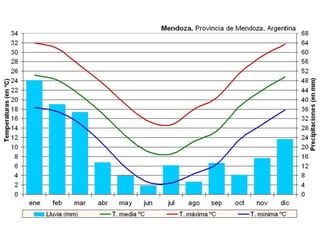
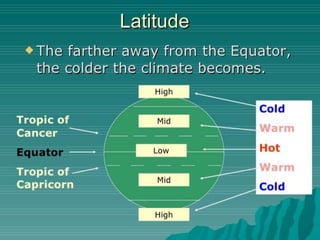
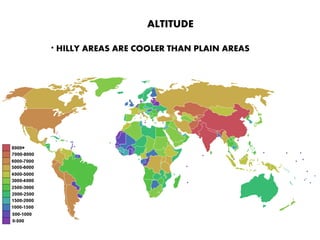
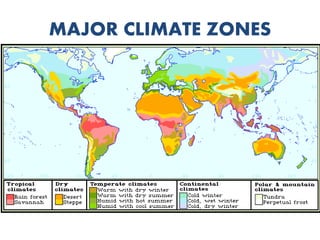
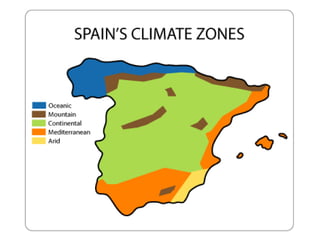
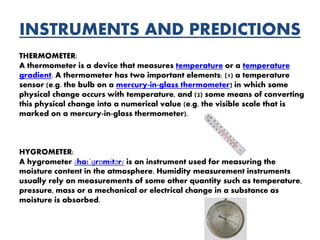
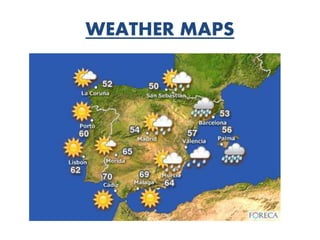
The atmosphere is composed primarily of nitrogen and oxygen that surrounds the Earth and is held in place by gravity. It protects life by absorbing UV rays, provides warmth through the greenhouse effect, and moderates temperature extremes. The ozone layer located 15-35km above the surface protects the Earth from UV rays by absorbing most of them. Weather occurs over short periods of time, while climate describes patterns over 30+ years and determines temperature and precipitation averages. Climate is influenced by several factors like latitude, altitude, distance from oceans, wind and pressure systems, and ocean currents.