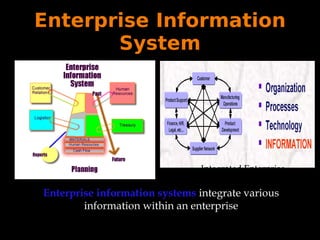
Enterprise computing refers to the use of computers and computer technology within business organizations. There are several types of enterprise information systems that are used in businesses, including executive support systems, decision support systems, management information systems, knowledge management systems, office automation systems, and transaction processing systems. Each type of system has a specific purpose, such as helping senior management make strategic decisions, processing routine transactions efficiently, or creating and sharing knowledge within an organization. While enterprise information systems can provide benefits like improved management and a unified platform, they also have disadvantages like being difficult and expensive to implement and requiring fundamental changes to business operations.