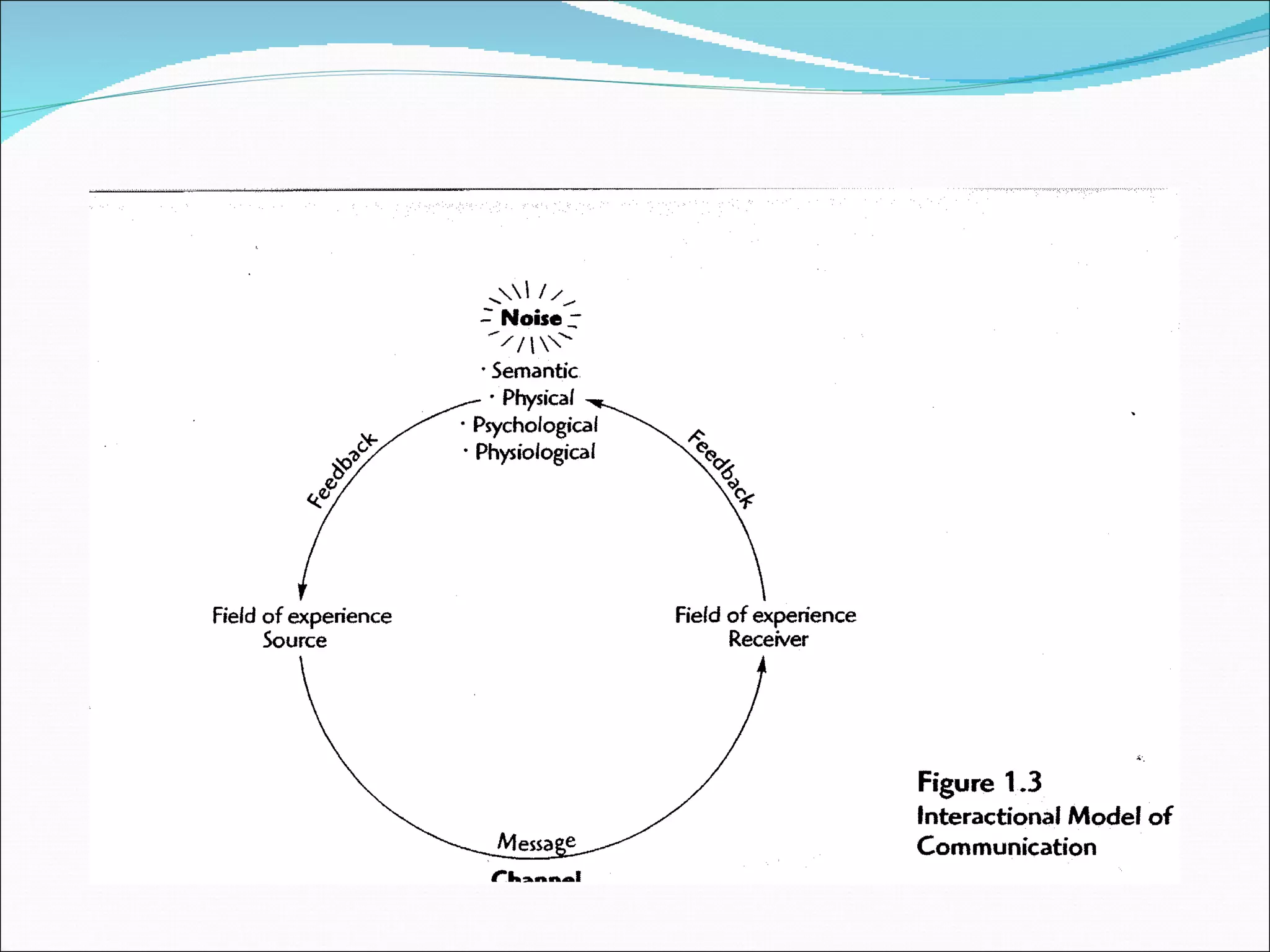
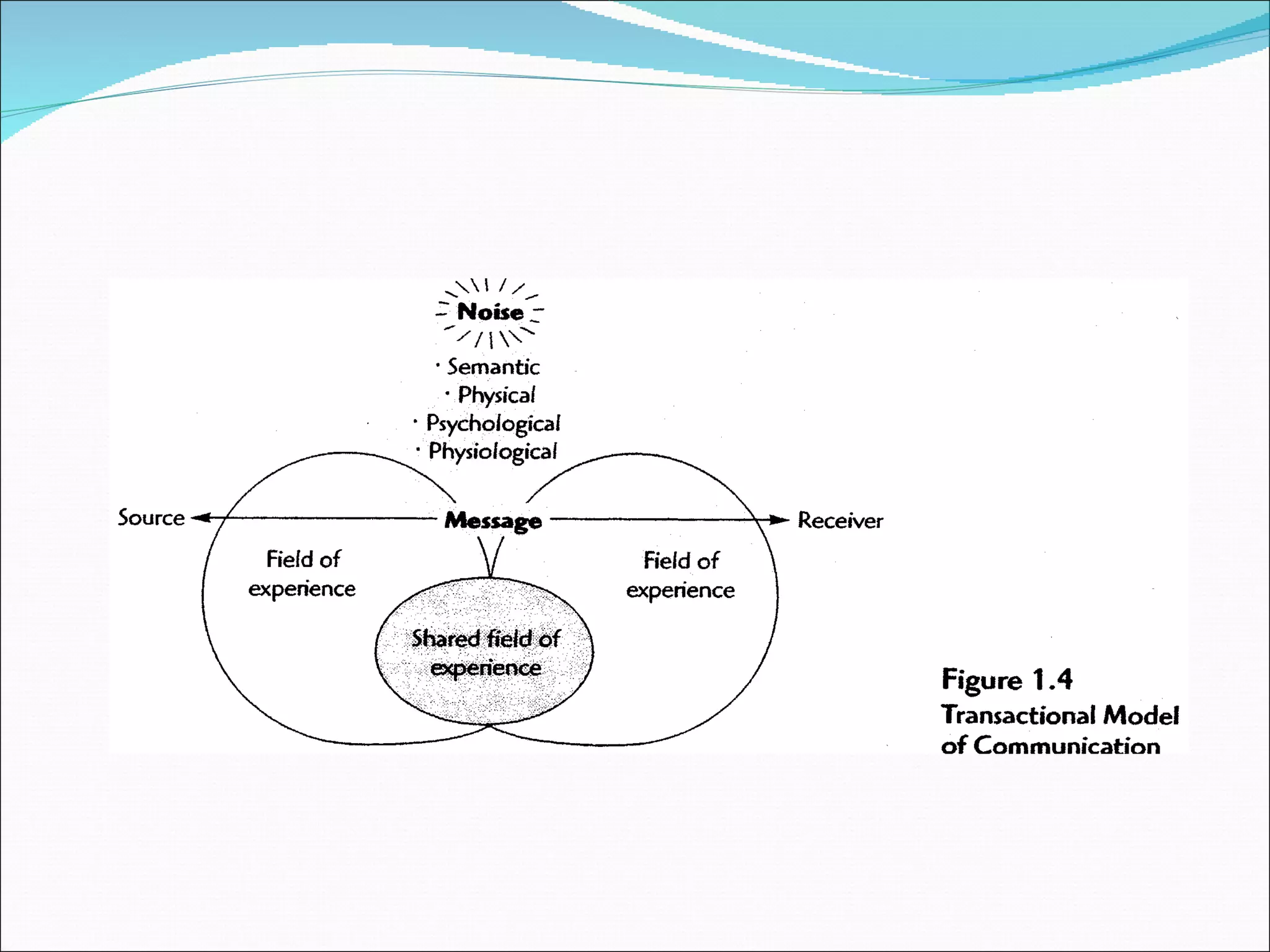
![Public Relations Communications Models Moksh Juneja Source: Managing Public Relations [James E. Grunig and Todd Hunt, Harcourt, Bace Jovanovich (1984), p. 21]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publicrelationsmanagementsession2corporatecommunicationsandprcommunicationmodels-12617353986882-phpapp02/75/Public-Relations-Management-Session-2-Corporate-Communications-And-Pr-Communication-Models-17-2048.jpg)
![Public Relations Communications Models Moksh Juneja Source: Managing Public Relations [James E. Grunig and Todd Hunt, Harcourt, Bace Jovanovich (1984), p. 21]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publicrelationsmanagementsession2corporatecommunicationsandprcommunicationmodels-12617353986882-phpapp02/75/Public-Relations-Management-Session-2-Corporate-Communications-And-Pr-Communication-Models-18-2048.jpg)







![THE CORPORATE COMMUNICATIONS WHEEL O The New Corporate Communications Wheel: Balmer and Greyser. Adapted from D. Bernstein (1984) [42] The Corporate Communications Wheel: Balmer and Greyser. Adapted from D. Bernstein (1984) Advertising Products/ Services Direct Marketing and Correspondence Corporate & Marketing PR Personal Presentation Impersonal Presentation Literature Point of Sale Permanent Media New Media Sponsorship THE CORPORATION Brand Business Partnerships Alliances O R I V N E N M E N T O R I V N E N M E N T The New Corporate Communications Wheel: Balmer and Greyser. Adapted from D. Bernstein (1984) [42] and The Industry Corporate Country of Origin Influential Groups The Trade Government(s) The Media Financial Customers General Public Internal Prospective Employees Local Business Partners](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publicrelationsmanagementsession2corporatecommunicationsandprcommunicationmodels-12617353986882-phpapp02/75/Public-Relations-Management-Session-2-Corporate-Communications-And-Pr-Communication-Models-29-2048.jpg)



![Thank you Contact Moksh Juneja Social Media Catalyst Mobile: +91 9322121170 Email: [email_address] Moksh Juneja](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/publicrelationsmanagementsession2corporatecommunicationsandprcommunicationmodels-12617353986882-phpapp02/75/Public-Relations-Management-Session-2-Corporate-Communications-And-Pr-Communication-Models-33-2048.jpg)